13 Oracle GoldenGate Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can configure and manage Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in Oracle Database.
- About Oracle GoldenGate
Oracle GoldenGate is a heterogeneous replication system with integrated support for replication between Oracle and other databases. - About Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
When Oracle GoldenGate replicates changes between Oracle databases, you can configure and manage Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in the Oracle databases. - Configuring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can configure Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in Oracle Database with theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage. This is specific to Oracle GoldenGate version 12.3 and later. No CDR configuration parameters need to be specified in the Golden Gate replicat file, other than aMAPstatement that includes the table to be replicated. - Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can manage Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in Oracle Database with theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage. - Monitoring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can monitor Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in an Oracle database by querying data dictionary views.
Parent topic: Oracle GoldenGate Capabilities in Oracle Database
13.1 About Oracle GoldenGate
Oracle GoldenGate is a heterogeneous replication system with integrated support for replication between Oracle and other databases.
Oracle GoldenGate is integrated with Oracle Database to capture DML and DDL changes from the redo logs and apply the changes at the target. Oracle GoldenGate provides capture, routing, transformation, and delivery of transactional data across Oracle databases or heterogeneous databases in real time.
When Oracle GoldenGate captures changes that originated at an Oracle database, each change is encapsulated in a row logical change record (LCR). A row LCR is a structured representation of a DML row change. Each row LCR includes the operation type, old column values, and new column values. Multiple row LCRs can be part of a single database transaction.
See Also:
-
"Row LCRs"
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate
13.2 About Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
When Oracle GoldenGate replicates changes between Oracle databases, you can configure and manage Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in the Oracle databases.
Note:
The documentation in this book is for the automatic conflict detection and resolution feature that is specific to Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2) and later, which is configured in an Oracle database. It also requires Oracle GoldenGate version 12.3 and later. There is also a general Oracle GoldenGate feature for conflict detection and resolution, which is called Oracle GoldenGate conflict detection and resolution (CDR). Oracle GoldenGate CDR is configured in the Replicat parameter file, and it is documented in the Oracle GoldenGate documentation.
You can configure only one of the following types of automatic conflict detection and resolution for a single table:
-
The automatic conflict detection and resolution feature that is specific to Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2)
-
Oracle GoldenGate CDR
- Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can configure automatic conflict detection and resolution in an Oracle GoldenGate configuration that replicates tables between Oracle databases. To configure conflict detection and resolution for a table, call theADD_AUTO_CDRprocedure in theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage. - Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution
With timestamp conflict detection, a conflict occurs when the timestamp in the old column list of the row logical change record (row LCR) differs from the timestamp for the corresponding row in the table. - Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution
With delta conflict detection, a conflict occurs when a value in the old column list of the row logical change record (row LCR) differs from the value for the corresponding row in the table. - Column Groups
A column group is a logical grouping of one or more columns in a replicated table. When you add a column group, conflict detection and resolution is performed on the columns in the column group separately from the other columns in the table.
13.2.1 Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can configure automatic conflict detection and resolution in an Oracle GoldenGate configuration that replicates tables between Oracle databases. To configure conflict detection and resolution for a table, call the ADD_AUTO_CDR procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package.
Automatic conflict detection and resolution does not require application changes for the following reasons:
-
Oracle Database automatically creates and maintains invisible timestamp columns.
-
Inserts, updates, and deletes use the delete tombstone log table to determine if a row was deleted.
-
LOB column conflicts can be detected.
-
Oracle Database automatically configures supplemental logging on required columns.
Supplemental logging is required to ensure that each row LCR has the information required to detect and resolve a conflict. Supplemental logging places additional information in the redo log for the columns of a table when a DML operation is performed on the table. When you configure a table for Oracle GoldenGate conflict detection and resolution, supplemental logging is configured automatically for all of the columns in the table.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Utilities for information about supplemental logging
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate
Parent topic: About Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.2.2 Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution
With timestamp conflict detection, a conflict occurs when the timestamp in the old column list of the row logical change record (row LCR) differs from the timestamp for the corresponding row in the table.
When you run the ADD_AUTO_CDR procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package to configure a table for automatic Oracle GoldenGate conflict detection and resolution, a hidden timestamp column is added to the table. This hidden timestamp column records the time of a row change, and this information is used to detect and resolve conflicts.
When a row LCR is applied, a conflict can occur for an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operation. The following table describes each type of conflict and how it is resolved with latest timestamp conflict detection and resolution.
Table 13-1 Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution
| Operation | Conflict Detection | Conflict Resolution |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A conflict is detected when the table has the same value for a key column as the new value in the row LCR. |
If the timestamp of the row LCR is later than the timestamp in the table row, then the values in the row LCR replace the values in the table. If the timestamp of the row LCR is earlier than the timestamp in the table row, then the row LCR is discarded, and the table values are retained. |
|
|
A conflict is detected in each of the following cases:
|
If there is a value mismatch and the timestamp of the row LCR is later than the timestamp in the table row, then the values in the row LCR replace the values in the table. If there is a value mismatch and the timestamp of the row LCR is earlier than the timestamp in the table row, then the row LCR is discarded, and the table values are retained. If the table row does not exist and the timestamp of the row LCR is later than the timestamp in the tombstone table row, then the row LCR is converted from an If the table row does not exist and the timestamp of the row LCR is earlier than the timestamp in the tombstone table row, then the row LCR is discarded. If the table row does not exist and there is no corresponding row in the tombstone table, then the row LCR is converted from an |
|
|
A conflict is detected in each of the following cases:
|
If the timestamp of the row LCR is later than the timestamp in the table, then delete the row from the table. If the timestamp of the row LCR is earlier than the timestamp in the table, then the row LCR is discarded, and the table values are retained. If the delete is successful, then log the row LCR by inserting it into the tombstone table. If the table row does not exist, then log the row LCR by inserting it into the tombstone table. |
See Also:
"Column Groups"Parent topic: About Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.2.3 Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution
With delta conflict detection, a conflict occurs when a value in the old column list of the row logical change record (row LCR) differs from the value for the corresponding row in the table.
To configure delta conflict detection and resolution for a table, run the ADD_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RES procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package. The delta resolution method does not depend on a timestamp or an extra resolution column. With delta conflict resolution, the conflict is resolved by adding the difference between the new and old values in the row LCR to the value in the table. This resolution method is generally used for financial data such as an account balance. For example, if a bank balance is updated at two sites concurrently, then the converged value accounts for all debits and credits.
The following figure provides an example that illustrates delta conflict detection and resolution.
Figure 13-1 Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution
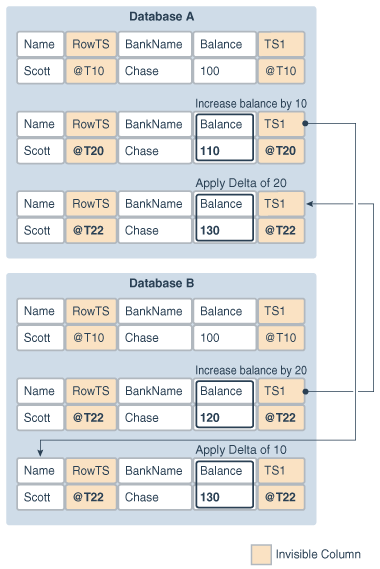
Description of "Figure 13-1 Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution"
This example shows a row being replicated at database A and database B. The Balance column is designated as the column on which delta conflict resolution is performed, and the TS1 column is the invisible timestamp column to track the time of each change to the Balance column. A change is made to the Balance value in the row in both databases at nearly the same time (@T20 in database A and @T22 in database B). These changes result in a conflict, and delta conflict resolution is used to resolve the conflict in the following way:
-
At database A, the value of
Balancewas changed from100to110. Therefore, the value was increased by 10. -
At database B, the value of
Balancewas changed from100to120. Therefore, the value was increased by 20. -
To resolve the conflict at database A, the value of the difference between the new and old values in the row LCR to the value in the table. The difference between the new and old values in the LCR is 20 (120–100=20). Therefore, the current value in the table (110) is increased by 20 so that the value after conflict resolution is 130.
-
To resolve the conflict at database B, the value of the difference between the new and old values in the row LCR to the value in the table. The difference between the new and old values in the LCR is 10 (110–100=10). Therefore, the current value in the table (120) is increased by 10 so that the value after conflict resolution is 130.
After delta conflict resolution, the value of the Balance column is the same for the row at database A and database B.
Parent topic: About Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.2.4 Column Groups
A column group is a logical grouping of one or more columns in a replicated table. When you add a column group, conflict detection and resolution is performed on the columns in the column group separately from the other columns in the table.
When you configure a table for Oracle GoldenGate conflict detection and resolution with the ADD_AUTO_CDR procedure, all of the scalar columns in the table are added to a default column group. To define other column groups for the table, run the ADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP procedure. Any columns in the table that are not part of a user-defined column group remain in the default column group for the table.
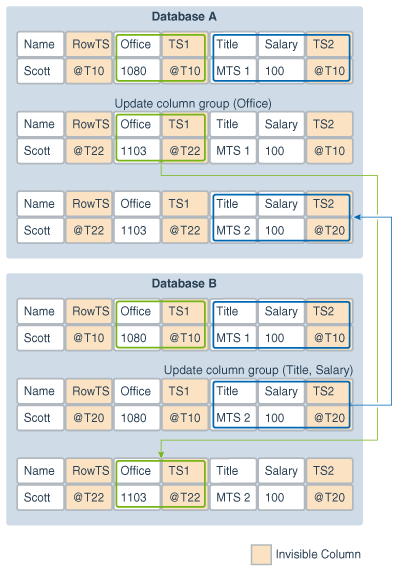
Column groups enable different databases to update different columns in the same row at nearly the same time without causing a conflict. When column groups are configured for a table, conflicts can be avoided even if different databases update the same row in the table. A conflict is not detected if the updates change the values of columns in different column groups. The following figure provides an example that illustrates column groups.
This example shows a row being replicated at database A and database B. The following two column groups are configured for the replicated table at each database:
-
One column group includes the
Officecolumn. The invisible timestamp column for this column group isTS1. -
Another column group includes the
TitleandSalarycolumns. The invisible timestamp column for this column group isTS2.
These column groups enable database A and database B to update the same row at nearly the same time without causing a conflict. Specifically, the following changes are made:
-
At database A, the value of
Officewas changed from1080to1030. -
At database B, the value of
Titlewas changed fromMTS1toMTS2.
Because the Office column and the Title column are in different column groups, the changes are replicated without a conflict being detected. The result is that values in the row are same at both databases after each change has been replicated.
Piecewise LOB Updates
A set of lob operations composed of LOB WRITE, LOB ERASE, and LOB TRIM is a piecewise LOB update. When a table that contains LOB columns is configured for conflict detection and resolution, each LOB column is placed in its own column group, and the column group has its own hidden timestamp column. The timestamp column is updated on the first piecewise LOB operation.
For a LOB column, a conflict is detected and resolved in the following ways:
-
If the timestamp for the LOB’s column group is later than the corresponding LOB column group in the row, then the piecewise LOB update is applied.
-
If the timestamp for the LOB’s column group is earlier than the corresponding LOB column group in the row, then the LOB in the table row is retained.
-
If the row does not exist in the table, then an error is raised.
Parent topic: About Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.3 Configuring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can configure Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in Oracle Database with the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package. This is specific to Oracle GoldenGate version 12.3 and later. No CDR configuration parameters need to be specified in the Golden Gate replicat file, other than a MAP statement that includes the table to be replicated.
- Configuring Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution
TheADD_AUTO_CDRprocedure in theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage configures latest timestamp conflict detection and resolution. TheADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPprocedure adds optional column groups. - Configuring Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution
TheADD_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RESprocedure in theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage configures delta conflict detection and resolution.
13.3.1 Configuring Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution
The ADD_AUTO_CDR procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package configures latest timestamp conflict detection and resolution. The ADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP procedure adds optional column groups.
ADD_AUTO_CDR procedure, it adds an invisible timestamp column for each row in the specified table and configures timestamp conflict detection and resolution. When you use the ADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP procedure to add one or more column groups, it adds a timestamp for the column group and configures timestamp conflict detection and resolution for the column group.
GRANT_ADMIN_PRIVILEGE procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package.
- Connect to each database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
ADD_AUTO_CDRprocedure and specify the table to configure for latest timestamp conflict detection and resolution. - Optional: Run the
ADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPprocedure and specify one or more column groups in the table. - Repeat the previous steps in each Oracle database that replicates the table.
Example 13-1 Configuring Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution for a Table
This example configures latest timestamp conflict detection and resolution for the hr.employees table.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.ADD_AUTO_CDR(
schema_name => 'hr',
table_name => 'employees');
END;
/Example 13-2 Configuring Column Groups
This example configures the following column groups for timestamp conflict resolution on the hr.employees table:
-
The
job_identifier_cgcolumn group includes thejob_id,department_id, andmanager_idcolumns. -
The
compensation_cgcolumn group includes thesalaryandcommission_pctcolumns.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.ADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP(
schema_name => 'hr',
table_name => 'employees',
column_list => 'job_id,department_id,manager_id',
column_group_name => 'job_identifier_cg');
END;
/
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.ADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP(
schema_name => 'hr',
table_name => 'employees',
column_list => 'salary,commission_pct',
column_group_name => 'compensation_cg');
END;
/See Also:
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate replication and configuring an Oracle GoldenGate administrator
Parent topic: Configuring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.3.2 Configuring Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution
The ADD_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RES procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package configures delta conflict detection and resolution.
GRANT_ADMIN_PRIVILEGE procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package.
- Connect to each database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
ADD_AUTO_CDRprocedure and specify the table to configure for latest timestamp conflict detection and resolution. - Run the
ADD_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RESprocedure and specify the column on which delta conflict detection and resolution is performed. - Repeat the previous steps in each Oracle database that replicates the table.
Example 13-3 Configuring Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution for a Table
This example configures delta conflict detection and resolution for the order_total column in the oe.orders table.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.ADD_AUTO_CDR(
schema_name => 'oe',
table_name => 'orders');
END;
/
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.ADD_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RES(
schema_name => 'oe',
table_name => 'orders',
column_name => 'order_total');
END;
/See Also:
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate replication and configuring an Oracle GoldenGate administrator
Parent topic: Configuring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.4 Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can manage Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in Oracle Database with the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package.
- Altering Conflict Detection and Resolution for a Table
TheALTER_AUTO_CDRprocedure in theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage alters conflict detection and resolution for a table. - Altering a Column Group
TheALTER_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPprocedure alters a column group. - Purging Tombstone Rows
ThePURGE_TOMBSTONESprocedure removes tombstone rows that were recorded before a specified date and time. This procedure removes the tombstone rows for all tables configured for conflict resolution in the database. - Removing Conflict Detection and Resolution From a Table
TheREMOVE_AUTO_CDRprocedure in theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage removes automatic conflict detection and resolution from a table. This procedure also removes any column groups and delta conflict detection and resolution configured for the table. - Removing a Column Group
TheREMOVE_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPprocedure removes a column group. - Removing Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution
TheREMOVE_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RESprocedure in theDBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADMpackage removes delta conflict detection and resolution for a column.
13.4.1 Altering Conflict Detection and Resolution for a Table
The ALTER_AUTO_CDR procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package alters conflict detection and resolution for a table.
- Connect to each database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
ALTER_AUTO_CDRprocedure and specify the table to configure for latest timestamp conflict detection and resolution. - Repeat all of the previous steps in each Oracle database that replicates the table.
Example 13-4 Altering Conflict Detection and Resolution for a Table
This example alters conflict detection and resolution for the hr.employees table to specify that delete conflicts are tracked in a tombstone table.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.ALTER_AUTO_CDR(
schema_name => 'hr',
table_name => 'employees',
tombstone_deletes => TRUE);
END;
/See Also:
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate
Parent topic: Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.4.2 Altering a Column Group
The ALTER_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP procedure alters a column group.
- Connect to the inbound server database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
ALTER_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPprocedure and specify one or more column groups in the table. - Repeat all of the previous steps in each Oracle database that replicates the table.
Example 13-5 Altering a Column Group
This example removes the manager_id column from the job_identifier_cg column group for the hr.employees table.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.ALTER_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP(
schema_name => 'hr',
table_name => 'employees',
column_group_name => 'job_identifier_cg',
remove_column_list => 'manager_id');
END;
/Note:
If there is more than one column, then use a comma-separated list.See Also:
-
"Configuring Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution"
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate.
Parent topic: Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.4.3 Purging Tombstone Rows
The PURGE_TOMBSTONES procedure removes tombstone rows that were recorded before a specified date and time. This procedure removes the tombstone rows for all tables configured for conflict resolution in the database.
- Connect to each database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
PURGE_TOMBSTONESprocedure and specify the date and time.
Example 13-6 Purging Tombstone Rows
This example purges all tombstone rows recorded before 3PM on December, 1, 2015 Eastern Standard Time. The timestamp must be entered in TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE format.
EXEC DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.PURGE_TOMBSTONES('2015-12-01 15:00:00.000000 EST');See Also:
-
"Configuring Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution"
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate
Parent topic: Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.4.4 Removing Conflict Detection and Resolution From a Table
The REMOVE_AUTO_CDR procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package removes automatic conflict detection and resolution from a table. This procedure also removes any column groups and delta conflict detection and resolution configured for the table.
- Connect to each database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
REMOVE_AUTO_CDRprocedure and specify the table. - Repeat all of the previous steps in each Oracle database that replicates the table.
Example 13-7 Removing Conflict Detection and Resolution for a Table
This example removes conflict detection and resolution for the hr.employees table.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.REMOVE_AUTO_CDR(
schema_name => 'hr',
table_name => 'employees');
END;
/See Also:
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate.
Parent topic: Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.4.5 Removing a Column Group
The REMOVE_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP procedure removes a column group.
- Connect to each database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
REMOVE_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPprocedure and specify the name of the column group. - Repeat all of the previous steps in each Oracle database that replicates the table.
Example 13-8 Removing a Column Group
This example removes the compensation_cg column group from the hr.employees table.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.REMOVE_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP(
schema_name => 'hr',
table_name => 'employees',
column_group_name => 'compensation_cg');
END;
/See Also:
-
"Configuring Latest Timestamp Conflict Detection and Resolution"
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate.
Parent topic: Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.4.6 Removing Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution
The REMOVE_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RES procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package removes delta conflict detection and resolution for a column.
- Connect to the inbound server database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Run the
REMOVE_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RESprocedure and specify the column. - Repeat all of the previous steps in each Oracle database that replicates the table.
Example 13-9 Removing Delta Conflict Detection and Resolution for a Table
This example removes delta conflict detection and resolution for the order_total column in the oe.orders table.
BEGIN
DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM.REMOVE_AUTO_CDR_DELTA_RES(
schema_name => 'oe',
table_name => 'orders',
column_name => 'order_total');
END;
/See Also:
-
The Oracle GoldenGate documentation for more information about Oracle GoldenGate.
Parent topic: Managing Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.5 Monitoring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
You can monitor Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution in an Oracle database by querying data dictionary views.
- Displaying Information About the Tables Configured for Conflicts
TheALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_TABLESview displays information about the tables configured for Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution. - Displaying Information About Conflict Resolution Columns
TheALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMNSview displays information about the columns configured for Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution. - Displaying Information About Column Groups
TheALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPSview displays information about the column groups configured for Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution.
13.5.1 Displaying Information About the Tables Configured for Conflicts
The ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_TABLES view displays information about the tables configured for Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution.
- Connect to the database.
- Query the
ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_TABLESview.
Example 13-10 Displaying Information About the Tables Configured for Conflict Detection and Resolution
This query displays the following information about the tables that are configured for conflict detection and resolution:
-
The table owner for each table
-
The table name for each table
-
The tombstone table used to store rows deleted for update-delete conflicts, if a tombstone table is configured for the table
-
The hidden timestamp column used for conflict resolution for each table
COLUMN TABLE_OWNER FORMAT A15
COLUMN TABLE_NAME FORMAT A15
COLUMN TOMBSTONE_TABLE FORMAT A15
COLUMN ROW_RESOLUTION_COLUMN FORMAT A25
SELECT TABLE_OWNER,
TABLE_NAME,
TOMBSTONE_TABLE,
ROW_RESOLUTION_COLUMN
FROM ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_TABLES
ORDER BY TABLE_OWNER, TABLE_NAME;
Your output looks similar to the following:
TABLE_OWNER TABLE_NAME TOMBSTONE_TABLE ROW_RESOLUTION_COLUMN
--------------- --------------- --------------- -------------------------
HR EMPLOYEES DT$_EMPLOYEES CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS DT$_ORDERS CDRTS$ROW
Related Topics
Parent topic: Monitoring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.5.2 Displaying Information About Conflict Resolution Columns
The ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMNS view displays information about the columns configured for Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution.
- Connect to the database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Query the
ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMNSview.
Example 13-11 Displaying Information About Column Groups
This query displays the following information about the tables that are configured for conflict detection and resolution:
-
The table owner for each table
-
The table name for each table
-
If the column is in a column group, then the name of the column group
-
The column name
-
If the column is configured for latest timestamp conflict resolution, then the name of the hidden timestamp column for the column
COLUMN TABLE_OWNER FORMAT A10
COLUMN TABLE_NAME FORMAT A10
COLUMN COLUMN_GROUP_NAME FORMAT A17
COLUMN COLUMN_NAME FORMAT A15
COLUMN RESOLUTION_COLUMN FORMAT A23
SELECT TABLE_OWNER,
TABLE_NAME,
COLUMN_GROUP_NAME,
COLUMN_NAME,
RESOLUTION_COLUMN
FROM ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMNS
ORDER BY TABLE_OWNER, TABLE_NAME;
Your output looks similar to the following:
TABLE_OWNE TABLE_NAME COLUMN_GROUP_NAME COLUMN_NAME RESOLUTION_COLUMN
---------- ---------- ----------------- --------------- -----------------------
HR EMPLOYEES COMPENSATION_CG COMMISSION_PCT CDRTS$COMPENSATION_CG
HR EMPLOYEES COMPENSATION_CG SALARY CDRTS$COMPENSATION_CG
HR EMPLOYEES JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG MANAGER_ID CDRTS$JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG
HR EMPLOYEES JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG JOB_ID CDRTS$JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG
HR EMPLOYEES JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG DEPARTMENT_ID CDRTS$JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG
HR EMPLOYEES IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ PHONE_NUMBER CDRTS$ROW
HR EMPLOYEES IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ LAST_NAME CDRTS$ROW
HR EMPLOYEES IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ HIRE_DATE CDRTS$ROW
HR EMPLOYEES IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ FIRST_NAME CDRTS$ROW
HR EMPLOYEES IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ EMAIL CDRTS$ROW
HR EMPLOYEES IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ EMPLOYEE_ID CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ ORDER_MODE CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ ORDER_ID CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ ORDER_DATE CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ CUSTOMER_ID CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS DELTA$ ORDER_TOTAL
OE ORDERS IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ PROMOTION_ID CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ ORDER_STATUS CDRTS$ROW
OE ORDERS IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ SALES_REP_ID CDRTS$ROWIn this output, the columns with IMPLICIT_COLUMNS$ for the column group name are configured for row conflict detection and resolution, but they are not part of a column group. The columns with DELTA$ for the column group name are configured for delta conflict detection and resolution, and these columns do not have a resolution column.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Monitoring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution
13.5.3 Displaying Information About Column Groups
The ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPS view displays information about the column groups configured for Oracle GoldenGate automatic conflict detection and resolution.
ADD_AUTO_CDR procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package. You can configure column groups using the ADD_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUP procedure in the DBMS_GOLDENGATE_ADM package.
- Connect to the database as the Oracle GoldenGate administrator.
- Query the
ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPSview.
Example 13-12 Displaying Information About Column Groups
This query displays the following information about the tables that are configured for conflict detection and resolution:
-
The table owner
-
The table name
-
The name of the column group
-
The hidden timestamp column used for conflict resolution for each column group
COLUMN TABLE_OWNER FORMAT A15
COLUMN TABLE_NAME FORMAT A15
COLUMN COLUMN_GROUP_NAME FORMAT A20
COLUMN RESOLUTION_COLUMN FORMAT A25
SELECT TABLE_OWNER,
TABLE_NAME,
COLUMN_GROUP_NAME,
RESOLUTION_COLUMN
FROM ALL_GG_AUTO_CDR_COLUMN_GROUPS
ORDER BY TABLE_OWNER, TABLE_NAME;
Your output looks similar to the following:
TABLE_OWNER TABLE_NAME COLUMN_GROUP_NAME RESOLUTION_COLUMN
--------------- --------------- -------------------- -------------------------
HR EMPLOYEES COMPENSATION_CG CDRTS$COMPENSATION_CG
HR EMPLOYEES JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG CDRTS$JOB_IDENTIFIER_CG
Parent topic: Monitoring Automatic Conflict Detection and Resolution