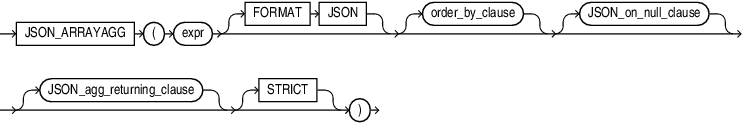
JSON_ARRAYAGG
Syntax
(See order_by_clause::= in the documentation on SELECT for the syntax of this clause)
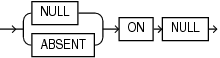
JSON_on_null_clause::=
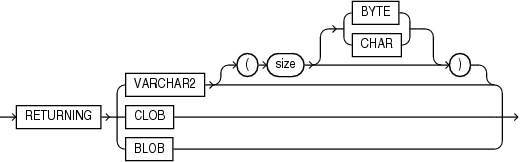
JSON_agg_returning_clause::=
Purpose
The SQL/JSON function JSON_ARRAYAGG is an aggregate function. It takes as its input a column of SQL expressions, converts each expression to a JSON value, and returns a single JSON array that contains those JSON values.
expr
For expr, you can specify any SQL expression that evaluates to a JSON object, a JSON array, a numeric literal, a text literal, or null. This function converts a numeric literal to a JSON number value and a text literal to a JSON string value.
FORMAT JSON
Use this optional clause to indicate that the input string is JSON, and will therefore not be quoted in the output.
order_by_clause
This clause allows you to order the JSON values within the JSON array returned by the statement. Refer to the order_by_clause in the documentation onSELECT for the full semantics of this clause.
JSON_on_null_clause
Use this clause to specify the behavior of this function when expr evaluates to null.
-
NULLONNULL- If you specify this clause, then the function returns the JSON null value. -
ABSENTONNULL- If you specify this clause, then the function omits the value from the JSON array. This is the default.
JSON_agg_returning_clause
Use this clause to specify the data type of the character string returned by this function. You can specify the following data types:
-
VARCHAR2[(size[BYTE,CHAR])]When specifying the
VARCHAR2data type elsewhere in SQL, you are required to specify a size. However, in this clause you can omit the size. -
CLOB
If you omit this clause, or if you specify VARCHAR2 but omit the size value, then JSON_ARRAYAGG returns a character string of type VARCHAR2(4000).
Refer to "Data Types" for more information on the preceding data types.
STRICT
Specify the STRICT clause to verify that the output of the JSON generation function is correct JSON. If the check fails, a syntax error is raised.
Refer to JSON_OBJECT for examples.
WITH UNIQUE KEYS
Specify WITH UNIQUE KEYS to guarantee that generated JSON objects have unique keys.
Examples
The following statements creates a table id_table, which contains ID numbers:
CREATE TABLE id_table (id NUMBER);
INSERT INTO id_table VALUES(624);
INSERT INTO id_table VALUES(null);
INSERT INTO id_table VALUES(925);
INSERT INTO id_table VALUES(585);The following example constructs a JSON array from the ID numbers in table id_table:
SELECT JSON_ARRAYAGG(id ORDER BY id RETURNING VARCHAR2(100)) ID_NUMBERS FROM id_table; ID_NUMBERS ------------- [585,624,925]