17 Administering Application Containers
You can administer application containers, including application roots and application PDBs. You can also administer the applications installed in application containers.
Note:
You can complete the tasks in this chapter using SQL*Plus or Oracle SQL Developer.About Application Container Administration
Some aspects of administering an application container are similar to administering the CDB root and the CDB as a whole, while other aspects are similar to administering a PDB.
Administering an application container is similar to administering a CDB because you can manage both the application root and the application PDBs that are plugged into the application root. However, administering an application container is also similar to managing a PDB because changes to the application container do not affect other application containers or PDBs in the CDB.
The following table describes administrative tasks for application containers that are similar to administrative tasks that manage a CDB or CDB root.
Table 17-1 Application Container Administrative Tasks Similar to Those of a CDB
| Administrative Task | Description | More Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Configuring application common users and commonly granted privileges |
Application common users and privileges are similar to common users and commonly granted privileges in a CDB root, but in an application container, common users and commonly granted privileges only exist within the containers of the application container, including the application root, application PDBs that belong to the application root, and an optional application seed that belongs to the application root. |
|
|
Creating application containers |
A common user whose current container is the CDB root can create application containers that are plugged into the CDB root by specifying the |
|
|
Creating application PDBs |
A common user whose current container is the application root can create application PDBs that are plugged into the application root. |
|
|
Switching to containers |
A common user with the proper privileges can switch between containers in an application container, including the application root, application PDBs that belong to the application root, and an optional application seed that belongs to the application root. |
"Switching to a Container Using the ALTER SESSION Statement" |
|
Issuing |
The |
|
|
Issuing data definition language (DDL) statements |
In an application container, some DDL statements can apply to all containers in the application container or to the current container only. |
The following table describes administrative tasks for application containers that are similar to administrative tasks that manage a PDB.
Table 17-2 Application Container Administrative Tasks Similar to Those of a PDB
| Administrative Task | Description | More Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Connecting to the application root |
The application root has its own service name, and users can connect to the application root in the same way that they connect to a PDB. Similarly, each application PDB has its own service name, and the application seed has its own service name. |
|
|
Issuing the |
An |
|
|
Issuing the SQL*Plus |
SQL*Plus |
|
|
Issuing the |
An |
|
|
Managing tablespaces |
Administrators can create, modify, and drop tablespaces for an application root and for application PDBs. Each container has its own tablespaces. |
|
|
Managing data files and temp files |
Administrators can create, modify, and drop data files and temp files for an application root and for application PDBs. Each container has its own files. |
Oracle Database Administrator’s Guide for information about managing data files and temp files |
|
Managing schema objects |
You can create, modify, and drop schema objects in an application root and in each application PDB in the same way that you would in a PDB. You can also create triggers that fire for a specific application root or application PDB. However, application containers support application common objects, which can be shared between the containers in an application container. Application common objects cannot be created in PDBs. |
About Modifying an Application Root
The ALTER DATABASE statement can modify an application root. The ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement can modify the open mode of application PDBs.
The following table lists which containers are modified by clauses in ALTER DATABASE and ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statements issued in an application root. The table also lists statements that are not allowed in an application root.
Note:
Statements issued when the current container is the application root never affect the CDB root or PDBs that do not belong to the current application root.Table 17-3 Statements That Modify Containers in an Application Root
| Modify Application Root Only | Modify One or More Application PDBs | Cannot Be Issued in an Application Root |
|---|---|---|
|
When connected as an application common user whose current container is the application root,
You can use these clauses to set nondefault values for specific application PDBs. |
When connected as an application common user whose current container is the application root, When the current container is an application PDB, When connected as an application common user whose current container is the application root, |
When connected as an application common user whose current container is the application root, |
Managing Applications in an Application Container
You install, upgrade, or patch an application in an application container.
You can also uninstall an application from an application container. You perform these operations in the application root. The application container propagates the application changes to the application PDBs when the application PDBs synchronize with the application in the application root.
Related Topics
About Application Management
In an application container, an application is a named, versioned set of application metadata and common data. The application is stored in the application root.
In this context, the term “application” means “application back-end.” Application common objects include user accounts, tables, PL/SQL packages, and so on. You can share an application with the application PDBs that belong to the application root. When you perform application changes, application PDBs can synchronize with the application in the application root.
Basic Steps of Application Maintenance
You can install, upgrade, and patch an application in an application root.
You must issue an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... BEGIN statement to start the operation and an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... END statement to end the operation. You can issue these statements in the same user session or in different user sessions.
The following is the typical process for creating and maintaining an application in an application container:
-
Create the application container.
-
Install the application in the application root using
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... BEGIN INSTALL.This step includes creating the application data model and configuring the application common users and application common objects.
Note:
SQL*Loader is the only supported utility for bulk inserts into tables during application install, upgrade, and patch operations.
-
Create the application PDBs in the application root.
-
Synchronize each application PDB that should install the application with the application root. The statement is
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... SYNC. -
Load the data for each application PDB.
-
Maintain the application. Upgrade using
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... BEGIN UPGRADE, and patch usingALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... BEGIN PATCH. -
Synchronize application PDBs that should apply changes from upgrades and patches.
-
Add new application PDBs whenever necessary.
-
If necessary, uninstall the application using
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... BEGIN UNINSTALL.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Security Guide to learn how to audit application maintenance operations
Application Versions
The application container also manages the versions of the application and the patches to the application.
The application container manages versions as follows:
-
When you install an application, you must specify the application version number.
-
When you upgrade an application, you must specify the old application version number and the new application version number.
-
When you patch an application, you must specify the minimum application version number for the patch and the patch number.
As the application evolves, the application container maintains all of the versions and patch changes that you apply.
You can also configure the application container so that different application PDBs use different application versions. For example, if you provide an application to various customers, and each customer has its own application PDB, some customers might wait longer to upgrade the application. In this case, some application PDBs can use the latest version of the application, whereas other application PDBs can use an older version of the application.
Application Module Names and Service Names
The application module name is set by the DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO.SET_MODULE procedure or the equivalent OCI attribute setting.
The module name is necessary during application maintenance because of other activity that might be occurring in the database. For example, statements issued by background processes should not be captured in the application capture tables. Also, other users might execute statements that are unrelated to the application. A module name check distinguishes what should be captured from what should not be captured. Only sessions whose module name matches the module name of the session where APPLICATION BEGIN was issued are considered for capture.
DBA_APPLICATIONS to determine the module name of the
session in which APPLICATION BEGIN was
executed:SELECT app_capture_module FROM dba_applications WHERE app_name='APEX';Some clauses, such as the SHARING clause, are valid only when issued between an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... BEGIN statement and an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... END statement. For these clauses, if the module name for a session does not match, then this session is not included in between the BEGIN and END statements, causing statements that include the clause to fail with ORA-65021 or other errors.
The most common cause for a module name mismatch is the default module name. For example, SQL*Plus sets a default module name when a connection is made to the database. A connection as a SYSDBA user results in one default module name (for example, sqlplus@host1 (TNS V1-V3)), whereas a connection as a non-SYSDBA user results in a different default module name (for example, SQL*Plus). When SYSDBA and non-SYSDBA users are both performing maintenance, you must explicitly set the module name in each session to the same value, and not rely the default settings in SQL*Plus.
APPLICATION BEGIN was executed. Query
DBA_APPLICATIONS to determine the service name of the session in
which APPLICATION BEGIN was
executed:SELECT app_capture_service FROM dba_applications WHERE app_name='APEX';Example 17-1 Checking the Session's Module Name
This example shows how the default module name changes depending on whether the connected user has SYSDBA privileges.
SQL> CONNECT / AS SYSDBA
Connected.
SQL> select module from v$session where audsid = SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','sessionid');
MODULE
----------------------------------------------------------------
sqlplus@host1 (TNS V1-V3)
SQL> CONNECT dba1
Password: *************
Connected.
SQL> select module from v$session where audsid = SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','sessionid');
MODULE
----------------------------------------------------------------
SQL*PlusSee Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference to learn how to set the application module name
Installing Applications in an Application Container
You can install an application in an application container.
About Installing Applications in an Application Container
You issue ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements to install an application in the application root.
You install the application in the application root only. Application PDBs that synchronize with the application install the application automatically. With the automated method, you can perform the installation using one or more of the following techniques: scripts, SQL statements, and graphical user interface tools.
Start of the installation with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN INSTALL statement and the end of the install with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END INSTALL statement. Each installation must be associated with an application name and version number, which are specified in the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements.
Related Topics
Installing an Application in an Application Container with Automated Propagation
In automated propagation, the application is installed in the application PDBs that synchronize with the application in the application root.
Prerequisites
You must meet the following prerequisites:
-
The current user must have the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEsystem privilege, and the privilege must be commonly granted in the application root. -
The application root must be in open read/write.
To install an application using automated propagation:
-
In SQL*Plus or SQL Developer, ensure that the current container is a PDB.
-
Run the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN INSTALLstatement in the following form:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name BEGIN INSTALL 'application_version_number';For example, run the following statement if the application_name is
salesappand the application_version_number is 4.2:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp BEGIN INSTALL '4.2'; -
Install the application using scripts, SQL statements, or graphical user interface tools.
-
Run the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END INSTALLstatement in the following form:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name END INSTALL 'application_version_number';For example, run the following statement if the application_name is
salesappand the application_version_number is 4.2:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp END INSTALL '4.2';Note:
Ensure that the application_name and application_version_number match in theALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN INSTALLstatement and theALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END INSTALLstatement. -
Synchronize all of the application PDBs that must install the application by issuing an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATIONstatement with theSYNCclause.
Upgrading Applications in an Application Container
Major changes to an application constitute application upgrades. You can upgrade an application in an application container.
About Upgrading Applications in an Application Container
You issue ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements to upgrade an application in the application root.
Related Topics
Purpose of Application Upgrade
You can upgrade the application definition once in the application root so that other application PDBs can synchronize with the upgraded definition.
Application PDBs do not automatically inherit the upgraded application definition in the application root. Application PDBs synchronize with an application in the root when you manually run an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement with the SYNC clause. You can upgrade using one or more of the following techniques: scripts, SQL statements, and graphical user interface tools.
How an Application Upgrade Works
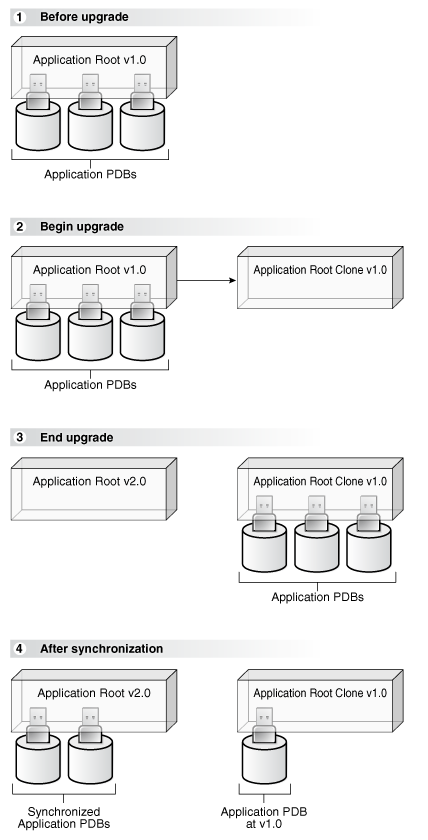
When you upgrade an application, Oracle Database automatically clones the application root.
During the upgrade, application PDBs point to the root clone. Applications continue to run during the upgrade. Application PDBs can perform DML on metadata-linked and extended data-linked tables and views. Application PDBs can query metadata-linked objects, extended data-linked objects, and data-linked objects.
After the upgrade, the application root clone remains and continues to support any application PDB that still use the preupgrade version of the application in the root clone. Application PDBs that upgrade are pointed to the upgraded application root. Application PDBs that do not upgrade might continue to use the clone, and application PDBs that are plugged into the application root might also use the same application version as the root clone.
Note:
Unlike an application upgrade, a patch does not create an application root clone. If an application PDB is not synchronized after a patch, then queries are directed to the application root, which has already been patched.
The following figure illustrates the application upgrade process.
Figure 17-1 Upgrading Applications in an Application Container
Description of "Figure 17-1 Upgrading Applications in an Application Container"
Note:
When the application root is in any open mode, the application root clone is in read-only mode. When the application root is closed, the application root clone is also closed.
User Interface for Application Upgrade
To upgrade an application definition in the application root, use the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... UPGRADE command.
Start the upgrade with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN UPGRADE statement and end with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END UPGRADE statement. Each upgrade must be associated with an application name, starting version number, and ending version number, which are specified in the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements.
Note:
If Transparent Data Encryption is enabled in the application root, then an external password store must be configured.
Upgrading an Application in an Application Container
After an upgrade, application changes caused by the upgrade propagate to the application PDBs that synchronize with the application root.
Prerequisites
-
The CDB must be in local undo mode.
-
The current user must have the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEsystem privilege, and the privilege must be commonly granted in the application root. -
The application root must be in open read/write.
-
If Transparent Data Encryption is enabled in the application root, then an external password store must be configured.
To upgrade an application in an application container:
-
In SQL*Plus or SQL Developer, ensure that the current container is the application root.
-
Run the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN UPGRADEstatement in the following form:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name BEGIN UPGRADE 'application_start_version_number' TO 'application_end_version_number';For example, run the following statement if the application_name is
salesapp, the application_start_version_number is 4.2, and the application_end_version_number is 4.3:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp BEGIN UPGRADE '4.2' TO '4.3'; -
Upgrade the application using scripts, SQL statements, or graphical user interface tools.
-
Run the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END UPGRADEstatement in the following form:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name END UPGRADE TO 'application_end_version_number';For example, run the following statement if the application_name is
salesappand the application_end_version_number is 4.3:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp END UPGRADE TO '4.3';Note:
Ensure that the application_name and application_end_version_number match in theALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN UPGRADEstatement and theALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END UPGRADEstatement. -
Synchronize all of the application PDBs that must upgrade the application by issuing an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATIONstatement with theSYNCclause.
Patching Applications in an Application Container
Minor changes to an application constitute application patches.
Examples of minor changes can include bug fixes and security patches. You can patch an application in an application container.
About Patching Applications in an Application Container
To patch an application in the application root, issue ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements.
You patch the application in the application root only. The application PDBs that synchronize with the application apply the changes. You can perform the patch using one or more of the following techniques: scripts, SQL statements, and graphical user interface tools.
The patch is restricted to a small set of operations. In general, destructive operations, such as dropping a table, are not allowed in a patch. If you attempt to patch an application, and the operation raises an “operation not supported in an application patch” error, then upgrade the application instead of patching it to make the necessary changes.
Note:
Unlike an application upgrade, a patch does not create an application root clone. If an application PDB is not synchronized after a patch, then queries are directed to the application root, which has already been patched.
Indicate the start of the patch with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN PATCH statement and the end of the patch with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END PATCH statement. Each patch must be associated with an application name, starting version number, and ending version number. Specify these values in the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements.
Patching an Application in an Application Container with Automated Propagation
Application changes for the patch are propagated to the application PDBs that synchronize with the application in the application root.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites must be met:
-
The current user must have the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEsystem privilege, and the privilege must be commonly granted in the application root. -
The application root must be in open read/write mode.
Migrating an Existing Application to an Application Container
You can migrate an application that is installed in a PDB to an application container.
You can migrate the application to the application root or to an application PDB. For example, you might migrate an application installed in a PDB plugged into an Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2) CDB to an application container in an Oracle Database 18c CDB.
About Migrating an Existing Application to an Application Container
You can migrate an application to an application root by creating an application root using an existing PDB.
If the application is installed in more than one PDB, then you can use one of the PDBs to create the application root. You can use one of the methods available for copying a PDB to an application root, such as cloning the PDB or plugging in the PDB as an application root.
When common users, roles, or profiles exist in the PDB used to create the application root, you must run procedures in the DBMS_PDB package to associate them with the application. When an application root created from a PDB is first opened, each local user, role, and profile is marked as common. The procedures in the DBMS_PDB package associate the user, role, or profile with the application. Therefore, all DDL operations on the user, role, or profile must subsequently be done within an application BEGIN...END block of this application.
When shared database objects exist in the application root, you must run procedures in the DBMS_PDB package to associate the database objects with the application as application common objects. Therefore, all DDL operations on the application common objects must subsequently be done within an application BEGIN...END block of this application.
After the application root is in place, you can create application PDBs in the new application container using the existing PDBs. The application PDBs that you create must contain the application objects, including their data. Additional steps are necessary to synchronize the application version and patch number and to establish shared database objects in the application PDBs.
Scenario with One Hundred PDBs Running the Same Application
Assume that you currently have one hundred PDBs that are running the same application, and you want to migrate these PDBs to an application container. These PDBs have the application common objects and common users, roles, and profiles required by the application. To migrate the PDBs to an application container, follow these steps:
-
Choose one of the PDBs, and use the instructions in "Creating an Application Root Using an Existing PDB" to create the application root with this PDB.
As part of this step, you associate the database objects, users, roles, and profiles with the application by running procedures in the
DBMS_PDBpackage. -
Use the instructions in "Creating an Application PDB Using an Existing PDB" to create one hundred application PDBs using the PDBs that are running the application.
See Also:
Creating an Application Root Using an Existing PDB
Migrate an application that is installed in a PDB by copying the PDB to an application container.
Prerequisites
An Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2) or later CDB must exist.
Creating an Application PDB Using an Existing PDB
After migrating an existing application to an application root, you can use an existing PDB that uses the application to create an application PDB.
Prerequisites
You must meet the following prerequisites:
-
An Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2) or later CDB must exist, and the application root to which the application PDB will belong must exist.
-
The PDB must contain all application common objects used by the application.
-
The application must be installed in the application root.
Related Topics
Synchronizing Applications in an Application PDB
Synchronizing an application updates the application in the application PDB to the latest version and patch in the application root.
Installing, upgrading, patching, or uninstalling an application in an application root does not change its application PDBs until they are synchronized. When the application PDB is the current container, synchronize manually using one of the following forms of ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... SYNC:
-
Synchronize a single application as follows, where app1 is the name of the application:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION app1 SYNC;Optionally, specify
SYNC TO PATCH patchnoto synchronize app1 to the specified patch, andSYNC TO versionto synchronize app1 to the specified version. -
Synchronize all applications as follows:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ALL SYNC;
Prerequisites and Restrictions
-
The current user must have
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEsystem privilege. -
When specifying multiple applications using
ALL, theSYNC TOclause is not supported. -
Specifying multiple applications using
ALLreplays applicationBEGINandENDblocks in the order in which they were captured. When applications depend on one another, synchronizing them in a single statement is necessary for functional correctness.
- In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the application PDB.
- Run an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATIONstatement with theSYNCclause.
Example 17-2 Synchronizing a Specific Application in an Application PDB
This example synchronizes an application named salesapp in an application PDB with the latest application changes in the application root.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp SYNC;Example 17-3 Synchronizing an Application to a Specified Patch
This example synchronizes an application named salesapp in an application PDB to patch 100.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp SYNC TO PATCH 100;Example 17-4 Synchronizing an Application to a Specified Application Release
This example synchronizes an application named salesapp in an application PDB to release 2.0 of the application.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp SYNC TO '2.0';Example 17-5 Synchronizing All of the Applications in an Application PDB
This example synchronizes all of the applications in an application PDB with the latest application changes in the application root.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ALL SYNC;Example 17-6 Synchronizing Implicitly Created Applications in an Application PDB
This example synchronizes all of the implicitly-created applications in an application PDB with the latest application changes to the implicitly created applications in the application root.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION APP$CON SYNC;See Also:
Synchronizing an Application Root Replica with a Proxy PDB
When application containers in different CDBs have the same application, their application roots can be kept synchronized by creating a master application root, a replica application root, and a proxy PDB.
About Synchronizing an Application Root Replica with a Proxy PDB
A proxy PDB can synchronize an application root and a replica of the application root.
An application might be installed in several application containers. Installing, upgrading, and patching the application are more efficient when you use proxy PDBs.
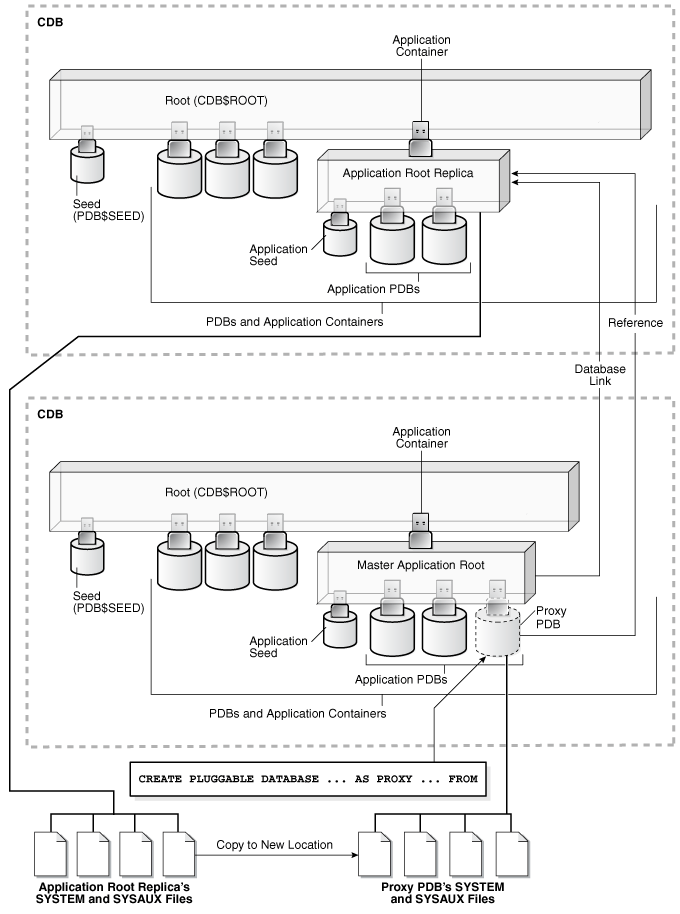
In this configuration, one application container has the master application root. The master application root is where you install, upgrade, and patch the application. Application root replicas are exact copies of the master application root. Each application root replica is referenced by a proxy PDB in the master application root.
When a proxy PDB is synchronized with the application changes in the master application root, it propagates the changes to its referenced application root replica. After the application root replica is synchronized, application PDBs that are plugged into the application root replica can synchronize with the replica and in this way receive the changes.
The following figure shows a configuration that synchronizes an application root replica using a proxy PDB.
Figure 17-2 Synchronizing an Application Root Replica with a Proxy PDB
Description of "Figure 17-2 Synchronizing an Application Root Replica with a Proxy PDB"
In addition, when an application root replica is configured and has its own application PDBs, a query that includes the CONTAINERS clause in the master application root can return data from the current application container and from the application container with the application root replica. The query can show results from the application root replica and from any open application PDBs plugged into the replica.
Creating a Proxy PDB That References an Application Root Replica
When multiple application containers run the same application, the application in the application containers can be kept synchronized using proxy PDBs.
Example 17-7 Synchronizing an Application Root Replica with a Proxy PDB
This example assumes that two CDBs exist: hqdb and depdb. The goal is to keep the same application synchronized in an application container in each CDB. To accomplish this goal, this example configures the following application containers:
-
The
hqdbCDB contains the application container with the master application root calledmsappcon.-
An application called
sampleappis installed in themsappconmaster application root. -
The
msappconapplication root contains two application PDBs namedmspdb1andmspdb2. -
The
msappconapplication root also contains a proxy PDB namedprxypdbthat references the application root replica in the other CDB.
-
-
The
depdbCDB contains the application container with the application root replica calleddepappcon.-
An application called
sampleappis propagated from the proxy PDBprxypdbin themsappconmaster application root and installed in thedepappconmaster application root. -
The
depappconapplication root contains two application PDBs nameddeppdb1anddeppdb2.
-
This example shows how changes to the sampleapp application in the msappcon master application root are applied to the application PDBs in both CDBs when the application PDBs are synchronized.
-
Create the application container with the master application root in the
hqdbCDB.-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the
hqdbCDB root. -
Create the application container from the PDB seed with the following statement:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE msappcon AS APPLICATION CONTAINER ADMIN USER msappconadm IDENTIFIED BY password STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G) DEFAULT TABLESPACE appcontbs DATAFILE '/disk1/oracle/dbs/mssappcon/msappcon01.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/', '/disk1/oracle/dbs/msappcon/'); -
Open the new master application root in read/write mode:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE msappcon OPEN;
-
-
Install an application in the master application root.
-
Change container to the master application root:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=msappcon; -
Begin the application installation:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp BEGIN INSTALL '1.0'; -
Install the application.
For example, you can create database objects:
CREATE TABLE apptb SHARING=METADATA (id NUMBER(6), widget_name VARCHAR2(20)); -
End the application installation:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp END INSTALL '1.0';
-
-
Create and synchronize one or more application PDBs in the master application root.
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the master application root.
-
Create application PDBs in the master application root.
For example, create two application PDBs from the PDB seed:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE mspdb1 ADMIN USER mspdb1admin IDENTIFIED BY password STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G) DEFAULT TABLESPACE mspdb1tbs DATAFILE '/disk1/oracle/dbs/mspdb1/mspdb101.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/', '/disk1/oracle/dbs/mspdb1/'); CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE mspdb2 ADMIN USER mspdb2admin IDENTIFIED BY password STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G) DEFAULT TABLESPACE mspdb2tbs DATAFILE '/disk1/oracle/dbs/mspdb2/mspdb201.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/', '/disk1/oracle/dbs/mspdb2/'); -
Open both application PDBs:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE mspdb1 OPEN; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE mspdb2 OPEN; -
Synchronize the application PDBs with the master application root:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=mspdb1; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC; ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=mspdb2; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC;
-
-
Create the application container with the application root replica in the
depdbCDB.-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the
depdbCDB root. -
Create the application container from the PDB seed with the following statement:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE depappcon AS APPLICATION CONTAINER ADMIN USER depappconadm IDENTIFIED BY password STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G) DEFAULT TABLESPACE appcontbs DATAFILE '/disk2/oracle/dbs/depsappcon/depappcon01.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk2/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/', '/disk2/oracle/dbs/depappcon/');Note:
-
If the port of the listener used by the application root replica is not 1521, then a
PORTclause is required. -
If the host of the application root replica is different from the host of the master application root, then a
HOSTclause is required.
-
-
Open the new application root replica in read/write mode:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE depappcon OPEN;
-
-
Create and synchronize the proxy PDB in the master application root.
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the master application root.
-
Create a database link to the application root replica:
CREATE PUBLIC DATABASE LINK depappcon CONNECT TO depappconadm IDENTIFIED BY password USING 'depappcon'; -
Create the proxy PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE prxypdb AS PROXY FROM depappcon@depappcon FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk2/oracle/dbs/depsappcon/', '/disk1/oracle/dbs/prxypdb/'); -
Open the proxy PDB:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE prxypdb OPEN; -
Synchronize the proxy PDB with the master application root:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=prxypdb; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC;
-
-
Create and synchronize one or more application PDBs in the application root replica.
-
Change container to the application root replica:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=depappcon; -
Create application PDBs in the application root replica.
For example, create two application PDBs from the PDB seed:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE deppdb1 ADMIN USER deppdb1admin IDENTIFIED BY password STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G) DEFAULT TABLESPACE deppdb1tbs DATAFILE '/disk2/oracle/dbs/deppdb1/deppdb101.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk2/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/', '/disk2/oracle/dbs/deppdb1/'); CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE deppdb2 ADMIN USER deppdb2admin IDENTIFIED BY password STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G) DEFAULT TABLESPACE deppdb2tbs DATAFILE '/disk2/oracle/dbs/deppdb2/deppdb201.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk2/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/', '/disk2/oracle/dbs/deppdb2/'); -
Open both application PDBs:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE deppdb1 OPEN; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE deppdb2 OPEN; -
Synchronize the application PDBs with the master application root:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=deppdb1; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC; ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=deppdb2; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC;
-
-
Check the structure of the
apptbtable in an application PDB in the application root replica.-
From the application root replica, switch containers to the
deppdb1application PDB:ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=deppdb1; -
Describe the
apptbtable:desc apptbYour output is similar to the following:
Name Null? Type ------------------------------- -------- ------------ ID NUMBER(6) WIDGET_NAME VARCHAR2(20)
-
-
In the master application root, upgrade the application.
-
Change container to the master application root:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=msappcon; -
Begin the application upgrade.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp BEGIN UPGRADE '1.0' TO '1.1'; -
Modify the application.
For example, add a row to the
apptbtable:ALTER TABLE apptb ADD (widget_type VARCHAR2(30)); -
End the application upgrade:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp END UPGRADE TO '1.1';
-
-
Synchronize the proxy PDB with the master application root:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=prxypdb; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC; -
Synchronize the application PDBs in the application root replica and check for the application upgrade.
-
Synchronize the application PDBs:
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=deppdb1; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC; ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=deppdb2; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION sampleapp SYNC; -
From the application root replica, switch containers to the
deppdb1application PDB:ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=deppdb1; -
Describe the
apptbtable:desc apptbYour output is similar to the following:
Name Null? Type ------------------------------- -------- ------------ ID NUMBER(6) WIDGET_NAME VARCHAR2(20) WIDGET_TYPE VARCHAR2(30)Notice that the change in the application upgrade is reflected in the output because the
widget_typecolumn has been added to theapptbtable.
-
Setting the Compatibility Version of an Application
The compatibility version of an application is the earliest version of the application possible for the application PDBs that belong to the application container.
The compatibility version is enforced when the compatibility version is set and when an application PDB is created. If there are application root clones that resulted from application upgrades, then all application root clones that correspond to versions earlier than the compatibility version are implicitly dropped.
You specify the compatibility version of an application by issuing one of the following SQL statements when the application root is the current container:
-
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name SET COMPATIBILITY VERSION 'application_version_number';application_name is the name of the application, and application_version_number is the earliest compatible version.
-
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name SET COMPATIBILITY VERSION CURRENT;application_name is the name of the application. The current version is the version of the application in the application root.
Note:
You cannot plug in an application PDB that uses an application version earlier than the compatibility setting of the application container.
- In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the application root.
- Run an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION SET COMPATIBILITY VERSIONstatement.
Example 17-8 Setting the Compatibility Version to a Specific Version Number
This example sets the compatibility version for an application named salesapp to version 4.2.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp
SET COMPATIBILITY VERSION '4.2';Example 17-9 Setting the Compatibility Version to the Current Application Version
This example sets the compatibility version for an application named salesapp to the current application version.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp
SET COMPATIBILITY VERSION CURRENT;See Also:
"About Upgrading Applications in an Application Container" for information about application root clonesPerforming Bulk Inserts During Application Install, Upgrade, and Patch Operations
SQL*Loader is the only supported utility for bulk inserts into tables during application install, upgrade, and patch operations. Only conventional path loads are supported for bulk inserts during application install, upgrade, and patch operations.
The correct SQL*Loader module name must be specified between the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN and the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END statements. The module name is SQL Loader Conventional Path Load.
Example 17-10 Performing a Conventional Path Load During an Application Installation
In this example, the conventional path load is performed in an application root.
-
In SQL*Plus, switch to the application root.
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=cdb1_approot1; -
Set the correct module.
BEGIN DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO.SET_MODULE( 'SQL Loader Conventional Path Load', ''); END; -
Start the application installation.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION APP1 BEGIN INSTALL '1'; -
Use SQL*Loader to perform the conventional path load.
HOST sqlldr u1/u1@cdb1_approot1 control=my_bulk_load.ctl - rows=3 log=my_bulk_load.log -
End the application installation.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION APP1 END INSTALL '1';
See Also:
Oracle Database Utilities for information about SQL*LoaderUninstalling Applications from an Application Container
You can uninstall an application in an application container.
About Uninstalling Applications from an Application Container
You issue ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements to uninstall an application from the application root.
You uninstall the application from the application root only, and application PDBs that synchronize with the application uninstall the application automatically. The uninstall operation can be done with one or more of the following: scripts, SQL statements, and graphical user interface tools.
You must indicate the start of the uninstallation with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN UNINSTALL statement and the end of the uninstallation with an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END UNINSTALL statement. Each uninstallation must be associated with an application name and version number, which are specified in the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION statements.
Uninstalling an application does not remove the application from the data dictionary. It marks the application as UNINSTALLED so that upgrade, patch, and uninstall of the application is disallowed.
Destructive changes to application objects are allowed during application uninstallation. Applications running in an application PDB continue to function during uninstallation and after the application is uninstalled from the application root. The application can continue to function in the application PDB because the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN UNINSTALL statement creates a clone of the application root called an application root clone. An application root clone serves as a metadata repository for old versions of application objects, so that application PDBs that have not been synchronized with latest version of the application can continue to function. Because the clone is created while the application PDB is open, local undo must be configured at the CDB level before an application can be uninstalled.
Note:
An application upgrade also creates an application root clone.
See Also:
-
"About Upgrading Applications in an Application Container" for information about application root clones
Uninstalling an Application from an Application Container
To uninstall an application in from application container, run the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN UNINSTALL statement to begin the uninstallation and the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END UNINSTALL statement to end it. The application uninstalled from the application PDBs that synchronize with the application in the application root.
-
The CDB must be in local undo mode.
-
The current user must have the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEsystem privilege, and the privilege must be commonly granted in the application root. -
The application root must be in open read/write mode.
Managing Application Common Objects
Application common objects are shared, user-created database objects in an application container. Application common objects are created in an application root.
About Application Common Objects
Application common objects are created in an application root and are shared with the application PDBs that belong to the application root.
There are three types of application common object: metadata-linked, data-linked, and extended data-linked. The following types of database objects can be application common objects:
-
Analytic views
-
Attribute dimensions
-
Directories
-
External procedure libraries
-
Hierarchies
-
Java classes, resources, and sources
-
Object tables, types, and views
-
Sequences
-
Packages, stored functions, and stored procedures
-
Synonyms
-
Tables (including global temporary tables)
-
Triggers
-
Views
See Also:
Creation of Application Common Objects
Create application common objects by issuing a CREATE statement when the current container is the application root and specifying the SHARING clause.
You can specify the sharing attribute by including the SHARING clause in the CREATE statement or by setting the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter in the application root. When you set the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter, the setting is the default sharing attribute for all database objects of a supported type created in the application root. However, when a SHARING clause is included in a CREATE statement, its setting overrides the setting for the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter.
You can specify one of the following for the sharing attribute:
-
METADATA: A metadata link shares the database object’s metadata, but its data is unique to each container. These database objects are referred to as metadata-linked application common objects. This setting is the default. -
DATA: A data link shares the database object, and its data is the same for all containers in the application container. Its data is stored only in the application root. These database objects are referred to as data-linked application common objects. -
EXTENDED DATA: An extended data link shares the database object, and its data in the application root is the same for all containers in the application container. However, each application PDB in the application container can store data that is unique to the application PDB. For this type of database object, data is stored in the application root and, optionally, in each application PDB. These database objects are referred to as extended data-linked application common objects. -
NONE: The database object is not shared.
For most types of application common objects, the only valid settings for the SHARING clause are METADATA and NONE. The following types of application common objects allow additional settings for the SHARING clause:
-
For tables (excluding object tables), the
SHARINGclause can be set toMETADATA,DATA,EXTENDED DATA, orNONE. For object tables, onlyMETADATAorNONEis valid. -
For views (excluding object views), the
SHARINGclause can be set toMETADATA,DATA,EXTENDED DATA, orNONE. For object views, onlyMETADATAorNONEis valid. -
For sequences, the
SHARINGclause can be set toMETADATA,DATA, orNONE.With a metadata-linked sequence, each application PDB has its own sequence. When the metadata-linked sequence is incremented using the
NEXTVALpseudocolumn in one application PDB, it does not affect the value of the sequence in the other application PDBs in the application container.With a data-linked sequence, each application PDB shares the same sequence in the application root. When the metadata-linked sequence is incremented using the
NEXTVALpseudocolumn in one application PDB, all other application PDBs in the same application container also see the change.
Application common objects can be created or changed only as part of an application installation, upgrade, or patch. An application PDB applies changes to application common objects when it synchronizes with the application that made the changes. If an application PDB is closed when an application common object is created, dropped, or modified, then the appropriate changes are applied in the application PDB when it is opened and synchronized with the application.
The names of application common objects must not conflict with those of local database objects in any of the application PDBs that belong to the application root or Oracle-supplied common objects in the CDB root. If a newly opened application PDB contains a local database object whose name conflicts with that of an application common object, then the application PDB is opened in RESTRICTED mode. In this case, you must resolve the naming conflict before the application PDB can be opened in normal mode.
About Metadata-Linked Application Common Objects
For metadata-linked application common objects, the metadata for the object is stored once in the application root.
A metadata link in each application PDB that belongs to the application root enables the application PDBs to share the metadata for the object, including the object name and structure. The data for the object is unique to each container, including the application root and each application PDB that belongs to the application root.
Data definition language (DDL) operations on a metadata-linked application common object can be run in the application root only as part of an application installation, upgrade, or patch. However, the data can be modified in an application PDB using normal data manipulation language (DML) operations.
For example, consider a company with several regional offices. The company wants the structure of the information about employees to be consistent, but each office has different employees. If this company has a human resources application in an application container, it can create a separate application PDB for each regional office and use a metadata-linked table to store employee information. The data structure of the table, such as the columns, is the same in the application PDB for each regional office, but the employee data is different.
Another example might involve a company that builds and maintains a sales application that is used by several different businesses. Each business uses the same sales application, but the data for each business is different. For example, each business has different customers and therefore different customer data. To ensure that each client uses the same data structure for its application, the company might create an application container with metadata-linked application common objects. Each business that uses the sales application has its own application PDB, and the data structure is the same in each application PDB, but the data is different.
About Extended Data-Linked Application Common Objects
For data-linked application common objects, both the metadata and the data for the object is stored once in the application root. A data link in each application PDB that belongs to the application root enables the application PDBs to share the metadata and data of the object.
DDL operations on a data-linked application common object can be run in the application root only as part of an application installation, upgrade, or patch. In addition, the data can be modified using normal DML operations only in the application root. The data cannot be modified in application PDBs.
For example, consider a company with several regional offices. The company wants the information about the products they sell, such as the product names and descriptions, to be consistent at all of the regional offices. If this company has a sales application in an application container, then it can create a separate application PDB for each regional office and use a data-linked table to store product information. Each application PDB can query the product information, and the product information is consistent at each regional office.
Data-linked application common objects are also useful for data that is standard and does not change. For example, a table that stores the postal codes for a country might be a data-linked application common object in an application container. All of the application PDBs access the same postal code data in the application root.
Note:
If the data-linked application common object is part of a configuration that synchronizes an application root replica with a proxy PDB, then DML operations on a data-linked object in the application root can be done outside of an application action, but the DML operation is not automatically propagated to the application root replication through the proxy PDB. If you want the DML operation to be propagated to the application root replica, then the DML operation on a data-linked object in the application root must be done within an application installation, upgrade, or patch.
About Extended Data-Linked Application Common Objects
For an extended data-linked object, each application PDB can create its own data while sharing the common data in the application root. Only data stored in the application root is common for all application PDBs.
DDL operations on an extended data-linked application common object can be run in the application root only as part of an application installation, upgrade, or patch. However, the data can be modified in the application root or in an application PDB using normal DML operations.
For example, a sales application in an application container might support several application PDBs, and all of the application PDBs need the postal codes in the United States for shipping purposes. In this case the postal codes can be stored in the application root so that all of the application PDBs can access it. However, one application PDB also makes sales in Canada, and this application PDB requires the postal codes for the United States and Canada. This one application PDB can store the postal codes for Canada in an extended data-linked object in the application PDB instead of in the application root.
Note:
-
Tables and views are the only types of database objects that can be extended data-linked objects.
-
If the extended data-linked application common object is part of a configuration that synchronizes an application root replica with a proxy PDB, then DML operations on an extended data-linked object in the application root can be done outside of an application action, but the DML operation is not automatically propagated to the application root replication through the proxy PDB. If you want the DML operation to be propagated to the application root replica, then the DML operation on an extended data-linked object in the application root must be done within an application installation, upgrade, or patch.
Restrictions for Application Common Objects
Some restrictions apply to application common objects.
Queries on application common objects can return data from a container that is not the current container. For example, when the current container is an application root, queries that include the CONTAINERS clause can return data from application PDBs for metadata-linked application common objects. Also, when the current container is an application PDB, queries on data-linked and extended data-linked application common objects return data that resides in the application root.
Columns of the following types return no data in queries that return data from a container other than the current container:
-
The following user-defined types: object types, varrays, REFs, and nested tables
-
The following Oracle-supplied types:
ANYTYPE,ANYDATASET, URI types,SDO_TOPO_GEOMETRY,SDO_GEORASTER, andExpression
In addition, queries on object tables and object views return no data from containers other than the current container.
Related Topics
Creating Application Common Objects
You create an application common object in an application root either by ensuring that the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter is set to the correct value or by including the SHARING clause in the CREATE SQL statement.
Example 17-11 Setting the DEFAULT_SHARING Initialization Parameter
This example sets the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter to DATA both in memory and in the SPFILE. When a database object that supports sharing is created in the application root, and no SHARING clause is included in the CREATE SQL statement, the database object uses the sharing attribute specified in the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter.
ALTER SYSTEM SET DEFAULT_SHARING=DATA SCOPE=BOTH;Example 17-12 Creating a Metadata-Linked Object
This example creates the employees_md metadata-linked table by including the SHARING=METADATA clause. The application_name is salesapp and the application_version_number is 4.2, and the object is created during application installation.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp BEGIN INSTALL '4.2';
CREATE TABLE employees_md SHARING=METADATA
(employee_id NUMBER(6),
first_name VARCHAR2(20),
last_name VARCHAR2(25) CONSTRAINT emp_last_name_nn_demo NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR2(25) CONSTRAINT emp_email_nn_demo NOT NULL,
phone_number VARCHAR2(20),
hire_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE
CONSTRAINT emp_hire_date_nn_demo NOT NULL,
job_id VARCHAR2(10) CONSTRAINT emp_job_nn_demo NOT NULL,
salary NUMBER(8,2) CONSTRAINT emp_salary_nn_demo NOT NULL,
commission_pct NUMBER(2,2),
manager_id NUMBER(6),
department_id NUMBER(4),
dn VARCHAR2(300),
CONSTRAINT emp_salary_min_demo CHECK (salary > 0),
CONSTRAINT emp_email_uk_demo UNIQUE (email));
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp END INSTALL '4.2';Example 17-13 Creating a Data-Linked Object
This example creates the product_descriptions_ob data-linked table by including the SHARING=DATA clause. The application_name is salesapp and the application_version_number is 4.2, and the object is created during application installation.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp BEGIN INSTALL '4.2';
CREATE TABLE product_descriptions_ob SHARING=DATA (
product_id NUMBER(6),
language_id VARCHAR2(3),
translated_name NVARCHAR2(50)
CONSTRAINT translated_name_nn NOT NULL,
translated_description NVARCHAR2(2000)
CONSTRAINT translated_desc_nn NOT NULL);
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp END INSTALL '4.2';Example 17-14 Creating an Extended Data-Linked Object
This example creates the postalcodes extended data-linked table by including the EXTENDED keyword and the SHARING clause. The application_name is salesapp and the application_version_number is 4.2, and the object is created during application installation.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp BEGIN INSTALL '4.2';
CREATE TABLE postalcodes SHARING=EXTENDED DATA
(code VARCHAR2(7),
country_id NUMBER,
place_name VARCHAR2(20));
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp END INSTALL '4.2';Example 17-15 Creating an Object That Is Not Shared in an Application Root
This example creates the departments_ns table and specifies that it is not a shared common application object by including the SHARING=NONE clause. After creation, this database object can be accessed only in the application root.
CREATE TABLE departments_ns SHARING=NONE
(department_id NUMBER(4),
department_name VARCHAR2(30) CONSTRAINT dept_name_nn NOT NULL,
manager_id NUMBER(6),
location_id NUMBER(4),
dn VARCHAR2(300));Note:
TheALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN and END statements are not required when you create an object that is not a shared common object. However, if you create an object that is not shared in between ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN and END statements, then the object is created in application PDBs that synchronize with the application.
Issuing DML Statements on Application Common Objects
The rules are different for issuing DML statements on metadata-linked, data-linked, and extended data-linked application common objects.
Issuing DML on Metadata-Linked Common Objects
You can issue DML on metadata-linked application objects as normal.
For metadata-linked application common objects, the object definitions are the same in all application PDBs, but the data is different. Users and applications can issue DML statements on these objects in the same way as for ordinary database objects. The DML only affects the current container.
Querying Using the CONTAINERS Clause
For metadata-linked objects, the CONTAINERS clause enables you to query a table or view across all PDBs in an application container.
For metadata-linked objects, the CONTAINERS clause is useful when DML is run in the application root. The query performs a UNION ALL, returning all rows from the object in the root and all open application PDBs (except those in RESTRICTED mode).
To query a subset of the PDBs, specify the CON_ID or CON$NAME in predicate. If the queried table or view does not already contain a CON_ID column, then the query adds a CON_ID column to the query result, which identifies the container whose data a given row represents.
Prerequisites
Note the following prerequisites:
-
To query data in an application container, you must be a common user connected to the application root.
-
The table or view must exist in the application root and all PDBs in the application container.
-
The table or view must be in your own schema. It is not necessary to specify
schema, but if you do, then you must specify your own schema.
To query a metadata-linked object in an application container:
-
Log in to the application root as an application common user.
-
Specify the
CONTAINERSclause in aSELECTstatement.For example, the following statement counts the number of rows in the
sh.customerstable in the root and every application PDB (sample output included):SELECT c.CON_ID, COUNT(*) FROM CONTAINERS(sh.customers) c GROUP BY c.CON_ID ORDER BY 1; CON_ID COUNT(*) ---------- ---------- 3 20002 6 426 8 7232
Setting the Default Container or DML
You can set the CONTAINERS_DEFAULT attribute on any metadata-linked object so that DML issued in the application root is wrapped in the CONTAINERS clause by default.
Set ENABLE CONTAINERS_DEFAULT in either an ALTER TABLE or ALTER VIEW statement. The CONTAINERS_DEFAULT column in the DBA_TABLES and DBA_VIEWS views shows whether the database object is enabled for the CONTAINERS clause by default.
To set the default container for DML involving a metadata-linked table or view:
-
Log in to the application root as an application common user.
-
Issue an
ALTER TABLEorALTER VIEWstatement with theENABLE CONTAINERS_DEFAULTclause in the application root.The following statement sets the default container for
sh.customers:ALTER TABLE sh.customers ENABLE CONTAINERS_DEFAULT;After setting this attribute, queries and DML statements issued in the application root use the
CONTAINERSclause by default forsh.customers.
Issuing DML on Data-Linked Common Objects
For data-linked application objects, issue DML as normal in the application root. For extended data-linked application objects, issue DML as normal in the application root and in application PDBs.
For data-linked application objects, DML in the application root affects the data accessible by all PDBs in the application container. You cannot issue DML on data-linked application objects in application PDBs.
For extended data-linked application objects, DML in the application root affects the data accessible by all PDBs in the application container. DML in an application PDB only affects data that is unique to the application PDB.
Consider an application root that has data-linked or extended data-linked objects. Also, assume that this root is the master for application root replicas synchronized with proxy PDBs. In this case, DML only synchronizes with the replicas when DML occurs during an application installation, upgrade, or patch. Specifically, DML must occur in the root between ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... {BEGIN|END} statements. Other DML applies only to the current root and is not synchronized with root replicas.
To issue DML for an application common object that is not part of an application root replica configuration:
-
Connect to the appropriate container in the application container as a user with the privileges required to issue DML statements on the database object.
-
Issue DML statements normally.
To issue DML for a data-linked or extended data-linked object that is part of an application root replica configuration:
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the master application root in the application root replica in the configuration.
The current user must have the privileges required to issue the DML statements on the database object.
-
Run the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... BEGINstatement for beginning an application installation, upgrade, or patch.If you are modifying the application common object as part of an application upgrade, then issue the upgrade statement in the following form:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name BEGIN UPGRADE 'application_start_version_number' TO 'application_end_version_number';For example, run the following statement if the application_name is
salesapp, the application_start_version_number is 4.2, and the application_end_version_number is 4.3:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp BEGIN UPGRADE '4.2' TO '4.3'; -
Issue the DML statements on the data-linked application common object.
-
Run the
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... ENDstatement.For example, if you are modifying the application common object as part of an application upgrade, then run the statement in the following form:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name END UPGRADE TO 'application_end_version_number';For example, run the following statement if the application_name is
salesapp, the application_start_version_number is 4.2, and the application_end_version_number is 4.3:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp END UPGRADE TO '4.3';Note:
Ensure that the application_name and application_end_version_number match in theALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN UPGRADEstatement andALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END UPGRADEstatements. -
To synchronize all application PDBs that must apply these changes, issue an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATIONstatement with theSYNCclause when the application PDB is the current container.
Modifying Application Common Objects with DDL Statements
When you modify an application common object in an application root with certain DDL statements, you must modify the object between ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN and ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END statements, and application PDBs must synchronize with the application to apply the changes.
ALTER, RENAME, or DROP SQL statement on the database object to perform a DDL change.
Issuing DML Statements on Containers in an Application Container
A DML statement issued in an application root can modify one or more containers in the application container. In addition, you can specify one or more default container targets for DML statements.
About Issuing DML Statements on Containers in an Application Container
DML statements can affect database objects in more than one container in an application container.
In an application root, a single DML statement that includes the CONTAINERS clause can modify a table or view in one or more containers in the application container. To use the CONTAINERS clause, specify the table or view being modified in the CONTAINERS clause and the containers in the WHERE clause. A target container can be specified in an INSERT VALUES statement by specifying a value for CON_ID in the VALUES clause. Also, a target container can be specified in an UPDATE or DELETE statement by specifying a CON_ID predicate in the WHERE clause.
sales.customers table in the containers with a CON_ID of 7 or 8:UPDATE CONTAINERS(sales.customers) ctab
SET ctab.city_name='MIAMI'
WHERE ctab.CON_ID IN(7,8) AND
CUSTOMER_ID=3425;The values specified for the CON_ID in the WHERE clause must be for containers in the current application container.
You can specify default target containers for DML operations. If a DML statement does not specify values for the CON_ID in the WHERE clause, then the target containers of the DML operation are those specified in the database property CONTAINERS_DEFAULT_TARGET in the application root. When issued in an application root, the following DML statement modifies the default target containers for the application container:
UPDATE CONTAINERS(sales.customers) ctab
SET ctab.city_name='MIAMI'
WHERE CUSTOMER_ID=3425;SELECT PROPERTY_VALUE
FROM DATABASE_PROPERTIES
WHERE PROPERTY_NAME='CONTAINERS_DEFAULT_TARGET';In addition, you can enable the CONTAINERS_DEFAULT attribute for a table or view in an application root. When this attribute is enabled, the CONTAINERS clause is used for queries and DML statements on the database object by default, and the CONTAINERS clause does not need to be specified in the SQL statements. To enable the CONTAINERS_DEFAULT attribute for a table or view in an application root, run the an ALTER TABLE or ALTER VIEW statement with the ENABLE CONTAINERS_DEFAULT clause.
The following restrictions apply to the CONTAINERS clause:
-
The
CONTAINERS DEFAULT TARGETclause does not affectSELECTstatements. -
INSERTasSELECTstatements where the target of theINSERTis inCONTAINERS()is not supported. -
A multitable
INSERTstatement where the target of theINSERTis inCONTAINERS()is not supported. -
DML statements using the
CONTAINERSclause require that the database listener is configured using TCP (instead of IPC) and that thePORTandHOSTvalues are specified for each target PDB using thePORTandHOSTclauses, respectively.
Related Topics
Specifying the Default Container for DML Statements in an Application Container
To specify the default container for DML statements in an application container, issue the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement with the CONTAINERS DEFAULT TARGET clause.
WHERE clause, the DML statement affects the default container for the application container. The default container can be any container in the application container, including the application root or an application PDB. Only one default container is allowed.
Example 17-16 Specifying the Default Container for DML Statements in an Application Container
This example specifies that APDB1 is the default container for DML statements in the application container.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE CONTAINERS DEFAULT TARGET = (APDB1);Example 17-17 Clearing the Default Container
This example clears the default container setting. When it is not set, the default container is the application root.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE CONTAINERS DEFAULT TARGET = NONE;Partitioning by PDB with Container Maps
Container maps enable the partitioning of data at the application PDB level when the data is not physically partitioned at the table level.
About Container Maps
A container map is a database property that specifies a partitioned map table defined in an application root.
Use a container map to partition the data in metadata-linked objects. Container maps partition data in application PDBs based on a commonly-used column.
For example, you might create a metadata-linked table named countries_mlt (with a column cname) that stores different data in each application PDB. The map table named pdb_map_tbl partitions by list on the cname column. The partitions amer_pdb, euro_pdb, and asia_pdb correspond to the names of the application PDBs.
A container map can define a logical partition key on a column for a common object. Because the container is resolved internally based on the container map, this mapping removes the requirement to define a query with a CON_ID predicate or use the CONTAINERS clause in the query.
Some types of row-based consolidation use a tenant ID with a single PDB that contains multiple tenants. Container maps are useful for migrating to a configuration that uses a different PDB for each tenant.
Map Objects
The map object is the partitioned table.
The names of the partitions in the map table match the names of the application PDBs in the application container. The metadata-linked object is not physically partitioned at the table level, but it can be queried using the partitioning strategy used by the container map.
To associate the map table with the metadata-linked table, specify the map table in ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... CONTAINER_MAP while connected to the application root. You can create no more than one container map in an application container. You cannot create container maps in the CDB root.
Note:
-
Data must be loaded into the PDB tables in a manner that is consistent with the partitions defined in map object.
-
When there are changes to the application PDBs in an application container, the map object is not synchronized automatically to account for these changes. For example, an application PDB that is referenced in a map object can be unplugged, renamed, or dropped. The map object must be updated manually to account for such changes.
Starting in Oracle Database 18c, for a CONTAINERS() query to use a map, the partitioning column in the map table does not need to match a column in the metadata-linked table. Assume that the table sh.sales is enabled for the container map pdb_map_tbl, and cname is the partitioning column for the map table. Even though sh.sales does not include a cname column, the map table routes the following query to the appropriate PDB: SELECT * FROM CONTAINERS(sh.sales) WHERE cname = 'US' ORDER BY time_id.
List-Partitioned Container Map: Example
This example uses a container map to route queries to PDBs that store data for a geographical region.
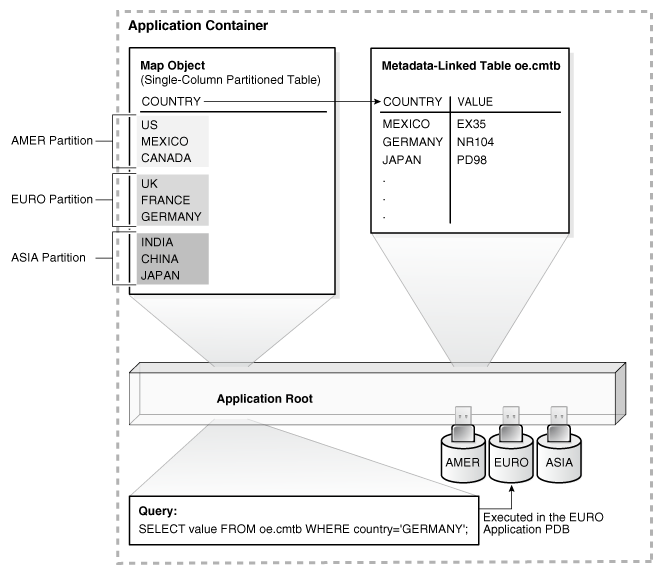
The following illustration of an application root shows a map object, a metadata-linked table, and a query on the metadata-linked table. The query is executed in the appropriate application PDB.
The illustration shows an application container with three application PDBs named AMER, EURO, and ASIA. The PDBs store data for the corresponding regions. A metadata-linked table named oe.cmtb stores information for an application. This table has a COUNTRY column. For this partitioning strategy, partition by list is used to create a map object that creates a partition for each region. The country value, which is GERMANY in the query shown in the illustration, determines the region, which is EURO.
See Also:
"Creating a Container Map" for a detailed description of this example
Range-Partitioned Container Map: Example
This example uses a container map to route queries to PDBs that store data for a particular department.
Consider another example that uses a range-partitioned table for the map object. The following SQL statement creates the map object in the application root:
CREATE TABLE app_con_admin.conmap (
department_id NUMBER NOT NULL)
PARTITION BY RANGE (department_id) (
PARTITION apppdb1 VALUES LESS THAN (100),
PARTITION apppdb2 VALUES LESS THAN (200),
PARTITION apppdb3 VALUES LESS THAN (300));apppdb1, apppdb2, and apppdb3 based on the commonly-used column department_id. The following SQL statement sets the CONTAINER_MAP database property to the app_con_admin.conmap table in the application root:ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SET CONTAINER_MAP='app_con_admin.conmap';CONTAINERS clause. For example, the following queries return similar results:SELECT employee_id
FROM CONTAINERS(hr.employees)
WHERE department_id = 10
AND CON_ID IN (44);
SELECT employee_id
FROM hr.employees
WHERE department_id = 10;As shown in the first query with the CONTAINERS clause, when the query only pertains to a single application PDB, the query must specify the container ID of this application PDB in the WHERE clause. This requirement might cause application changes.
The second query uses the container map, replacing the CONTAINERS clause. The second query does not specify the container because the container map directs the query to the correct application PDB. Queries that use container maps are generally more efficient than queries that use the CONTAINERS clause.
The container map must be created by a common user with ALTER DATABASE system privilege. Queries run against an object that is enabled for container map. Query privileges are determined by privileges granted on the object.
Creating a Container Map
Create a container map by creating a map object and setting the CONTAINER_MAP database property to the map object.
Prerequisites
To create a container map, you must meet the following prerequisites:
-
Before creating a container map, an application container with application PDBs must exist in the CDB.
-
The application container must have at least one application installed in it.
To create a container map:
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the application root.
-
Set the
CONTAINER_MAPdatabase property to the map object.In the following statement, replace map_table_schema with the owner of the table, and replace map_table_name with the name of the table:
ALTER DATABASE SET CONTAINER_MAP = 'map_table_schema.map_table_name'; -
Start an application installation, upgrade, or patch.
-
If the metadata-linked table that will be used by the container map does not exist, then create it.
-
Enable the container map for the table to be queried by issuing an
ALTER TABLE ... ENABLE CONTAINER_MAPstatement. -
Ensure that the table to be queried is enabled for the
CONTAINERSclause by issuing anALTER TABLE ... ENABLE CONTAINERS_DEFAULTstatement. -
End the application installation, upgrade, or patch started previously.
Example 17-18 Creating and Using a Container Map
This example creates a simple application that uses a container map. Assume that an application container has three application PDBs named AMER, EURO, and ASIA. The application PDBs store data for the different regions (America, Europe, and Asia, respectively). A metadata-linked table stores information for an application and has a COUNTRY column. For this partitioning strategy, partition by list is used to create a map object that creates a partition for each region, and the country value is used to determine the region.
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the application root.
-
Create the map object.
CREATE TABLE salesadm.conmap (country VARCHAR2(30) NOT NULL) PARTITION BY LIST (country) ( PARTITION AMER VALUES ('US','MEXICO','CANADA'), PARTITION EURO VALUES ('UK','FRANCE','GERMANY'), PARTITION ASIA VALUES ('INDIA','CHINA','JAPAN') ); -
Set the
CONTAINER_MAPdatabase property to the map object.ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SET CONTAINER_MAP='salesadm.conmap'; -
Begin an application installation.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp BEGIN INSTALL '1.0'; -
Create a metadata-linked table that will be queried using the container map.
CREATE TABLE oe.cmtb SHARING=METADATA ( value VARCHAR2(30), country VARCHAR2(30)); -
Enable the container map for the table to be queried.
ALTER TABLE oe.cmtb ENABLE CONTAINER_MAP; -
Ensure that the table to be queried is enabled for the
CONTAINERSclause.ALTER TABLE oe.cmtb ENABLE CONTAINERS_DEFAULT; -
End the application installation.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp END INSTALL '1.0'; -
Switch session into each application PDB and synchronize it.
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=amer; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp SYNC; ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=euro; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp SYNC; ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=asia; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION salesapp SYNC; -
Insert values into the
oe.cmtbtable in each application PDB based on the partitioning strategy.ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=amer; INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('AMER VALUE','US'); INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('AMER VALUE','MEXICO'); INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('AMER VALUE','CANADA'); COMMIT; ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=euro; INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('EURO VALUE','UK'); INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('EURO VALUE','FRANCE'); INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('EURO VALUE','GERMANY'); COMMIT; ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=asia; INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('ASIA VALUE','INDIA'); INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('ASIA VALUE','CHINA'); INSERT INTO oe.cmtb VALUES ('ASIA VALUE','JAPAN'); COMMIT; -
Switch session into the application root and query the data using the container map.
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=sales; SELECT value FROM oe.cmtb WHERE country='MEXICO'; SELECT value FROM oe.cmtb WHERE country='GERMANY'; SELECT value FROM oe.cmtb WHERE country='JAPAN';The output for the first query should be
AMER VALUE, the output for the second query should beEURO VALUE, and the output for the third query should beASIA VALUE. These values illustrate that the container map is working correctly.