42.8 FEATURE_ID
Syntax
feature_id::=
Analytic Syntax
feature_id_analytic::=
mining_attribute_clause::=
mining_analytic_clause::=
See Also:
"Analytic Functions" for information on the syntax, semantics, and restrictions of mining_analytic_clause
Purpose
FEATURE_ID returns the identifier of the highest value feature for each row in the selection. The feature identifier is returned as an Oracle NUMBER.
Syntax Choice
FEATURE_ID can score the data in one of two ways: It can apply a mining model object to the data, or it can dynamically mine the data by executing an analytic clause that builds and applies one or more transient mining models. Choose Syntax or Analytic Syntax:
-
Syntax — Use the first syntax to score the data with a pre-defined model. Supply the name of a feature extraction model.
-
Analytic Syntax — Use the analytic syntax to score the data without a pre-defined model. Include
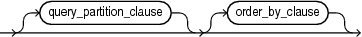
INTOn, wherenis the number of features to extract, andmining_analytic_clause, which specifies if the data should be partitioned for multiple model builds. Themining_analytic_clausesupports aquery_partition_clauseand anorder_by_clause. (See "analytic_clause::=".)
The syntax of the FEATURE_ID function can use an optional GROUPING hint when scoring a partitioned model. See GROUPING Hint.
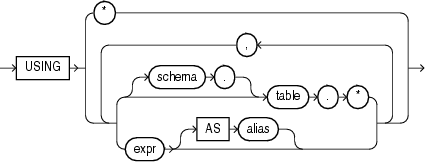
mining_attribute_clause
mining_attribute_clause identifies the column attributes to use as predictors for scoring. When the function is invoked with the analytic syntax, these predictors are also used for building the transient models. The mining_attribute_clause behaves as described for the PREDICTION function. (See "mining_attribute_clause".)
See Also:
-
Oracle Machine Learning for SQL User’s Guide for information about scoring.
-
Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Concepts for information about feature extraction.
Note:
The following example is excerpted from the Oracle Machine Learning for SQL examples. For more information about the examples, see Appendix A in Oracle Machine Learning for SQL User’s Guide.
Example
This example lists the features and corresponding count of customers in a data set.
SELECT FEATURE_ID(nmf_sh_sample USING *) AS feat, COUNT(*) AS cnt
FROM nmf_sh_sample_apply_prepared
GROUP BY FEATURE_ID(nmf_sh_sample USING *)
ORDER BY cnt DESC, feat DESC;
FEAT CNT
---------- ----------
7 1443
2 49
3 6
6 1
1 1