3 Configuration and Administration Tools Overview
Configuring Enterprise User Security for an Oracle database primarily involves creating directory objects to store enterprise user and database information. For some implementations, it can also require creating special network configuration files (ldap.ora) that enable your databases to locate the correct directory server on the network.
3.1 Enterprise User Security Tools Overview
Enterprise users are database users whose identities are stored and centrally managed in an LDAP directory, such as Oracle Internet Directory. Table 3-1 provides a summary of Enterprise User Security configuration and management tasks and the tools to complete them. The tool names are links to sections that describe them.
Table 3-1 Enterprise User Security Tasks and Tools Summary
| Task | Tools |
|---|---|
|
Create users and manage their passwords |
|
|
Configure databases Oracle home for directory usage over the network |
|
|
Register and un-register databases in Oracle Internet Directory |
|
|
Manage Oracle wallets for Enterprise User Security |
|
|
|
|
Manage identity management realms in Oracle Internet Directory For information about this tool and realms, refer to Oracle Identity Management Guide to Delegated Administration. |
|
|
Perform bulk migrations of database users to Oracle Internet Directory |
3.2 Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console
Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console is a tool based on Delegated Administration Services. This is a self service application that allows administrated access to the applications data managed in the directory. This tool comes ready to use with Oracle Internet Directory.
The Oracle Identity Management Guide to Delegated Administration discusses Delegated Administration Services and the Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console tool.
3.3 Oracle Net Configuration Assistant
Oracle Net Configuration Assistant is a wizard-based tool with a graphical user interface. Its primary uses are to configure basic Oracle Net network components, such as listener names and protocol addresses, and to configure your Oracle home for directory server usage. The latter use is what makes this tool important for configuring Enterprise User Security.
If you use Domain Name System (DNS) discovery (automatic domain name lookup) to locate Oracle Internet Directory on your network, then this assistant is not necessary. Note that using DNS discovery is the recommended configuration.
Before you can register a database with the directory, you must do either one of the following two tasks:
-
Configure DNS discovery of Oracle Internet Directory on your network.
See Also:
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Internet Directory for information about DNS server discovery
-
If DNS discovery is not configured on your network, then use Oracle Net Configuration Assistant to create an
ldap.orafile for your Oracle home.
Your database initially uses the ldap.ora file to locate the correct Oracle Internet Directory server on your network. This configuration file contains the hostname, port number, and identity management realm information for your directory server.
Once database registration is complete, the realm is ascertained through the database DN stored in the database wallet.
The following section describes more information about Oracle Net Configuration Assistant: Starting Oracle Net Configuration Assistant.
3.3.1 Starting Oracle Net Configuration Assistant
To start Oracle Net Configuration Assistant:
-
(UNIX) From
$ORACLE_HOME/bin, enter the following at the command line:netca
-
(Windows) Choose Start, Programs, Oracle-HOME_NAME, Configuration and Migration Tools, Net Configuration Assistant
After you start this tool, you will be presented with the opening page shown in Figure 3-1.
Choose the Directory Usage Configuration option on this page, click Next, and choose the directory server where you wish to store your enterprise users. Then, click Finish to create a properly configured ldap.ora file for your Oracle home.
Figure 3-1 Opening Page of Oracle Net Configuration Assistant
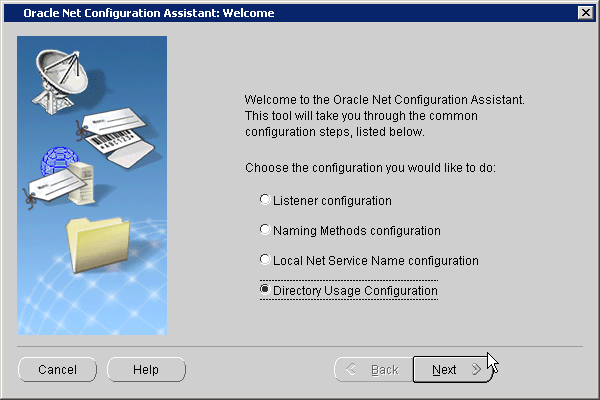
Description of "Figure 3-1 Opening Page of Oracle Net Configuration Assistant"
See Also:
-
"Task 5: (Optional) Configure your Oracle home for directory usage" for more information about using this tool to configure your Oracle home for Enterprise User Security
-
Oracle Net Configuration Assistant online help and Oracle Database Net Services Administrator's Guide for a complete documentation of this tool
3.4 Database Configuration Assistant
Database Configuration Assistant is a wizard-based tool used to create and configure Oracle databases.
Use Database Configuration Assistant to register a database with the directory. In that process, Database Configuration Assistant creates a distinguished name (DN) for the database and the corresponding entry and subtree in Oracle Internet Directory.
The following section describes more information about Database Configuration Assistant: Starting Database Configuration Assistant.
3.4.1 Starting Database Configuration Assistant
To start Database Configuration Assistant:
-
(UNIX) From
$ORACLE_HOME/bin, enterdbcaat the command line: -
(Windows) Choose Start > Programs > Oracle - HOME_NAME > Configuration and Migration Tools > Database Configuration Assistant
See Also:
-
"To register a database with the directory:" for information about using this tool to register your database
-
Oracle Database Administrator’s Guide for more information about this tool
-
3.5 Oracle Wallet Manager
Security administrators use Oracle Wallet Manager, which is an application that wallet owners use to manage and edit the security credentials in their Oracle wallets. A wallet is a password-protected container used to store authentication and signing credentials, including private keys, certificates, and trusted certificates needed by SSL The wallets it creates can be read by Oracle Database, Oracle Application Server 10g, and the Oracle Identity Management infrastructure.
See Also:
3.5.1 Starting Oracle Wallet Manager
To start Oracle Wallet Manager:
-
(Windows) Select Start, Programs, Oracle-HOME_NAME, Integrated Management Tools, Wallet Manager
-
(UNIX) At the command line, enter
owm.
3.5.2 The orapki Command-Line Utility
The orapki command-line utility enables administrators to manage wallets, certificate revocation lists, and other public key infrastructure (PKI) elements from the command line. It can be used inside scripts, enabling administrators to automate many routine PKI tasks. The orapki commands enable you to do the following tasks:
Table 3-2 Summary of orapki Commands
| Object Affected | Operations Possible with orapki Commands |
|---|---|
|
Certificate |
Create or display |
|
CRL (certificate revocation list) |
Delete, display, hash, list, or upload |
|
Wallet |
Create, display, add, or export |
See Also:
orapki Utility in the Oracle Database Security Guide
3.6 Oracle Enterprise Manager
Enterprise User Security employs Oracle Enterprise Manager to administer enterprise users, administrative groups, enterprise domains, and enterprise roles stored in Oracle Internet Directory. You can use the Web-based user interface provided by Oracle Enterprise Manager to administer Enterprise User Security.
Enterprise users are users provisioned and managed centrally in an LDAP-compliant directory, such as Oracle Internet Directory, for database access. Enterprise domains are directory constructs containing databases, enterprise roles (the access privileges assigned to enterprise users), and proxy permissions (which enable enterprise users to connect to databases as other users).
See Also:
Introducing Enterprise User Security for a discussion of Enterprise User Security administrative groups, enterprise domains, enterprise roles, enterprise users, shared schemas, and user-schema mappings
Use the following steps to access the Enterprise User Security link in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control:
-
Enter the URL for Cloud Control in a browser window. For example:
https://mydbhost:1158/em
-
Log in as an administrative database user.
-
To navigate to your database, select Databases from the Targets menu.
-
Click the database name in the list that appears. The database page appears.
-
Under the Administration menu, select Security, Enterprise User Security. The Oracle Internet Directory Login page appears.
-
Enter the distinguished name (DN) of a directory user, who has administrative privileges for the identity management realm, in the User field. Enter the user password in the Password field. Click Login.
The Enterprise User Security page appears.
3.7 User Migration Utility
User Migration Utility is a command-line tool that enables you to perform bulk migrations of database users to Oracle Internet Directory where they are stored and managed as enterprise users. This tool performs a bulk migration in two phases: In phase one, it populates a table with database user information. During phase two, the database user information is migrated to the directory.
This tool is automatically installed in the following location when you install an Oracle Database client:
$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/bin/umu
The basic syntax for this utility is as follows:
umu parameter_keyword_1=value1:value2
parameter_keyword_2=value parameter_keyword_3=value1:value2:value3 ... parameter_keyword_n=value
Note that when a parameter takes multiple values, they are separated with colons (:).
See Also:
Using the User Migration Utility for complete instructions (including usage examples) for using this tool to migrate database users to a directory
3.8 Duties of an Enterprise User Security Administrator/DBA
Enterprise User Security administrators plan, implement, and administer enterprise users. Table 3-3 lists the primary tasks of Enterprise User Security administrators, the tools used to perform the tasks, and the links to where the tasks are documented.
Table 3-3 Common Enterprise User Security Administrator Configuration and Administrative Tasks
| Task | Tools Used | See Also |
|---|---|---|
|
Create an identity management realm in Oracle Internet Directory |
Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console (Delegated Administration Service) |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Internet Directory for information about how to perform this task |
|
Upgrade an identity management realm in Oracle Internet Directory |
Oracle Internet Directory Configuration Assistant |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Internet Directory and the online Help for this tool |
|
Set up DNS to enable automatic discovery of Oracle Internet Directory over the network. Note that this is the recommended configuration. |
Oracle Internet Directory Configuration Assistant |
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Internet Directory (Domain Name System server discovery) and the online Help for this tool |
|
Create an |
Oracle Net Configuration Assistant |
"Task 5: (Optional) Configure your Oracle home for directory usage" |
|
Register a database in the directory |
Database Configuration Assistant |
|
|
Configure password authentication for Enterprise User Security |
Oracle Enterprise Manager |
"Configuring Enterprise User Security for Password Authentication" |
|
Configure Kerberos authentication for Enterprise User Security |
|
"Configuring Enterprise User Security for Kerberos Authentication" |
|
Configure SSL authentication for Enterprise User Security |
|
"Configuring Enterprise User Security for SSL Authentication" |
|
Create or modify user entries and Oracle administrative groups in the directory |
Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console (Delegated Administration Service) |
|
|
Create or modify enterprise roles and domains in the directory |
Oracle Enterprise Manager |
|
|
Create or modify wallets for directory, databases, and clients |
|
|
|
Change a user's database or directory password |
Oracle Internet Directory Self-Service Console (Delegated Administration Service) |
|
|
Change a database's directory password |
Database Configuration Assistant |
|
|
Manage user wallets on the local system or update database and directory wallet passwords |
Oracle Wallet Manager |
|
|
Request initial Kerberos ticket when KDC is not part of the operating system, such as Kerberos V5 from MIT |
|
Oracle Database Security Guide for information about using the |
|
Migrate large numbers of local or external database users to the directory for Enterprise User Security |
User Migration Utility |