21 Configuring Kerberos Authentication
Kerberos is a trusted third-party authentication system that relies on shared secrets and presumes that the third party is secure.
- Enabling Kerberos Authentication
To enable Kerberos authentication for Oracle Database, you must first install it, and then follow a set of configuration steps. - Utilities for the Kerberos Authentication Adapter
The Oracle Kerberos authentication adapter utilities are designed for an Oracle client with Oracle Kerberos authentication support installed. - Connecting to an Oracle Database Server Authenticated by Kerberos
After Kerberos is configured, you can connect to an Oracle database server without using a user name or password. - Configuring Interoperability with Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC
You can configure Oracle Database to interoperate with a Microsoft Windows Server domain controller key distribution center (KDC). - Configuring Kerberos Authentication Fallback Behavior
You can configure fallback behavior (password-based authentication) in case the Kerberos authentication fails. - Troubleshooting the Oracle Kerberos Authentication Configuration
Oracle provides guidance for common Kerberos configuration problems.
Parent topic: Managing Strong Authentication
21.1 Enabling Kerberos Authentication
To enable Kerberos authentication for Oracle Database, you must first install it, and then follow a set of configuration steps.
- Step 1: Install Kerberos
You should install Kerberos Version 5. - Step 2: Configure a Service Principal for an Oracle Database Server
You must create a service principal for Oracle Database before the server can validate the identity of clients that authenticate themselves using Kerberos. - Step 3: Extract a Service Key Table from Kerberos
Next, you are ready to extract the service key table from Kerberos and copy it to the Oracle database server/Kerberos client system. - Step 4: Install an Oracle Database Server and an Oracle Client
After you extract a service key table from Kerberos, you are ready to install the Oracle Database server and an Oracle client. - Step 5: Configure Oracle Net Services and Oracle Database
After you install the Oracle Database server and client, you can configure Oracle Net Services on the server and client. - Step 6: Configure Kerberos Authentication
You must set the required parameters in the Oracle database server and clientsqlnet.orafiles. - Step 7: Create a Kerberos User
You must create the Kerberos user on the Kerberos authentication server where the administration tools are installed. - Step 8: Create an Externally Authenticated Oracle User
Next, you are ready to create an externally authenticated Oracle user. - Step 9: Get an Initial Ticket for the Kerberos/Oracle User
Before you can connect to the database, you must ask the Key Distribution Center (KDC) for an initial ticket.
Parent topic: Configuring Kerberos Authentication
21.1.1 Step 1: Install Kerberos
You should install Kerberos Version 5.
The source distribution for notes about building and installing Kerberos provide details. After you install Kerberos, if you are using IBM AIX on POWER systems (64-bit), you should ensure that Kerboros 5 is the preferred authentication method.
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.2 Step 2: Configure a Service Principal for an Oracle Database Server
You must create a service principal for Oracle Database before the server can validate the identity of clients that authenticate themselves using Kerberos.
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.3 Step 3: Extract a Service Key Table from Kerberos
Next, you are ready to extract the service key table from Kerberos and copy it to the Oracle database server/Kerberos client system.
dbserver.example.com:
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.4 Step 4: Install an Oracle Database Server and an Oracle Client
After you extract a service key table from Kerberos, you are ready to install the Oracle Database server and an Oracle client.
-
See the Oracle Database operating system-specific installation documentation for instructions on installing the Oracle database server and client software.
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.5 Step 5: Configure Oracle Net Services and Oracle Database
After you install the Oracle Database server and client, you can configure Oracle Net Services on the server and client.
-
See the following documentation for information on configuring Oracle Net Services on the Oracle database server and client.
-
Oracle Database operating system-specific installation documentation
-
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.6 Step 6: Configure Kerberos Authentication
You must set the required parameters in the Oracle database server and client sqlnet.ora files.
Note:
The settings in the sqlnet.ora file apply to all pluggable databases (PDBs). However, this does not mean that all PDBs must authenticate with one KDC if you are using Kerberos; the settings in the sqlnet.ora file and Kerberos configuration files can support multiple KDCs.
- Step 6A: Configure Kerberos on the Client and on the Database Server
First, you must configure Kerberos authentication service parameters on the client and on the database server. - Step 6B: Set the Initialization Parameters
Next, you are ready to set theOS_AUTHENT_PREFIXinitialization parameter. - Step 6C: Set sqlnet.ora Parameters (Optional)
You can set optionalsqlnet.oraparameters, in addition to the required parameters, for better security. - Step 6D: Configure Kerberos to Use TCP or UDP (Optional)
By default, Oracle Database uses TCP for Kerberos connections.
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.6.1 Step 6A: Configure Kerberos on the Client and on the Database Server
First, you must configure Kerberos authentication service parameters on the client and on the database server.
Parent topic: Step 6: Configure Kerberos Authentication
21.1.6.2 Step 6B: Set the Initialization Parameters
Next, you are ready to set the OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX initialization parameter.
Note:
You can create externally authenticated database users that have Kerberos user names of more than 30 bytes.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Step 6: Configure Kerberos Authentication
21.1.6.3 Step 6C: Set sqlnet.ora Parameters (Optional)
You can set optional sqlnet.ora parameters, in addition to the required parameters, for better security.
-
Optionally, set the parameters listed in the following table on both the client and the Oracle database server.
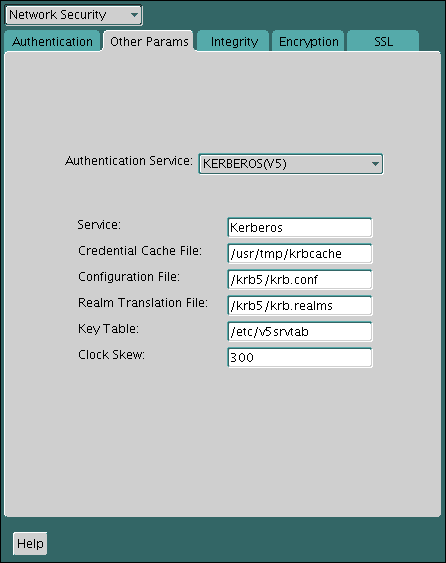
Table 21-1 Kerberos-Specific sqlnet.ora Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the complete path name to the Kerberos credentials cache (CC) file. The default value is operating system-dependent. For UNIX, it is Using the You can use the following formats to specify a value for
You can also set this parameter by using the For example: SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CC_NAME=/usr/tmp/krbcache |
|
|
This parameter specifies how many seconds can pass before a Kerberos credential is considered out-of-date. It is used when a credential is actually received by either a client or a database server. An Oracle database server also uses it to decide if a credential needs to be stored to protect against a replay attack. The default is 300 seconds. For example: SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CLOCKSKEW=1200 |
|
|
This parameter specifies the complete path name to the Using the For example: SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF=/krb/krb.conf SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF=AUTO_DISCOVER |
|
|
This parameter indicates that the Kerberos configuration file is created by the system, and does not need to be specified by the client. The configuration file uses DNS lookup to obtain the realm for the default KDC, and maps realms to KDC hosts. For example: SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_LOCATION=/krb |
|
|
This parameter specifies the complete path name to the Kerberos principal/secret key mapping file. It is used by the Oracle database server to extract its key and decrypt the incoming authentication information from the client. The default is operating system-dependent. For UNIX, it is For example: SQLNET.KERBEROS5_KEYTAB=/etc/v5srvtab |
|
|
This parameter specifies the complete path name to the Kerberos realm translation file. The translation file provides a mapping from a host name or domain name to a realm. The default is operating system-dependent. For UNIX, it is For example: SQLNET.KERBEROS5_REALMS=/krb5/krb.realms |
Parent topic: Step 6: Configure Kerberos Authentication
21.1.6.4 Step 6D: Configure Kerberos to Use TCP or UDP (Optional)
By default, Oracle Database uses TCP for Kerberos connections.
Parent topic: Step 6: Configure Kerberos Authentication
21.1.7 Step 7: Create a Kerberos User
You must create the Kerberos user on the Kerberos authentication server where the administration tools are installed.
The realm must already exist.
Note:
The utility names in this section are executable programs. However, the Kerberos user name krbuser and realm EXAMPLE.COM are examples only. They can vary among systems.
-
Run
/krb5/admin/kadmin.localas root to create a new Kerberos user, such askrbuser.For example, to create a Kerberos user is UNIX-specific:
# /krb5/admin/kadmin.local kadmin.local: addprinc krbuser Enter password for principal: "krbuser@example.com": (password does not display) Re-enter password for principal: "krbuser@example.com": (password does not display) kadmin.local: exit
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.8 Step 8: Create an Externally Authenticated Oracle User
Next, you are ready to create an externally authenticated Oracle user.
Note:
The database administrator should ensure that multiple database users are not identified externally by the same Kerberos principal name.
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.1.9 Step 9: Get an Initial Ticket for the Kerberos/Oracle User
Before you can connect to the database, you must ask the Key Distribution Center (KDC) for an initial ticket.
okinit program and providing a password.
sqlnet.ora file) can be specified either in the connect string or in tnsnames.ora.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Enabling Kerberos Authentication
21.2 Utilities for the Kerberos Authentication Adapter
The Oracle Kerberos authentication adapter utilities are designed for an Oracle client with Oracle Kerberos authentication support installed.
- okinit Utility Options for Obtaining the Initial Ticket
Theokinitutility obtains and caches Kerberos tickets. - oklist Utility Options for Displaying Credentials
Theoklistutility displays the list of tickets held. - okdstry Utility Options for Removing Credentials from the Cache File
Theokdstry(okdestroy) utility removes credentials from the cache file. - okcreate Utility Options for Automatic Keytab Creation
Theokcreateutility automates the creation of keytabs from either the KDC or a service endpoint.
Parent topic: Configuring Kerberos Authentication
21.2.1 okinit Utility Options for Obtaining the Initial Ticket
The okinit utility obtains and caches Kerberos tickets.
This utility is typically used to obtain the ticket-granting ticket, using a password entered by the user to decrypt the credential from the key distribution center (KDC). The ticket-granting ticket is then stored in the user's credential cache.
The following table lists the options available with okinit. To use the functionality that is described in this table, you must set the sqlnet.ora SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MIT parameter to TRUE. (Note that SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MIT is deprecated, but is retained for backward compatibility for okinit.)
Table 21-2 Options for the okinit Utility
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Requests forwardable or non-forwardable tickets. This option is necessary to follow database links. |
|
|
Specifies the lifetime of the ticket-granting ticket and all subsequent tickets. By default, the ticket-granting ticket is good for eight (8) hours, but shorter or longer-lived credentials may be desired. The KDC can ignore this option or put site-configured limits on what can be specified. The lifetime value is a string that consists of a number qualified by okinit -l 2wld6h20m30s The example requests a ticket-granting ticket that has a lifetime of 2 weeks, 1 day, 6 hours, 20 minutes, and 30 seconds. |
|
|
Specifies the duration of the delay before the ticket can become valid. Tickets are issued with the invalid flag set. |
|
|
Requests renewable tickets with a total lifetime of |
|
|
Requests proxiable or non-proxiable tickets |
|
|
Requests tickets that are restricted to the local address of the host |
|
|
Requests tickets not restricted by address |
|
|
Treats the principal name as an enterprise name |
|
|
Requests that the ticket-granting ticket in the cache be passed to the KDC for validation. If the ticket is within the requested time range, then the cache is replaced with the validated ticket. |
|
|
Requests renewal of the ticket-granting ticket |
|
|
Requests a ticket, which is obtained from a key in the local host’s keytab |
|
|
Requests anonymous processing |
|
|
Requests canonicalization of the principal name, and enables the KDC to reply with a different client principal from the one that was requested |
|
|
Specifies the name of a cache as a cache location. For UNIX, the default is |
|
|
Specifies the name of a credential cache that already contains a ticket. When it obtains that ticket, if the information about how the ticket was obtained is stored in cache, then the same information will be used to affect how new credentials are obtained. |
|
|
If supported by the KDC, this cache is used to armor the request, preventing offline dictionary attacks and enabling the use of additional pre-authentication mechanisms. |
|
|
Specifies a pre-authentication attribute and value. Specifies one of the following values:
|
|
|
List command line options. |
Parent topic: Utilities for the Kerberos Authentication Adapter
21.2.2 oklist Utility Options for Displaying Credentials
The oklist utility displays the list of tickets held.
The following table lists the available oklist options. To use the functionality that is described in this table, you must set the sqlnet.ora SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MIT parameter to TRUE. (Note that SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MIT is deprecated, but is retained for backward compatibility for oklist.)
Table 21-3 Options for the oklist Utility
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Show flags with credentials. Relevant flags are:
|
|
|
Specify an alternative credential cache. In UNIX, the default is |
|
|
List the entries in the service table (default |
|
|
Displays the encryption types of the session key and the ticket for each credential in the credential cache, or each key in the keytab file. |
|
|
If a cache collection is available, displays a table summarizing the caches present in the collection. |
|
|
If a cache collection is available, displays the contents of all of the caches in the collection |
|
|
Runs utility without producing output. Utility will exit with status 1 if the cache cannot be read or is expired, else with status 0 |
|
|
Displays a list of addresses in the credential |
|
|
Shows numeric addresses instead of reverse-resolving addresses |
|
|
Lists configuration data that has been stored in the credentials cache when |
|
|
Displays the time entry timestamps for each keytab entry in the keytab file |
|
|
Displays the value of the encryption key in each keytab entry in the keytab file |
|
|
Displays the Kerberos version number and exit. |
The show flag option (-f) displays additional information, as shown in the following example:
% oklist -f 04-Aug-2015 21:57:51 28-Aug-2015 05:58:14 krbtgt/EXAMPLE.COM@EXAMPLE.COM Flags: FI
Parent topic: Utilities for the Kerberos Authentication Adapter
21.2.3 okdstry Utility Options for Removing Credentials from the Cache File
The okdstry (okdestroy) utility removes credentials from the cache file.
The following table lists the available okdstry options. To use the functionality that is described in this table, you must set the sqlnet.ora SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MIT parameter to TRUE. (Note that SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MIT is deprecated, but is retained for backward compatibility for okdstry.)
Table 21-4 Options for the okdstry Utility
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Destroys all caches in the collection, if a cache collection is available |
|
|
Runs quietly. Normally |
|
|
Uses |
Parent topic: Utilities for the Kerberos Authentication Adapter
21.2.4 okcreate Utility Options for Automatic Keytab Creation
The okcreate utility automates the creation of keytabs from either the KDC or a service endpoint.
The following table lists the available okcreate options.
Table 21-5 okcreate Utility Options for Automatic Keytab Creation
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the service name of the kerberized service for which to get a keytab.The default is |
|
|
Specifies either a comma-separated list of hosts for which to get the keytab, or the path to a text file that contains a list of the hosts. The default is |
|
|
Specifies the output path to store the resulting keytabs. The default is the current directory. Ensure that this directory is readable only by the root user. Never send keytabs over the network in clear text. |
|
|
For use if the operation is performed on the KDC. Do not use this option if you are using |
|
|
For use if the operation is performed on a Kerberized service. Do not use this option if you are using |
|
|
Specifies the user name for the KDC. Only use this setting on a Kerberized service endpoint. If you specify the |
|
|
Specifies the Kerberos realm |
|
|
Specifies the Kerberos principal |
|
|
Specifies the Kerberos query |
|
|
Specifies the KDC database name |
|
|
Specifies the salt list to be used for any new keys that are created |
|
|
Specifies to prompt for the KDC master password |
Parent topic: Utilities for the Kerberos Authentication Adapter
21.3 Connecting to an Oracle Database Server Authenticated by Kerberos
After Kerberos is configured, you can connect to an Oracle database server without using a user name or password.
Parent topic: Configuring Kerberos Authentication
21.4 Configuring Interoperability with Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC
You can configure Oracle Database to interoperate with a Microsoft Windows Server domain controller key distribution center (KDC).
- About Configuring Interoperability with a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC
Oracle Database complies with MIT Kerberos. - Step 1: Configure Oracle Kerberos Client for Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller
You can configure the Oracle Kerberos client to interoperate with a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC. - Step 2: Configure a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC for the Oracle Client
Next, you are ready to configure a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC to interoperate with an Oracle Client. - Step 3: Configure Oracle Database for a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC
You must configure the Oracle database for the domain controller on the host computer where the Oracle database is installed. - Step 4: Obtain an Initial Ticket for the Kerberos/Oracle User
Before a client can connect to the database, the client must request an initial ticket.
Parent topic: Configuring Kerberos Authentication
21.4.1 About Configuring Interoperability with a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC
Oracle Database complies with MIT Kerberos.
This enables Oracle Database to interoperate with tickets that are issued by a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) on a Microsoft Windows Server domain controller. This process enables Kerberos authentication with an Oracle database.
21.4.2 Step 1: Configure Oracle Kerberos Client for Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller
You can configure the Oracle Kerberos client to interoperate with a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC.
- Step 1A: Create the Client Kerberos Configuration Files
You must configure a set of client Kerberos configuration files that refer to the Windows 2008 domain controller as the Kerberos KDC. - Step 1B: Specify the Oracle Configuration Parameters in the sqlnet.ora File
Configuring an Oracle client to interoperate with a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) uses the samesqlnet.orafile parameters that are used for configuring Kerberos on the client and on the database server. - Step 1C: Optionally, Specify Additional Kerberos Principals Using tnsnames.ora
You can configure additional Kerberos principal users to connect from an Oracle Database client. - Step 1D: Specify the Listening Port Number
The Microsoft Windows Server domain controller KDC listens on UDP/TCP port 88.
21.4.2.1 Step 1A: Create the Client Kerberos Configuration Files
You must configure a set of client Kerberos configuration files that refer to the Windows 2008 domain controller as the Kerberos KDC.
21.4.2.2 Step 1B: Specify the Oracle Configuration Parameters in the sqlnet.ora File
Configuring an Oracle client to interoperate with a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) uses the same sqlnet.ora file parameters that are used for configuring Kerberos on the client and on the database server.
21.4.2.3 Step 1C: Optionally, Specify Additional Kerberos Principals Using tnsnames.ora
You can configure additional Kerberos principal users to connect from an Oracle Database client.
21.4.2.4 Step 1D: Specify the Listening Port Number
The Microsoft Windows Server domain controller KDC listens on UDP/TCP port 88.
-
Ensure that the system file entry for
kerberos5is set to UDP/TCP port 88.For the UNIX environment, ensure that the first
kerberos5entry in the/etc/servicesfile is set to 88.
21.4.3 Step 2: Configure a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC for the Oracle Client
Next, you are ready to configure a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC to interoperate with an Oracle Client.
- Step 2A: Create the User Account
You must create a user account for the Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC. - Step 2B: Create the Oracle Database Principal User Account and Keytab
After you create the user account, you are ready to create the Oracle Database principal user account.
See Also:
Microsoft documentation for information about how to create users in Active Directory.
21.4.3.1 Step 2A: Create the User Account
You must create a user account for the Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC.
-
On the Microsoft Windows Server domain controller, create a new user account for the Oracle client in Microsoft Active Directory.
21.4.3.2 Step 2B: Create the Oracle Database Principal User Account and Keytab
After you create the user account, you are ready to create the Oracle Database principal user account.
okcreate utility to register it with the principal keytab. You can run this utilty on the same KDC to create all the service keytabs rather than creating them individually, or you can run okcreate from a service endpoint that connects to the KDC, run the ncessary commands, and then copy the resulting keytab back to the service endpoint.
21.4.4 Step 3: Configure Oracle Database for a Microsoft Windows Server Domain Controller KDC
You must configure the Oracle database for the domain controller on the host computer where the Oracle database is installed.
- Step 3A: Set Configuration Parameters in the sqlnet.ora File
You must first set configuration parameters for the database. - Step 3B: Create an Externally Authenticated Oracle User
After you set the configuration parameters, you are ready to create an externally authenticated Oracle user.
21.4.4.1 Step 3A: Set Configuration Parameters in the sqlnet.ora File
You must first set configuration parameters for the database.
-
Specify values for the following parameters in the
sqlnet.orafile for the database server:SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF=pathname_to_Kerberos_configuration_file SQLNET.KERBEROS5_KEYTAB=pathname_to_Kerberos_principal/key_table SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MIT=TRUE SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_KERBEROS5_SERVICE=Kerberos_service_name SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES=(BEQ,KERBEROS5)
Note:
-
The
SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MITparameter has been deprecated, but is retained for backward compatibility for theokint,oklist, andokdstryutilities. -
Ensure that the
SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF_MITparameter is set toTRUEbecause the Windows Server operating system is designed to interoperate only with security services that are based on MIT Kerberos version 5. -
Be aware that the settings in the
sqlnet.orafile apply to all PDBs. However, this does not mean that all PDBs must authenticate with one KDC if using Kerberos; the settings in thesqlnet.orafile and Kerberos configuration files can support multiple KDCs.
21.4.4.2 Step 3B: Create an Externally Authenticated Oracle User
After you set the configuration parameters, you are ready to create an externally authenticated Oracle user.
-
Follow the procedure under Step 8: Create an Externally Authenticated Oracle User to create an externally authenticated Oracle user.
Ensure that you create the username in all uppercase characters (for example,
ORAKRB@SALES.US.EXAMPLE.COM).
See Also:
Step 6: Configure Kerberos Authentication for information about using Oracle Net Manager to set the sqlnet.ora file parameters.
21.5 Configuring Kerberos Authentication Fallback Behavior
You can configure fallback behavior (password-based authentication) in case the Kerberos authentication fails.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Configuring Kerberos Authentication
21.6 Troubleshooting the Oracle Kerberos Authentication Configuration
Oracle provides guidance for common Kerberos configuration problems.
Common problems are as follows:
-
If you cannot get your ticket-granting ticket using
okinit:-
Ensure that the default realm is correct by examining the
krb.conffile. -
Ensure that the KDC is running on the host specified for the realm.
-
Ensure that the KDC has an entry for the user principal and that the passwords match.
-
Ensure that the
krb.confandkrb.realmsfiles are readable by Oracle. -
Ensure that the
TNS_ADMINenvironment variable is pointing to the directory containing thesqlnet.oraconfiguration file.
-
-
If you have an initial ticket but still cannot connect:
-
After trying to connect, check for a service ticket.
-
Check that the
sqlnet.orafile on the database server side has a service name that corresponds to a service known by Kerberos. -
Check that the clocks on all systems involved are set to times that are within a few minutes of each other or change the
SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CLOCKSKEWparameter in thesqlnet.orafile.
-
-
If you have a service ticket and you still cannot connect:
-
Check the clocks on the client and database server.
-
Check that the
v5srvtabfile exists in the correct location and is readable by Oracle. Remember to set thesqlnet.oraparameters. -
Check that the
v5srvtabfile has been generated for the service named in thesqlnet.orafile on the database server side.
-
-
If everything seems to work fine, but then you issue another query and it fails:
-
Check that the initial ticket is forwardable. You must have obtained the initial ticket by running the
okinitutility. -
Check the expiration date on the credentials. If the credentials have expired, then close the connection and run
okinitto get a new initial ticket.
-
Parent topic: Configuring Kerberos Authentication