11 Using Application Contexts to Retrieve User Information
An application context stores user identification that can enable or prevent a user from accessing data in the database.
- About Application Contexts
An application context provides many benefits in controlling the access that a user has to data. - Types of Application Contexts
There are three general categories of application contexts. - Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database session-based application context enables you to retrieve session-based information about a user. - Global Application Contexts
You can use a global application context to access application values across database sessions, including an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment. - Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
A client session-based application context is stored in the User Global Area (UGA). - Application Context Data Dictionary Views
Oracle Database provides data dictionary views that provide information about application contexts.
Parent topic: Controlling Access to Data
11.1 About Application Contexts
An application context provides many benefits in controlling the access that a user has to data.
- What Is an Application Context?
An application context is a set of name-value pairs that Oracle Database stores in memory. - Components of the Application Context
An application context has two components, comprising a name-value pair. - Where Are the Application Context Values Stored?
Oracle Database stores the application context values in a secure data cache. - Benefits of Using Application Contexts
Most applications contain the kind of information that can be used for application contexts. - How Editions Affects Application Context Values
Oracle Database sets the application context in all editions that are affected by the application context package. - Application Contexts in a Multitenant Environment
Where you create an application in a multitenant environment determines where you must create the application context.
Parent topic: Using Application Contexts to Retrieve User Information
11.1.1 What Is an Application Context?
An application context is a set of name-value pairs that Oracle Database stores in memory.
The context has a label called a namespace (for example, empno_ctx for an application context that retrieves employee IDs). This context enables Oracle Database to find information about both database and nondatabase users during authentication.
Inside the context are the name-value pairs (an associative array): the name points to a location in memory that holds the value. An application can use the application context to access session information about a user, such as the user ID or other user-specific information, or a client ID, and then securely pass this data to the database.
You can then use this information to either permit or prevent the user from accessing data through the application. You can use application contexts to authenticate both database and non-database users.
Related Topics
Parent topic: About Application Contexts
11.1.2 Components of the Application Context
An application context has two components, comprising a name-value pair.
These components are as follows:
-
Name. Refers to the name of the attribute set that is associated with the value. For example, if the
empno_ctxapplication context retrieves an employee ID from theHR.EMPLOYEEStable, it could have a name such asemployee_id. -
Value. Refers to a value set by the attribute. For example, for the
empno_ctxapplication context, if you wanted to retrieve an employee ID from theHR.EMPLOYEEStable, you could create a value calledemp_idthat sets the value for this ID.
Think of an application context as a global variable that holds information that is accessed during a database session. To set the values for a secure application context, you must create a PL/SQL package procedure that uses the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure. In fact, this is the only way that you can set application context values if the context is not marked INITIALIZED EXTERNALLY or INITIALIZED GLOBALLY. You can assign the values to the application context attributes at run time, not when you create the application context. Because the trusted procedure, and not the user, assigns the values, it is a called secure application context. For client-session based application contexts, another way to set the application context is to use Oracle Call Interface (OCI) calls.
Parent topic: About Application Contexts
11.1.3 Where Are the Application Context Values Stored?
Oracle Database stores the application context values in a secure data cache.
This cache is available in the User Global Area (UGA) or the System (sometimes called "Shared") Global Area (SGA). This way, the application context values are retrieved during the session. Because the application context stores the values in this data cache, it increases performance for your applications. You can use an application context by itself, with Oracle Virtual Private Databases policies, or with other fine-grained access control policies.
Parent topic: About Application Contexts
11.1.4 Benefits of Using Application Contexts
Most applications contain the kind of information that can be used for application contexts.
For example, in an order entry application that uses a table containing the columns ORDER_NUMBER and CUSTOMER_NUMBER, you can use the values in these columns as security attributes to restrict access by a customer to his or her own orders, based on the ID of that customer.
Application contexts are useful for the following purposes:
-
Enforcing fine-grained access control (for example, in Oracle Virtual Private Database polices)
-
Preserving user identity across multitier environments
-
Enforcing stronger security for your applications, because the application context is controlled by a trusted procedure, not the user
-
Increasing performance by serving as a secure data cache for attributes needed by an application for fine-grained auditing or for use in PL/SQL conditional statements or loops
This cache saves the repeated overhead of querying the database each time these attributes are needed. Because the application context stores session data in cache rather than forcing your applications to retrieve this data repeatedly from a table, it greatly improves the performance of your applications.
-
Serving as a holding area for name-value pairs that an application can define, modify, and access
Parent topic: About Application Contexts
11.1.5 How Editions Affects Application Context Values
Oracle Database sets the application context in all editions that are affected by the application context package.
The values the application context sets are visible in all editions the application context affects. To find all editions in your database, and whether they are usable, you can query the ALL_EDITIONS data dictionary view.
Related Topics
Parent topic: About Application Contexts
11.1.6 Application Contexts in a Multitenant Environment
Where you create an application in a multitenant environment determines where you must create the application context.
If an application is installed in the application root or CDB root, then it becomes accessible across the application container or system container and associated application PDBs. You will need to create a common application context in this root.
When you create a common application context for use with an application container, note the following:
-
You can create application contexts by setting the
CONTAINERclause in theCREATE CONTEXTSQL statement. For example, to create a common application context in the application root, you must executeCREATE CONTEXTwithCONTAINERset toALL. To create the application context in a PDB, setCONTAINERtoCURRENT. -
You cannot use the same name for a local application context for a common application context. You can find the names of existing application contexts by running the following query:
SELECT OBJECT_NAME FROM DBA_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE ='CONTEXT'; -
The PL/SQL package that you create to manage a common application context must be a common PL/SQL package. That is, it must exist in the application root or CDB root. If you create the application context for a specific PDB, then you must store the associated PL/SQL package in that PDB.
-
The name-value pairs that you set under a common session application context from an application container or a system container for a common application context are not accessible from other application containers or system containers when a common user accesses a different container.
-
The name-value pairs that you set under a common global application context from an application container or a system container, are accessible only within the same container in the same user session.
-
An application can retrieve the value of an application context whether it resides in the application root, the CDB root, or a PDB.
-
During a plug-in operation of a PDB into a CDB or an application container, if the name of the common application context conflicts with a PDB’s local application context, then the PDB must open in restricted mode. A database administrator would then need to correct the conflict before opening the PDB in normal mode.
-
During an unplug operation, a common application context retains its common semantics, so that later on, if the PDB is plugged into another CDB where a common application context with the same name exists, it would continue to behave like a common object. If a PDB is plugged into an application container or a system container, where the same common application context does not exist, then it behaves like a local object.
To find if an application context is a local application context or an application common application context, query the SCOPE column of the DBA_CONTEXT or ALL_CONTEXT data dictionary view.
Parent topic: About Application Contexts
11.2 Types of Application Contexts
There are three general categories of application contexts.
These categories are as follows:
-
Database session-based application contexts. This type retrieves data that is stored in the database user session (that is, the UGA) cache. There are three categories of database session-based application contexts:
-
Initialized locally. Initializes the application context locally, to the session of the user.
-
Initialized externally. Initializes the application context from an Oracle Call Interface (OCI) application, a job queue process, or a connected user database link.
-
Initialized globally. Uses attributes and values from a centralized location, such as an LDAP directory.
-
-
Global application contexts. This type retrieves data that is stored in the System Global Area (SGA) so that it can be used for applications that use a sessionless model, such as middle-tier applications in a three-tiered architecture. A global application context is useful if the session context must be shared across sessions, for example, through connection pool implementations.
-
Client session-based application contexts. This type uses Oracle Call Interface functions on the client side to set the user session data, and then to perform the necessary security checks to restrict user access.
Table 11-1 summarizes the different types of application contexts.
Table 11-1 Types of Application Contexts
| Application Context Type | Stored in UGA | Stored in SGA | Supports Connected User Database Links | Supports Centralized Storage of Users' Application Context | Supports Sessionless Multitier Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Database session-based application context initialized locally |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
Database session-based application context initialized externally |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Database session-based application context initialized globally |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
Global application context |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Client session-based application context |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
11.3 Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database session-based application context enables you to retrieve session-based information about a user.
- About Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database session-based application context retrieves session information for database users. - Components of a Database Session-Based Application Context
A database session-based application context retrieves and sets data for the context and then sets this context when a user logs in. - Creating Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database session-based application context is a named object that stores the user's session information. - Creating a Package to Set a Database Session-Based Application Context
A PL/SQL package can be used to retrieve the session information and set the name-value attributes of the application context. - Logon Triggers to Run a Database Session Application Context Package
Users must run database session application context package after when they log in to the database instance. - Example: Creating a Simple Logon Trigger
TheCREATE TRIGGERstatement can create a simple logon trigger. - Example: Creating a Logon Trigger for a Production Environment
TheCREATE TRIGGERstatement can create a logon trigger for a production environment. - Example: Creating a Logon Trigger for a Development Environment
TheCREATE TRIGGERstatement can create a logon trigger for a development environment. - Tutorial: Creating and Using a Database Session-Based Application Context
This tutorial demonstrates how to create an application context that checks the ID of users who try to log in to the database. - Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Externally
Initializing database session-based application contexts externally increases performance because the application context is stored in the user global area (UGA). - Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Globally
When a database session-based application is stored in a centralized location, it can be used globally from an LDAP directory. - Externalized Database Session-Based Application Contexts
Many applications store attributes used for fine-grained access control within a database metadata table.
Parent topic: Using Application Contexts to Retrieve User Information
11.3.1 About Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database session-based application context retrieves session information for database users.
This type of application context uses a PL/SQL procedure within Oracle Database to retrieve, set, and secure the data it manages.
The database session-based application context is managed entirely within Oracle Database. Oracle Database sets the values, and then when the user exits the session, automatically clears the application context values stored in cache. If the user connection ends abnormally, for example, during a power failure, then the PMON background process cleans up the application context data.You do not need to explicitly clear the application context from cache.
The advantage of having Oracle Database manage the application context is that you can centralize the application context management. Any application that accesses this database will need to use this application context to permit or prevent user access to that application. This provides benefits both in improved performance and stronger security.
Note:
If your users are application users, that is, users who are not in your database, consider using a global application context instead.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.2 Components of a Database Session-Based Application Context
A database session-based application context retrieves and sets data for the context and then sets this context when a user logs in.
You must use three components to create and use a database session-based application context: the application context, a procedure to retrieve the data and set the context, and a way to set the context when the user logs in.
-
The application context. You use the
CREATE CONTEXTSQL statement to create an application context. This statement names the application context (namespace) and associates it with a PL/SQL procedure that is designed to retrieve session data and set the application context. -
A PL/SQL procedure to perform the data retrieval and set the context. Ideally, create this procedure within a package, so that you can include other procedures if you want (for example, to perform error checking tasks).
-
A way to set the application context when the user logs on. Users who log on to applications that use the application context must run a PL/SQL package that sets the application context. You can achieve this with either a logon trigger that fires each time the user logs on, or you can embed this functionality in your applications.
In addition, you can initialize session-based application contexts either externally or globally. Either method stores the context information in the user session.
-
External initialization. This type can come from an OCI interface, a job queue process, or a connected user database link.
-
Global initialization. This type uses attributes and values from a centralized location, such as an LDAP directory.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.3 Creating Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database session-based application context is a named object that stores the user's session information.
- About Creating Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database user session (UGA) stores session-based application context, using a user-created namespace. - Creating a Database Session-Based Application Context
TheCREATECONTEXTSQL statement can be used to create a database session-based application context. - Database Session-Based Application Contexts for Multiple Applications
For each application, you can create an application context that has its own attributes.
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.3.1 About Creating Database Session-Based Application Contexts
A database user session (UGA) stores session-based application context, using a user-created namespace.
Each application context must have a unique attribute and belong to a namespace. That is, context names must be unique within the database, not just within a schema.
You must have the CREATE ANY CONTEXT system privilege to create an application context, and the DROP ANY CONTEXT privilege to use the DROP CONTEXT statement if you want to drop the application context.
The ownership of the application context is as follows: Even though a user who has been granted the CREATE ANY CONTEXT and DROP ANY CONTEXT privileges can create and drop the application context, it is owned by the SYS schema. Oracle Database associates the context with the schema account that created it, but if you drop this user, the context still exists in the SYS schema. As user SYS, you can drop the application context.
You can find the names of existing application contexts by running the following query:
SELECT OBJECT_NAME FROM DBA_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE ='CONTEXT';
Parent topic: Creating Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.3.2 Creating a Database Session-Based Application Context
The CREATE CONTEXT SQL statement can be used to create a database session-based application context.
11.3.3.3 Database Session-Based Application Contexts for Multiple Applications
For each application, you can create an application context that has its own attributes.
Suppose, for example, you have three applications: General Ledger, Order Entry, and Human Resources.
You can specify different attributes for each application:
-
For the order entry application context, you could specify the attribute
CUSTOMER_NUMBER. -
For the general ledger application context, you could specify the attributes
SET_OF_BOOKSandTITLE. -
For the human resources application context, you could specify the attributes
ORGANIZATION_ID,POSITION, andCOUNTRY.
The data the attributes access is stored in the tables behind the applications. For example, the order entry application uses a table called OE.CUSTOMERS, which contains the CUSTOMER_NUMBER column, which provides data for the CUSTOMER_NUMBER attribute. In each case, you can adapt the application context to your precise security needs.
Parent topic: Creating Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.4 Creating a Package to Set a Database Session-Based Application Context
A PL/SQL package can be used to retrieve the session information and set the name-value attributes of the application context.
- About the Package That Manages the Database Session-Based Application Context
This defines procedures that manage the session data represented by the application context. - Using the SYS_CONTEXT Function to Retrieve Session Information
You can retrieve session information for the application context by using theSYS_CONTEXTfunction. - Checking the SYS_CONTEXT Settings
You can check theSYS_CONTEXTsettings, which are stored in theDUALtable. - Dynamic SQL with SYS_CONTEXT
During a session in which you expect a change in policy between executions of a given query, the query must use dynamic SQL. - SYS_CONTEXT in a Parallel Query
If you useSYS_CONTEXTinside a SQL function that is embedded in a parallel query, then the function includes the application context. - SYS_CONTEXT with Database Links
TheSYS_CONTEXTfunction is compatible with the use of database links. - DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT for Setting Session Information
AfterSYS_CONTEXTretrieves the session data of a user, you can set the application context values from the user session. - Example: Simple Procedure to Create an Application Context Value
You can use the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT statement in a procedure to set an application context value.
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.4.1 About the Package That Manages the Database Session-Based Application Context
This defines procedures that manage the session data represented by the application context.
This package is usually created in the security administrator schema. The package must perform the following tasks:
-
Retrieve session information. To retrieve the user session information, you can use the
SYS_CONTEXTSQL function. TheSYS_CONTEXTfunction returns the value of the parameter associated with the context namespace. You can use this function in both SQL and PL/SQL statements. Typically, you will use the built-inUSERENVnamespace to retrieve the session information of a user. You also can use theSYS_SESSION_ROLESnamespace to indicate whether the specified role is currently enabled for the session. -
Set the name-value attributes of the application context you created with CREATE CONTEXT. You can use the
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXTprocedure to set the name-value attributes of the application context. The name-value attributes can hold information such as the user ID, IP address, authentication mode, the name of the application, and so on. The values of the attributes you set remain either until you reset them, or until the user ends the session. Note the following:-
If the value of the parameter in the namespace already has been set, then
SET_CONTEXToverwrites this value. -
Be aware that any changes in the context value are reflected immediately and subsequent calls to access the value through the
SYS_CONTEXTfunction will return the most recent value.
-
-
Be executed by users. After you create the package, the user will need to execute the package when he or she logs on. You can create a logon trigger to execute the package automatically when the user logs on, or you can embed this functionality in your applications. Remember that the application context session values are cleared automatically when the user ends the session, so you do not need to manually remove the session data.
It is important to remember that the procedure is a trusted procedure: It is designed to prevent the user from setting his or her own application context attribute values. The user runs the procedure, but the procedure sets the application context values, not the user.
11.3.4.2 Using the SYS_CONTEXT Function to Retrieve Session Information
You can retrieve session information for the application context by using the SYS_CONTEXT function.
The SYS_CONTEXT function provides a default namespace, USERENV, which describes the current session of the user logged on. SYS_CONTEXT enables you to retrieve different types of session-based information about a user, such as the user host computer ID, host IP address, operating system user name, and so on. Remember that you only use USERENV to retrieve session data, not set it.
-
To use retrieve session information, set the namespace, parameter, and optionally, the length values of the
SYS_CONTEXTfunction.For example:
SYS_CONTEXT ('USERENV','HOST')
The syntax for the PL/SQL function SYS_CONTEXT is as follows:
SYS_CONTEXT ('namespace','parameter'[,length])
In this specification:
-
namespaceis the name of the application context. You can specify either a string or an expression that evaluates to a string. TheSYS_CONTEXTfunction returns the value of parameter associated with the context namespace at the current instant. If the value of the parameter in the namespace already has been set, thenSET_CONTEXToverwrites this value. -
parameteris a parameter within thenamespaceapplication context. This value can be a string or an expression. -
lengthis the default maximum size of the return type, which is 256 bytes, but you can override the length by specifying a value up to 4000 bytes. Enter a value that is aNUMBERdata type, or a value that can be can be implicitly converted toNUMBER. The data type of theSYS_CONTEXTreturn type is aVARCHAR2. This setting is optional.
Note:
The USERENV application context namespace replaces the USERENV function provided in earlier Oracle Database releases.
Related Topics
11.3.4.3 Checking the SYS_CONTEXT Settings
You can check the SYS_CONTEXT settings, which are stored in the DUAL table.
The DUAL table is a small table in the data dictionary that Oracle Database and user-written programs can reference to guarantee a known result. This table has one column called DUMMY and one row that contains the value X.
-
To check the
SYS_CONTEXTsettings, issue aSELECTSQL statement on theDUALtable.
For example, to find the host computer on which you are logged, assuming that you are logged on to the SHOBEEN_PC host computer under EMP_USERS:
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT ('USERENV', 'HOST') FROM DUAL;
SYS_CONTEXT(USERENV,HOST)
-------------------------
EMP_USERS\SHOBEEEN_PC11.3.4.4 Dynamic SQL with SYS_CONTEXT
During a session in which you expect a change in policy between executions of a given query, the query must use dynamic SQL.
You must use dynamic SQL because static SQL and dynamic SQL parse statements differently:
-
Static SQL statements are parsed at compile time. They are not parsed again at execution time for performance reasons.
-
Dynamic SQL statements are parsed every time they are executed.
Consider a situation in which Policy A is in force when you compile a SQL statement, and then you switch to Policy B and run the statement. With static SQL, Policy A remains in force. Oracle Database parses the statement at compile time, but does not parse it again upon execution. With dynamic SQL, Oracle Database parses the statement upon execution, then the switch to Policy B takes effect.
For example, consider the following policy:
EMPLOYEE_NAME = SYS_CONTEXT ('USERENV', 'SESSION_USER')
The policy EMPLOYEE_NAME matches the database user name. It is represented in the form of a SQL predicate in Oracle Virtual Private Database: the predicate is considered a policy. If the predicate changes, then the statement must be parsed again to produce the correct result.
11.3.4.5 SYS_CONTEXT in a Parallel Query
If you use SYS_CONTEXT inside a SQL function that is embedded in a parallel query, then the function includes the application context.
Consider a user-defined function within a SQL statement, which sets the user ID to 5:
CREATE FUNCTION set_id
RETURN NUMBER IS
BEGIN
IF SYS_CONTEXT ('hr', 'id') = 5
THEN RETURN 1; ELSE RETURN 2;
END IF;
END;
Now consider the following statement:
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE set_id( ) = 1;
When this statement is run as a parallel query, the user session, which contains the application context information, is propagated to the parallel execution servers (query child processes).
11.3.4.6 SYS_CONTEXT with Database Links
The SYS_CONTEXT function is compatible with the use of database links.
When SQL statements within a user session involve database links, Oracle Database runs the SYS_CONTEXT function at the host computer of the database link, and then captures the context information in the host computer.
If remote PL/SQL procedure calls are run on a database link, then Oracle Database runs any SYS_CONTEXT function inside such a procedure at the destination database of the link.
In this case, only externally initialized application contexts are available at the database link destination site. For security reasons, Oracle Database propagates only the externally initialized application context information to the destination site from the initiating database link site.
11.3.4.7 DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT for Setting Session Information
After SYS_CONTEXT retrieves the session data of a user, you can set the application context values from the user session.
To set the context values, you can use the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure. You must have the EXECUTE privilege for the DBMS_SESSION PL/SQL package.
The syntax for DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT is as follows:
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT ( namespace VARCHAR2, attribute VARCHAR2, value VARCHAR2, username VARCHAR2, client_id VARCHAR2);
In this specification:
-
namespaceis the namespace of the application context to be set, limited to 30 bytes. For example, if you were using a namespace calledcustno_ctx, you would specify it as follows:namespace => 'custno_ctx',
-
attributeis the attribute of the application context to be set, limited to 30 bytes. For example, to create thectx_attribattribute for thecustno_ctxnamespace:attribute => 'ctx_attrib',
-
valueis the value of the application context to be set, limited to 4000 bytes. Typically, this is the value retrieved by theSYS_CONTEXTfunction and stored in a variable. For example:value => ctx_value,
-
usernameis the database user name attribute of the application context. The default isNULL, which permits any user to access the session. For database session-based application contexts, omit this setting so that it uses theNULLdefault. This setting is optional.The
usernameandclient_idparameters are used for globally accessed application contexts. -
client_idis the application-specificclient_idattribute of the application context (64-byte maximum). The default isNULL, which means that no client ID is specified. For database session-based application contexts, omit this setting so that it uses theNULLdefault.
11.3.4.8 Example: Simple Procedure to Create an Application Context Value
You can use the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT statement in a procedure to set an application context value.
Example 11-1 shows how to create a simple procedure that creates an attribute for the empno_ctx application context.
Example 11-1 Simple Procedure to Create an Application Context Value
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE set_empno_ctx_proc(
emp_value IN VARCHAR2)
IS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT('empno_ctx', 'empno_attrib', emp_value);
END;
/In this example:
-
emp_value IN VARCHAR2takesemp_valueas the input parameter. This parameter specifies the value associated with the application context attributeempno_attrib. The limit is 4000 bytes. -
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT('empno_ctx', 'empno_attrib', emp_value)sets the value of the application context by using theDBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXTprocedure as follows:-
'empno_ctx'refers to the application context namespace. Enclose its name in single quotation marks. -
'empno_attrib'creates the attribute associated with the application context namespace. -
emp_valuespecifies the value for theempno_attribattribute. Here, it refers to theemp_valueparameter.
-
At this stage, you can run the set_empno_ctx_proc procedure to set the application context:
EXECUTE set_empno_ctx_proc ('42783');
(In a real world scenario, you would set the application context values in the procedure itself, so that it becomes a trusted procedure. This example is only used to show how data can be set for demonstration purposes.)
To check the application context setting, run the following SELECT statement:
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT ('empno_ctx', 'empno_attrib') empno_attrib FROM DUAL;
EMPNO_ATTRIB
--------------
42783
You can also query the SESSION_CONTEXT data dictionary view to find all the application context settings in the current session of the database instance. For example:
SELECT * FROM SESSION_CONTEXT; NAMESPACE ATTRIBUTE VALUE -------------------------------------------------- EMPNO_CTX EMP_ID 42783
11.3.5 Logon Triggers to Run a Database Session Application Context Package
Users must run database session application context package after when they log in to the database instance.
You can create a logon trigger that handles this automatically. You do not need to grant the user EXECUTE permissions to run the package.
Note the following:
-
If the PL/SQL package procedure called by the logon trigger has any unhandled exceptions or raises any exceptions (because, for example, a security check failed), then the logon trigger fails. When the logon trigger fails, the logon fails, that is, the user is denied permission to log in to the database.
-
Logon triggers may affect performance. In addition, test the logon trigger on a sample schema user first before creating it for the database. That way, if there is an error, you can easily correct it.
-
Be aware of situations in which if you have a changing set of books, or if positions change constantly. In these cases, the new attribute values may not be picked up right away, and you must force a cursor reparse to pick them up.
Note:
A logon trigger can be used because the user context (information such as EMPNO, GROUP, MANAGER) should be set before the user accesses any data.
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.6 Example: Creating a Simple Logon Trigger
The CREATE TRIGGER statement can create a simple logon trigger.
Example 11-2 shows a simple logon trigger that executes a PL/SQL procedure.
Example 11-2 Creating a Simple Logon Trigger
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER set_empno_ctx_trig AFTER LOGON ON DATABASE BEGIN sec_mgr.set_empno_ctx_proc; END;
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.7 Example: Creating a Logon Trigger for a Production Environment
The CREATE TRIGGER statement can create a logon trigger for a production environment.
Example 11-3 shows how to create a logon trigger that uses a WHEN OTHERS exception. Otherwise, if there is an error in the PL/SQL logic that creates an unhandled exception, then all connections to the database are blocked.
This example shows a WHEN OTHERS exception that writes errors to a table in the security administrator's schema. In a production environment, this is safer than sending the output to the user session, where it could be vulnerable to security attacks.
Example 11-3 Creating a Logon Trigger for a Production Environment
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER set_empno_ctx_trig AFTER LOGON ON DATABASE
BEGIN
sec_mgr.set_empno_ctx_proc;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
v_code := SQLCODE;
v_errm := SUBSTR(SQLERRM, 1 , 64);
-- Invoke another procedure,
-- declared with PRAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION,
-- to insert information about errors.
INSERT INTO sec_mgr.errors VALUES (v_code, v_errm, SYSTIMESTAMP);
END;
/
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.8 Example: Creating a Logon Trigger for a Development Environment
The CREATE TRIGGER statement can create a logon trigger for a development environment.
Example 11-4 shows how to create the same logon trigger for a development environment, in which you may want to output errors the user session for debugging purposes.
Example 11-4 Creating a Logon Trigger for a Development Environment
CREATE TRIGGER set_empno_ctx_trig
AFTER LOGON ON DATABASE
BEGIN
sysadmin_ctx.set_empno_ctx_pkg.set_empno;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(
-20000, 'Trigger sysadmin_ctx.set_empno_ctx_trig violation. Login denied.');
END;
/
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.9 Tutorial: Creating and Using a Database Session-Based Application Context
This tutorial demonstrates how to create an application context that checks the ID of users who try to log in to the database.
- Step 1: Create User Accounts and Ensure the User SCOTT Is Active
To begin this tutorial, you must create the necessary database accounts and endure that theSCOTTuser account is active. - Step 2: Create the Database Session-Based Application Context
As thesysadmin_ctxuser, you are ready to create the database session-based application context. - Step 3: Create a Package to Retrieve Session Data and Set the Application Context
Next, you must create a PL/SQL package that retrieves the session data and then sets the application context. - Step 4: Create a Logon Trigger for the Package
The logon trigger will execute when the user logs in. - Step 5: Test the Application Context
Now that the components are all in place, you are ready to test the application context. - Step 6: Remove the Components of This Tutorial
If you no longer need the components of this tutorial, then you can remove them.
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.9.1 Step 1: Create User Accounts and Ensure the User SCOTT Is Active
To begin this tutorial, you must create the necessary database accounts and endure that the SCOTT user account is active.
Related Topics
11.3.9.2 Step 2: Create the Database Session-Based Application Context
As the sysadmin_ctx user, you are ready to create the database session-based application context.
11.3.9.3 Step 3: Create a Package to Retrieve Session Data and Set the Application Context
Next, you must create a PL/SQL package that retrieves the session data and then sets the application context.
-
To create the package, use the
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGEstatement.
Example 11-5 shows how to create the package you need to retrieve the session data and set the application context. Before creating the package, ensure that you are still logged on as user sysadmin_ctx.
Example 11-5 Package to Retrieve Session Data and Set a Database Session Context
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE set_empno_ctx_pkg IS
PROCEDURE set_empno;
END;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY set_empno_ctx_pkg IS
PROCEDURE set_empno
IS
emp_id HR.EMPLOYEES.EMPLOYEE_ID%TYPE;
BEGIN
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID INTO emp_id FROM HR.EMPLOYEES
WHERE email = SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV', 'SESSION_USER');
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT('empno_ctx', 'employee_id', emp_id);
EXCEPTION
WHEN NO_DATA_FOUND THEN NULL;
END;
END;
/This package creates a procedure called set_empno that performs the following actions:
-
emp_id HR.EMPLOYEES.EMPLOYEE_ID%TYPEdeclares a variable,emp_id, to store the employee ID for the user who logs on. It uses the same data type as theEMPLOYEE_IDcolumn inHR.EMPLOYEES. -
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID INTO emp_id FROM HR.EMPLOYEESperforms aSELECTstatement to copy the employee ID that is stored in theemployee_idcolumn data from theHR.EMPLOYEEStable into theemp_idvariable. -
WHERE email = SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV', 'SESSION_USER')uses aWHEREclause to find all employee IDs that match the email account for the session user. TheSYS_CONTEXTfunction uses the predefinedUSERENVcontext to retrieve the user session ID, which is the same as theemailcolumn data. For example, the user ID and email address for Lisa Ozer are both the same:lozer. -
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT('empno_ctx', 'employee_id', emp_id)uses theDBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXTprocedure to set the application context:-
'empno_ctx': Calls the application contextempno_ctx. Encloseempno_ctxin single quotes. -
'employee_id': Creates the attribute value of theempno_ctxapplication context name-value pair, by naming itemployee_id. Encloseemployee_idin single quotes. -
emp_id: Sets the value for theemployee_idattribute to the value stored in theemp_idvariable.
To summarize, the
set_empno_ctx_pkg.set_empnoprocedure says, "Get the session ID of the user and then match it with the employee ID and email address of any user listed in theHR.EMPLOYEEStable." -
-
EXCEPTION ... WHEN_NO_DATA_FOUNDadds aWHEN NO_DATA_FOUNDsystem exception to catch anyno data founderrors that may result from theSELECTstatement. Without this exception, the package and logon trigger will work fine and set the application context as needed, but then any non-system administrator users other than the users listed in theHR.EMPLOYEEStable will not be able to log in to the database. Other users should be able to log in to the database, assuming they are valid database users. Once the application context information is set, then you can use this session information as a way to control user access to a particular application.
11.3.9.4 Step 4: Create a Logon Trigger for the Package
The logon trigger will execute when the user logs in.
-
As user
sysadmin_ctx, create a logon trigger forset_empno_ctx_pkg.set_empnopackage procedure.
CREATE TRIGGER set_empno_ctx_trig AFTER LOGON ON DATABASE BEGIN sysadmin_ctx.set_empno_ctx_pkg.set_empno; END; /
11.3.9.5 Step 5: Test the Application Context
Now that the components are all in place, you are ready to test the application context.
From here, the application can use the user session information to determine how much access the user can have in the database. You can use Oracle Virtual Private Database to accomplish this. .
11.3.10 Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Externally
Initializing database session-based application contexts externally increases performance because the application context is stored in the user global area (UGA).
- About Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Externally
You must use a special type of namespace to initialize session-based application context externally. - Default Values from Users
Oracle Database enables you to capture and use default values from users for your applications. - Values from Other External Resources
An application context can accept the initialization of attributes and values through external resources. - Example: Creating an Externalized Database Session-based Application Context
TheCREATE CONTEXTSQL statement can create an externalized database session-based application context. - Initialization of Application Context Values from a Middle-Tier Server
Middle-tier servers can initialize application context values on behalf of database users.
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.10.1 About Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Externally
You must use a special type of namespace to initialize session-based application context externally.
This namespace must accept the initialization of attribute values from external resources and then stores them in the local user session.
Initializing an application context externally enhances performance because it is stored in the UGA and enables the automatic propagation of attributes from one session to another. Connected user database links are supported only by application contexts initialized from OCI-based external sources.
11.3.10.2 Default Values from Users
Oracle Database enables you to capture and use default values from users for your applications.
Sometimes you need the default values from users. Initially, these default values may be hints or preferences, and then after validation, they become trusted contexts. Similarly, it may be more convenient for clients to initialize some default values, and then rely on a login event trigger or applications to validate the values.
For job queues, the job submission routine records the context being set at the time the job is submitted, and restores it when executing the batched job. To maintain the integrity of the context, job queues cannot bypass the designated PL/SQL package to set the context. Rather, the externally initialized application context accepts initialization of context values from the job queue process.
Automatic propagation of context to a remote session may create security problems. Developers or administrators can effectively handle the context that takes default values from resources other than the designated PL/SQL procedure by using logon triggers to reset the context when users log in.
11.3.10.3 Values from Other External Resources
An application context can accept the initialization of attributes and values through external resources.
Examples include an Oracle Call Interface (OCI) interface, a job queue process, or a database link.
Externally initialized application contexts provide the following features:
-
For remote sessions, automatic propagation of context values that are in the externally initialized application context namespace
-
For job queues, restoration of context values that are in the externally initialized application context namespace
-
For OCI interfaces, a mechanism to initialize context values that are in the externally initialized application context namespace
Although any client program that is using Oracle Call Interface can initialize this type of namespace, you can use login event triggers to verify the values. It is up to the application to interpret and trust the values of the attributes.
11.3.10.4 Example: Creating an Externalized Database Session-based Application Context
The CREATE CONTEXT SQL statement can create an externalized database session-based application context.
Example 11-6 shows how to create a database session-based application context that obtains values from an external source.
Example 11-6 Creating an Externalized Database Session-based Application Context
CREATE CONTEXT ext_ctx USING ext_ctx_pkg INITIALIZED EXTERNALLY;
11.3.10.5 Initialization of Application Context Values from a Middle-Tier Server
Middle-tier servers can initialize application context values on behalf of database users.
In this process, context attributes are propagated for the remote session at initialization time, and the remote database accepts the values if the namespace is externally initialized.
For example, a three-tier application creating lightweight user sessions through OCI or JDBC/OCI can access the PROXY_USER attribute in USERENV. This attribute enables you to determine if the user session was created by a middle-tier application. You could allow a user to access data only for connections where the user is proxied. If users connect directly to the database, then they would not be able to access any data.
You can use the PROXY_USER attribute from the USERENV namespace within Oracle Virtual Private Database to ensure that users only access data through a particular middle-tier application. For a different approach, you can develop a secure application role to enforce your policy that users access the database only through a specific proxy.
11.3.11 Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Globally
When a database session-based application is stored in a centralized location, it can be used globally from an LDAP directory.
- About Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Globally
You can use a centralized location to store the database session-based application context of the user. - Database Session-Based Application Contexts with LDAP
An application context that is initialized globally uses LDAP, a standard, extensible, and efficient directory access protocol. - How Globally Initialized Database Session-Based Application Contexts Work
To use a globally initialized secure application, you must first configure Enterprise User Security. - Initializing a Database Session-Based Application Context Globally
You can configure and store the initial application context for a user, such as the department name and title, in the LDAP directory.
Parent topic: Using Database Session-Based Application Contexts
11.3.11.1 About Initializing Database Session-Based Application Contexts Globally
You can use a centralized location to store the database session-based application context of the user.
A centralized location enables applications to set up a user context during initialization based upon user identity.
In particular, this feature supports Oracle Label Security labels and privileges. Initializing an application context globally makes it easier to manage contexts for large numbers of users and databases.
For example, many organizations want to manage user information centrally, in an LDAP-based directory. Enterprise User Security supports centralized user and authorization management in Oracle Internet Directory. However, there may be additional attributes an application must retrieve from Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to use for Oracle Virtual Private Database enforcement, such as the user title, organization, or physical location. Initializing an application context globally enables you to retrieve these types of attributes.
11.3.11.2 Database Session-Based Application Contexts with LDAP
An application context that is initialized globally uses LDAP, a standard, extensible, and efficient directory access protocol.
The LDAP directory stores a list of users to which this application is assigned. Oracle Database uses a directory service, typically Oracle Internet Directory, to authenticate and authorize enterprise users.
Note:
You can use third-party directories such as Microsoft Active Directory and Sun Microsystems SunONE as the directory service.
The orclDBApplicationContext LDAP object (a subclass of groupOfUniqueNames) stores the application context values in the directory. The location of the application context object is described in Figure 11-1, which is based on the Human Resources example.
The LDAP object inetOrgPerson enables multiple entries to exist for some attributes. However, be aware that when these entries are loaded into the database and accessed with the SYS_LDAP_USER_DEFAULT context namespace, then only the first of these entries is returned. For example, the inetOrgPerson object for a user allows multiple entries for telephoneNumber (thus allowing a user to have multiple telephone numbers stored). When you use the SYS_LDAP_USER_DEFAULT context namespace, only the first telephone number is retrieved. If the list of attributes and values that are provided are not sufficient for your needs, then you can use the DBMS_LDAP PL/SQL package to fetch additional values from the directory.
On the LDAP side, an internal C function is required to retrieve the orclDBApplicationContext value, which returns a list of application context values to the database. In this example, HR is the namespace; Title and Project are the attributes; and Manager and Promotion are the values.
Figure 11-1 Location of Application Context in LDAP Directory Information Tree
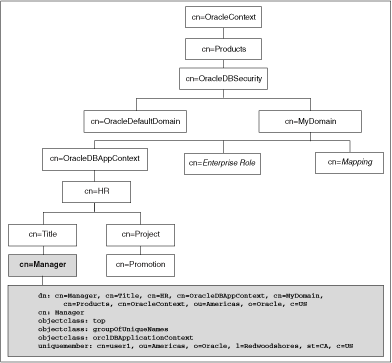
Description of "Figure 11-1 Location of Application Context in LDAP Directory Information Tree"
11.3.11.3 How Globally Initialized Database Session-Based Application Contexts Work
To use a globally initialized secure application, you must first configure Enterprise User Security.
Then, you configure the application context values for the user in the database and the directory.
When a global user (enterprise user) connects to the database, Enterprise User Security verifies the identity of the user connecting to the database. After authentication, the global user roles and application context are retrieved from the directory. When the user logs on to the database, the global roles and initial application context are already set.
11.3.11.4 Initializing a Database Session-Based Application Context Globally
You can configure and store the initial application context for a user, such as the department name and title, in the LDAP directory.
The values are retrieved during user login so that the context is set properly. In addition, any information related to the user is retrieved and stored in the SYS_USER_DEFAULTS application context namespace.
11.3.12 Externalized Database Session-Based Application Contexts
Many applications store attributes used for fine-grained access control within a database metadata table.
For example, an employees table could include cost center, title, signing authority, and other information useful for fine-grained access control. Organizations also centralize user information for user management and access control in LDAP-based directories, such as Oracle Internet Directory. Application context attributes can be stored in Oracle Internet Directory, and assigned to one or more enterprise users. They can also be retrieved automatically upon login for an enterprise user, and then used to initialize an application context.
11.4 Global Application Contexts
You can use a global application context to access application values across database sessions, including an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment.
- About Global Application Contexts
A global application context enables application context values to be accessible across database sessions, including Oracle RAC instances. - Uses for Global Application Contexts
There are three general uses for global application contexts. - Components of a Global Application Context
A global application context uses a package to manage its attributes and middle-tier application to manage the client session ID. - Global Application Contexts in an Oracle Real Application Clusters Environment
In an Oracle RAC environment, whenever a global application context is loaded or changed, it is visible only to the existing active instances. - Creating Global Application Contexts
TheCREATE CONTEXTSQL statement creates the global application context, which is then located in theSYSschema. - PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
TheDBMS_SESSIONPL/SQL package to manages global application contexts. - Embedding Calls in Middle-Tier Applications to Manage the Client Session ID
You can embed calls in middle-tier applications to manage client session IDs. - Tutorial: Creating a Global Application Context That Uses a Client Session ID
This tutorial demonstrates how you can create a global application context that uses a client session ID. - Global Application Context Processes
A simple global application context uses a database user account create the user session; a global application context is for lightweight users.
Parent topic: Using Application Contexts to Retrieve User Information
11.4.1 About Global Application Contexts
A global application context enables application context values to be accessible across database sessions, including Oracle RAC instances.
Oracle Database stores the global application context information in the System (sometimes called "Shared") Global Area (SGA) so that it can be used for applications that use a sessionless model, such as middle-tier applications in a three-tiered architecture.
These applications cannot use a session-based application context because users authenticate to the application, and then it typically connects to the database as a single identity. Oracle Database initializes the global application context once, rather than for each user session. This improves performance, because connections are reused from a connection pool.
You can clear a global application context value by running the ALTER SYSTEM FLUSH GLOBAL_CONTEXT SQL statement.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.2 Uses for Global Application Contexts
There are three general uses for global application contexts.
These uses are as follows:
-
You must share application values globally for all database users. For example, you may need to disable access to an application based on a specific situation. In this case, the values the application context sets are not user-specific, nor are they based on the private data of a user. The application context defines a situation, for example, to indicate the version of application module that is running.
-
You have database users who must move from one application to another. In this case, the second application the user is moving to has different access requirements from the first application.
-
You must authenticate nondatabase users, that is, users who are not known to the database. This type of user, who does not have a database account, typically connects through a Web application by using a connection pool. These types of applications connect users to the database as single user, using the One Big Application User authentication model. To authenticate this type of user, you use the client session ID of the user.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.3 Components of a Global Application Context
A global application context uses a package to manage its attributes and middle-tier application to manage the client session ID.
-
The global application context. You use the
CREATE CONTEXTSQL statement to create the global application context, and include theACCESSED GLOBALLYclause in the statement. This statement names the application context and associates it with a PL/SQL procedure that is designed to set the application data context data. The global application context is created and stored in the database schema of the security administrator who creates it. -
A PL/SQL package to set the attributes. The package must contain a procedure that uses the
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXTprocedure to set the global application context. TheSET_CONTEXTprocedure provides parameters that enable you to create a global application context that fits any of the three user situations described in this section. You create, store, and run the PL/SQL package on the database server. Typically, it belongs in the schema of the security administrator who created it. -
A middle-tier application to get and set the client session ID. For nondatabase users, which require a client session ID to be authenticated, you can use the Oracle Call Interface (OCI) calls in the middle-tier application to retrieve and set their session data. You can also use the
DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIERprocedure to set the client session ID. An advantage of creating a client session ID to store the nondatabase user's name is that you can query theCLIENT_IDcolumn ofDBA_AUDIT_TRAIL,DBA_FGA_AUDIT_TRAIL, andDBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary views to audit this user's activity.Note:
Be aware that the
DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO.SET_CLIENT_INFOsetting can overwrite the value.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.4 Global Application Contexts in an Oracle Real Application Clusters Environment
In an Oracle RAC environment, whenever a global application context is loaded or changed, it is visible only to the existing active instances.
Be aware that setting a global application context value in an Oracle RAC environment has performance overhead of propagating the context value consistently to all Oracle RAC instances.
If you flush the global application context (using the ALTER SYSTEM FLUSH GLOBAL_CONTEXT SQL statement) in one Oracle RAC instance, then all the global application context is flushed in all other Oracle RAC instances as well.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.5 Creating Global Application Contexts
The CREATE CONTEXT SQL statement creates the global application context, which is then located in the SYS schema.
- Ownership of the Global Application Context
A global application context is owned by theSYSschema. - Creating a Global Application Context
As with local application contexts, the global application context is created and stored in the security administrator’s database schema.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.5.1 Ownership of the Global Application Context
A global application context is owned by the SYS schema.
The ownership of the global application context is as follows: Even though a user who has been granted the CREATE ANY CONTEXT and DROP ANY CONTEXT privileges can create and drop the global application context, it is owned by the SYS schema.
Oracle Database associates the context with the schema account that created it, but if you drop this user, the context still exists in the SYS schema. As user SYS, you can drop the application context.
Parent topic: Creating Global Application Contexts
11.4.5.2 Creating a Global Application Context
As with local application contexts, the global application context is created and stored in the security administrator’s database schema.
You must have the CREATE ANY CONTEXT system privilege before you can create a global application context, and the DROP ANY CONTEXT privilege before you can drop the context with the DROP CONTEXT statement.
-
To create a global application context, use the
CREATE CONTEXTSQL statement to create the application context and include theACCESSED GLOBALLYclause in the statement.
For example:
CREATE OR REPLACE CONTEXT global_hr_ctx USING hr_ctx_pkg ACCESSED GLOBALLY CONTAINER = ALL;
Parent topic: Creating Global Application Contexts
11.4.6 PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
The DBMS_SESSION PL/SQL package to manages global application contexts.
- About the Package That Manages the Global Application Context
The package that is associated with a global application context uses theDBMS_SESSIONpackage to set and clear the global application context values. - How Editions Affects the Results of a Global Application Context PL/SQL Package
Global application context packages, Oracle Virtual Private Database packages, and fine-grained audit policies can be used across multiple editions. - DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT username and client_id Parameters
TheDBMS_SESSION.SYS_CONTEXTprocedure provides theclient_idandusernameparameters, to be used for global application contexts. - Sharing Global Application Context Values for All Database Users
You can share global application values for all database users to give them access to data in the database. - Example: Package to Manage Global Application Values for All Database Users
TheCREATE PACKAGEstatement can manage global application values for all database users. - Global Contexts for Database Users Who Move Between Applications
A global application context can be used for database users who move between application, even when the applications have different access requirements. - Global Application Context for Nondatabase Users
When a nondatabase user starts a client session, the application server generates a client session ID. - Example: Package to Manage Global Application Context Values for Nondatabase Users
TheCREATE PACKAGEstatement can manage global application context values for nondatabase users. - Clearing Session Data When the Session Closes
The application context exists within memory, so when the user exits a session, you must clear theclient_identifiercontext value.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.6.1 About the Package That Manages the Global Application Context
The package that is associated with a global application context uses the DBMS_SESSION package to set and clear the global application context values.
You must have the EXECUTE privilege for the DBMS_SESSION package before you use its procedures. Typically, you create and store this package in the database schema of a security administrator. The SYS schema owns the DBMS_SESSION package.
Unlike PL/SQL packages used to set a local application context, you do not include a SYS_CONTEXT function to get the user session data. You do not need to include this function because the owner of the session, recorded in the USERENV context, is the same for every user who is connecting.
You can run the procedures within the PL/SQL package for a global application context at any time. You do not need to create logon and logoff triggers to execute the package procedures associated with the global application context. A common practice is to run the package procedures from within the database application. Additionally, for nondatabase users, you use middle-tier applications to get and set client session IDs.
Related Topics
Parent topic: PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
11.4.6.2 How Editions Affects the Results of a Global Application Context PL/SQL Package
Global application context packages, Oracle Virtual Private Database packages, and fine-grained audit policies can be used across multiple editions.
Follow these guidelines:
-
If you want to have the PL/SQL package results be the same across all editions. To do so, create the package in the schema of a user who has not been editions enabled. To find users who are not editions enabled, you can query the
DBA_USERSandUSER_USERSdata dictionary views. Remember thatSYS,SYSTEM, and other default Oracle Database administrative accounts that are listed in theDBA_REGISTRYdata dictionary view are not and cannot be editions enabled. -
If you want to have the PL/SQL package results depend on the current state of the edition in which the package is run. Here, the results may be different across all editions to which the package applies. In this case, create the package in the schema of a user who has been editions enabled. If the schema is editions enabled, then it is likely that there will be different actual copies of the package in different editions, where each copy has different behavior. This is useful for the following types of scenarios:
-
The package must use a new application context.
-
The package must encode input values using a different scheme.
-
The package must apply different validation rules for users logging in to the database.
For PL/SQL packages that set a global application context, use a single getter function to wrap the primitive
SYS_CONTEXTcalls that will read the key-value application context pairs. You can put this getter function in the same package as the application context setter procedure. This approach lets you tag the value for the application context key to reflect a relevant concept. For example, the tag can be the edition in which the setter function is actual. Or, it can be the current edition of the session that set the context, which you can find by usingSYS_CONTEXT('USERENV', 'CURRENT_EDITION_NAME'). This tag can be any specific notion to which the setter function applies. -
Related Topics
Parent topic: PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
11.4.6.3 DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT username and client_id Parameters
The DBMS_SESSION.SYS_CONTEXT procedure provides the client_id and username parameters, to be used for global application contexts.
Table 11-2 explains how the combination of these settings controls the type of global application context you can create.
Table 11-2 Setting the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT username and client_id Parameters
| Combination Settings | Result |
|---|---|
|
|
This combination enables all database users to share access to the global application context values. These settings are also used for database session-based application contexts. |
|
|
This combination enables a global application context to be accessed by multiple sessions for users who must move between applications, as long as the |
|
|
This combination enables an application to be accessed by multiple user sessions, as long as the |
|
|
This combination enables the following two scenarios:
Setting the |
Related Topics
Parent topic: PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
11.4.6.4 Sharing Global Application Context Values for All Database Users
You can share global application values for all database users to give them access to data in the database.
-
To share global application values for all database users, set the
namespace,attribute, andvalueparameters in theSET_CONTEXTprocedure.
11.4.6.5 Example: Package to Manage Global Application Values for All Database Users
The CREATE PACKAGE statement can manage global application values for all database users.
Example 11-7 shows how to create a package that sets and clears a global application context for all database users.
Example 11-7 Package to Manage Global Application Values for All Database Users
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE hr_ctx_pkg
AS
PROCEDURE set_hr_ctx(sec_level IN VARCHAR2);
PROCEDURE clear_hr_context;
END;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY hr_ctx_pkg
AS
PROCEDURE set_hr_ctx(sec_level IN VARCHAR2)
AS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT(
namespace => 'global_hr_ctx',
attribute => 'job_role',
value => sec_level);
END set_hr_ctx;
PROCEDURE clear_hr_context
AS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXT('global_hr_ctx', 'job_role');
END clear_context;
END;
/In this example:
-
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT ... END set_hr_ctxuses theDBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXTprocedure to set values for thenamespace,attribute, andvalueparameters. Thesec_levelvalue is specified when the database application runs thehr_ctx_pkg.set_hr_ctxprocedure.The
usernameandclient_idvalues are not set, hence, they areNULL. This enables all users (database users) to have access to the values, which is appropriate for server-wide settings. -
namespace => 'global_hr_ctx'sets thenamespacetoglobal_hr_ctx, in theSET_CONTEXTprocedure. -
attribute => 'job_role'creates thejob_roleattribute. -
value => sec_levelsets the value for thejob_roleattribute tosec_level. -
PROCEDURE clear_hr_contextcreates theclear_hr_contextprocedure to clear the context values. See Clearing Session Data When the Session Closes for more information.
Typically, you execute this procedure within a database application. For example, if all users logging in are clerks, and you want to use "clerk" as a security level, you would embed a call within a database application similar to the following:
BEGIN
hr_ctx_pkg.set_hr_ctx('clerk');
END;
/
If the procedure successfully completes, then you can check the application context values as follows:
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('global_hr_ctx', 'job_role') job_role FROM DUAL;
JOB_ROLE
-----------
clerk
You can clear the global application context values for all database users by running the following procedure:
BEGIN hr_ctx_pkg.clear_hr_context; END; /
To check that the global context value is really cleared, the following SELECT statement should return no values:
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('global_hr_ctx', 'job_role') job_role FROM DUAL;
JOB_ROLE
-----------If Oracle Database returns error messages saying that you have insufficient privileges, then ensure that you have correctly created the global application context. You should also query the DBA_CONTEXT database view to ensure that your settings are correct, for example, that you are calling the procedure from the schema in which you created it.
If NULL is returned, then you may have inadvertently set a client identifier. To clear the client identifier, run the following procedure:
EXEC DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIER;
Parent topic: PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
11.4.6.6 Global Contexts for Database Users Who Move Between Applications
A global application context can be used for database users who move between application, even when the applications have different access requirements.
To do so, you must include the username parameter in the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure.
This parameter specifies that the same schema be used for all sessions.
You can use the following DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT parameters:
-
namespace -
attribute -
value -
username
Oracle Database matches the username value so that the other application can recognize the application context. This enables the user to move between applications.
By omitting the client_id setting, its value is NULL, the default. This means that values can be seen by multiple sessions if the username setting is the same for a database user who maintains the same context in different applications. For example, you can have a suite of applications that control user access with Oracle Virtual Private Database policies, with each user restricted to a job role.
Example 11-8 demonstrates how to set the username parameter so that a specific user can move between applications. The use of the username parameter is indicated in bold typeface.
Example 11-8 Package for Global Application Context Values for Moving Between Applications
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE hr_ctx_pkg
AS
PROCEDURE set_hr_ctx(sec_level IN VARCHAR2, user_name IN VARCHAR2);
PROCEDURE clear_hr_context;
END;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY hr_ctx_pkg
AS
PROCEDURE set_hr_ctx(sec_level IN VARCHAR2, user_name IN VARCHAR2)
AS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT(
namespace => 'global_hr_ctx',
attribute => 'job_role',
value => sec_level,
username => user_name);
END set_hr_ctx;
PROCEDURE clear_hr_context
AS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXT('global_hr_ctx');
END clear_context;
END;
/
Typically, you execute this procedure within a database application by embedding a call similar to the following example. Ensure that the value for the user_name parameter (scott in this case) is a valid database user name.
BEGIN
hr_ctx_pkg.set_hr_ctx('clerk', 'scott');
END;
A secure way to manage this type of global application context is within your applications, embed code to grant a secure application role to the user. This code should include EXECUTE permissions on the trusted PL/SQL package that sets the application context. In other words, the application, not the user, will set the context for the user.
Parent topic: PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
11.4.6.7 Global Application Context for Nondatabase Users
When a nondatabase user starts a client session, the application server generates a client session ID.
A nondatabase user is a user who is not known to the database, such as a Web application user.
Once this ID is set on the application server, it must be passed to the database server side. You can do this by using the DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER procedure to set the client session ID.
To set the context, you can set the client_id parameter in the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure, in a PL/SQL procedure on the server side. This enables you to manage the application context globally, yet each client sees only his or her assigned application context.
The client_id value is the key here to getting and setting the correct attributes for the global application context. Remember that the client identifier is controlled by the middle-tier application, and once set, it remains open until it is cleared.
A typical way to manage this type of application context is to place the session_id value (client_identifier) in a cookie, and send it to the end user's HTML page so that is returned on the next request. A lookup table in the application should also keep client identifiers so that they are prevented from being reused for other users and to implement an end-user session time out.
For nondatabase users, configure the following SET_CONTEXT parameters:
-
namespace -
attribute -
value -
username -
client_id
Related Topics
Parent topic: PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
11.4.6.8 Example: Package to Manage Global Application Context Values for Nondatabase Users
The CREATE PACKAGE statement can manage global application context values for nondatabase users.
Example 11-9 shows how to create a package that manages this type of global application context.
Example 11-9 Package to Manage Global Application Context Values for Nondatabase Users
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE hr_ctx_pkg
AS
PROCEDURE set_session_id(session_id_p IN NUMBER);
PROCEDURE set_hr_ctx(sec_level_attr IN VARCHAR2,
sec_level_val IN VARCHAR2);
PROCEDURE clear_hr_session(session_id_p IN NUMBER);
PROCEDURE clear_hr_context;
END;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY hr_ctx_pkg
AS
session_id_global NUMBER;
PROCEDURE set_session_id(session_id_p IN NUMBER)
AS
BEGIN
session_id_global := session_id_p;
DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER(session_id_p);
END set_session_id;
PROCEDURE set_hr_ctx(sec_level_attr IN VARCHAR2,
sec_level_val IN VARCHAR2)
AS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT(
namespace => 'global_hr_ctx',
attribute => sec_level_attr,
value => sec_level_val,
username => USER,
client_id => session_id_global);
END set_hr_ctx;
PROCEDURE clear_hr_session(session_id_p IN NUMBER)
AS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER(session_id_p);
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIER;
END clear_hr_session;
PROCEDURE clear_hr_context
AS
BEGIN
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXT('global_hr_ctx', session_id_global);
END clear_hr_context;
END;
/In this example:
-
session_id_global NUMBERcreates thesession_id_globalvariable, which will hold the client session ID. Thesession_id_globalvariable is referenced throughout the package definition, including the procedure that creates the global application context attributes and assigns them values. This means that the global application context values will always be associated with this particular session ID. -
PROCEDURE set_session_id ... END set_session_idcreates theset_session_idprocedure, which writes the client session ID to thesession_id_globalvariable. -
PROCEDURE set_hr_ctx ... END set_hr_ctxcreates theset_hr_ctxprocedure, which creates global application context attributes and enables you to assign values to these attributes. Within this procedure:-
username => USERspecifies theusernamevalue. This example sets it by calling the Oracle Database-suppliedUSERfunction, which adds the session owner from the context retrieval process. TheUSERfunction ensures that only the user who set the application context can access the context.If you had specified
NULL(the default for theusernameparameter), then any user can access the context.Setting both the
usernameandclient_idvalues enables two scenarios. For lightweight users, set theusernameparameter to a connection pool owner (for example,APPS_USER), and then setclient_idto the client session ID. If you want to use a stateless Web session, set theuser_nameparameter to the same database user who has logged in, and ensure that this user keeps the same client session ID. -
client_id => session_id_globalspecifiesclient_idvalue. This example sets it to thesession_id_globalvariable. This associates the context settings defined here with a specific client session ID, that is, the one that is set when you run theset_session_idprocedure. If you specify theclient_idparameter default,NULL, then the global application context settings could be used by any session.
-
-
PROCEDURE clear_hr_session ... END clear_hr_sessioncreates theclear_hr_sessionprocedure to clear the client session identifier. TheASclause sets it to ensure that you are clearing the correct session ID, that is, the one stored in variablesession_id_pdefined in theCREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODYhr_ctx_pkgprocedure. -
PROCEDURE clear_hr_context ... END clear_hr_contextcreates theclear_hr_contextprocedure, so that you can clear the context settings for the current user session, which were defined by theglobal_hr_ctxvariable.
11.4.6.9 Clearing Session Data When the Session Closes
The application context exists within memory, so when the user exits a session, you must clear the client_identifier context value.
-
To clear session data when a user exits a session, use either of the following methods in the server-side PL/SQL package:
-
Clearing the client identifier when a user exits a session. Use the
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIERprocedure. For example:DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIER;
-
Continuing the session but still clearing the context. If you want the session to continue, but you still need to clear the context, use the
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXTor theDBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_ALL_CONTEXTprocedure. For example:DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXT('my_ctx', 'my_attribute');The
CLEAR_CONTEXTprocedure clears the context for the current user. To clear the context values for all users, for example, when you need to shut down the application server, use theCLEAR_ALL_CONTEXTprocedure.Global application context values are available until they are cleared, so you should use
CLEAR_CONTEXTorCLEAR_ALL_CONTEXTto ensure that other sessions do not have access to these values. Be aware that any changes in the context value are reflected immediately and subsequent calls to access the value through theSYS_CONTEXTfunction will return the most recent value.
-
Parent topic: PL/SQL Package to Manage a Global Application Context
11.4.7 Embedding Calls in Middle-Tier Applications to Manage the Client Session ID
You can embed calls in middle-tier applications to manage client session IDs.
- About Managing Client Session IDs Using a Middle-Tier Application
The application server generates the client session ID. - Step 1: Retrieve the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
When a user starts a client session, the application server generates a client session ID. - Step 2: Set the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
Next, you are ready to set the client session ID using a middle-tier application. - Step 3: Clear the Session Data Using a Middle-Tier Application
The application context exists entirely within memory.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.7.1 About Managing Client Session IDs Using a Middle-Tier Application
The application server generates the client session ID.
From a middle-tier application, you can get, set, and clear the client session IDs. To do so, you can embed either Oracle Call Interface (OCI) calls or DBMS_SESSION PL/SQL package procedures into the middle-tier application code.
The application authenticates the user, sets the client identifier, and sets it in the current session. The PL/SQL package SET_CONTEXT sets the client_identifier value in the application context.
11.4.7.2 Step 1: Retrieve the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
When a user starts a client session, the application server generates a client session ID.
You can retrieve this ID for use in authenticating the user's access.
-
To retrieve this client ID, use the
OCIStmtExecutecall with any of the following statements:-
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('userenv', 'client_identifier') FROM DUAL; -
SELECT CLIENT_IDENTIFIER from V$SESSION; -
SELECT value FROM session_context WHERE attribute='CLIENT_IDENTIFIER';
-
For example, to use the OCIStmtExecute call to retrieve a client session ID value:
oratext clientid[31];
OCIDefine *defnp1 = (OCIDefine *) 0;
OCIStmt *statementhndle;
oratext *selcid = (oratext *)"SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('userenv',
'client_identifier') FROM DUAL";
OCIStmtPrepare(statementhndle, errhp, selcid,
(ub4) strlen((char *) selcid), (ub4) OCI_NTV_SYNTAX, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT);
OCIDefineByPos(statementhndle, &defnp1, errhp, 1, (dvoid *)clientid, 31,
SQLT_STR, (dvoid *) 0, (ub2 *) 0, (ub2 *) 0, OCI_DEFAULT);
OCIStmtExecute(servhndle, statementhndle, errhp, (ub4) 1, (ub4) 0,
(CONST OCISnapshot *) NULL, (OCISnapshot *) NULL, OCI_DEFAULT);
printf("CLIENT_IDENTIFIER = %s \n", clientid);In this example:
-
oratext,OCIDefine,OCIStmt, andoratextcreate variables to store the client session ID, reference call forOCIDefine, the statement handle, and theSELECTstatement to use. -
OCIStmtPreparprepares the statementselcidfor execution. -
OCIDefineByPosdefines the output variableclientidfor client session ID. -
OCIStmtExecuteexecutes the statement in theselcidvariable. -
printfprints the formatted output for the retrieved client session ID.
11.4.7.3 Step 2: Set the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
Next, you are ready to set the client session ID using a middle-tier application.
- About Setting the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
After you use theOCIStmtExecutecall to retrieve the client session ID, you are ready to set this ID. - Setting the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
Oracle Call Interface or theDBMS_SESSIONPL/SQL package can set the client session ID using a middle-tier application. - Checking the Value of the Client Identifier
For bothOCIAttrSetandDBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER, you can check the value of the client identifier.
11.4.7.3.1 About Setting the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
After you use the OCIStmtExecute call to retrieve the client session ID, you are ready to set this ID.
The DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure in the server-side PL/SQL package then sets this session ID and optionally, overwrites the application context values.
You must ensure that the middle-tier application code checks that the client session ID value (for example, the value written to user_id in the previous examples) matches the client_id setting defined in the server-side DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure. The sequence of calls on the application server side should be as follows:
-
Get the current client session ID. The session should already have this ID, but it is safer to ensure that it truly has the correct value.
-
Clear the current client session ID. This prepares the application to service a request from a different end user.
-
Set the new client session ID or the client session ID that has been assigned to the end user. This ensures that the session is using a different set of global application context values.
11.4.7.3.2 Setting the Client Session ID Using a Middle-Tier Application
Oracle Call Interface or the DBMS_SESSION PL/SQL package can set the client session ID using a middle-tier application.
11.4.7.3.3 Checking the Value of the Client Identifier
For both OCIAttrSet and DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER, you can check the value of the client identifier.
-
To check the value of the client identifier, use one of the of the following approaches:
-
To check it using the
SYS_CONTEXTfunction:SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('userenv', 'client_identifier') FROM DUAL; -
To check it by querying the
V$SESSIONview:SELECT CLIENT_IDENTIFIER from V$SESSION;
-
11.4.7.4 Step 3: Clear the Session Data Using a Middle-Tier Application
The application context exists entirely within memory.
When the user exits a session, you must clear the context for the client_identifier value. This releases memory and prevents other users from accidentally using any left over values
-
To clear session data when a user exits a session, use either of the following methods in the middle-tier application code:
-
Clearing the client identifier when a user exits a session. Use the
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIERprocedure. For example:DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIER;
-
Continuing the session but still clearing the context. If you want the session to continue, but you still need to clear the context, use the
DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXTor theDBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_ALL_CONTEXTprocedure. For example:DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXT(namespace, client_identifier, attribute);
The
CLEAR_CONTEXTprocedure clears the context for the current user. To clear the context values for all users, for example, when you need to shut down the application server, use theCLEAR_ALL_CONTEXTprocedure.Global application context values are available until they are cleared, so you should use
CLEAR_CONTEXTorCLEAR_ALL_CONTEXTto ensure that other sessions do not have access to these values.
-
11.4.8 Tutorial: Creating a Global Application Context That Uses a Client Session ID
This tutorial demonstrates how you can create a global application context that uses a client session ID.
- About This Tutorial
This tutorial shows how to create a global application context that uses a client session ID for a lightweight user application. - Step 1: Create User Accounts
A security administrator will manage the application context and its package, and a user account will own the connection pool. - Step 2: Create the Global Application Context
Next, you are ready to create the global application context. - Step 3: Create a Package for the Global Application Context
The PL/SQL package will manage the global application context that you created. - Step 4: Test the Newly Created Global Application Context
At this stage, you are ready to explore how this global application context and session ID settings work. - Step 5: Modify the Session ID and Test the Global Application Context Again
Next, clear and then modify the session ID and test the global application context again. - Step 6: Remove the Components of This Tutorial
If you no longer need the components of this tutorial, then you can remove them.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.8.1 About This Tutorial
This tutorial shows how to create a global application context that uses a client session ID for a lightweight user application.
It demonstrates how to control nondatabase user access by using a connection pool. This tutorial applies to the current PDB only.
11.4.8.2 Step 1: Create User Accounts
A security administrator will manage the application context and its package, and a user account will own the connection pool.
Related Topics
11.4.8.3 Step 2: Create the Global Application Context
Next, you are ready to create the global application context.
11.4.8.4 Step 3: Create a Package for the Global Application Context
The PL/SQL package will manage the global application context that you created.
11.4.8.5 Step 4: Test the Newly Created Global Application Context
At this stage, you are ready to explore how this global application context and session ID settings work.
-
Connect as the connection pool owner, user
apps_user.CONNECT apps_user@pdb_name Enter password: password
-
When the connection pool user logs on, the application sets the client session identifier as follows:
BEGIN sysadmin_ctx.cust_ctx_pkg.set_session_id(34256); END; /
-
Test the value of the client session identifier.
-
Set the session ID:
EXEC sysadmin_ctx.cust_ctx_pkg.set_session_id(34256);
-
Check the session ID:
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('userenv', 'client_identifier') FROM DUAL;The following output should appear:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CLIENT_IDENTIFIER') -------------------------------------------------- 34256
-
-
Set the global application context as follows:
EXEC sysadmin_ctx.cust_ctx_pkg.set_cust_ctx('Category', 'Gold Partner'); EXEC sysadmin_ctx.cust_ctx_pkg.set_cust_ctx('Benefit Level', 'Highest');(In a real-world scenario, the middle-tier application would set the global application context values, similar to how the client session identifier was set in Step 2.)
-
Enter the following
SELECT SYS_CONTEXTstatement to check that the settings were successful:col category format a13 col benefit_level format a14 SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('global_cust_ctx', 'Category') category, SYS_CONTEXT('global_cust_ctx', 'Benefit Level') benefit_level FROM DUAL;The following output should appear:
CATEGORY BENEFIT_LEVEL ------------- -------------- Gold Partner Highest
What apps_user has done here, within the client session 34256, is set a global application context on behalf of a nondatabase user. This context sets the Category and Benefit Level DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT attributes to be Gold Partner and Highest, respectively. The context exists only for user apps_user with client ID 34256. When a nondatabase user logs in, behind the scenes, he or she is really logging on as the connection pool user apps_user. Hence, the Gold Partner and Highest context values are available to the nondatabase user.
Suppose the user had been a database user and could log in without using the intended application. (For example, the user logs in using SQL*Plus.) Because the user has not logged in through the connection pool user apps_user, the global application context appears empty to our errant user. This is because the context was created and set under the apps_user session. If the user runs the SELECT SYS_CONTEXT statement, then the following output appears:
CATEGORY BENEFIT_LEVEL ------------- --------------
11.4.8.6 Step 5: Modify the Session ID and Test the Global Application Context Again
Next, clear and then modify the session ID and test the global application context again.
11.4.9 Global Application Context Processes
A simple global application context uses a database user account create the user session; a global application context is for lightweight users.
- Simple Global Application Context Process
In a simple global application context process, the application uses a database user to create a user session. - Global Application Context Process for Lightweight Users
You can set a global application contexts for lightweight users.
Parent topic: Global Application Contexts
11.4.9.1 Simple Global Application Context Process
In a simple global application context process, the application uses a database user to create a user session.
The value for the context attribute of a simple global application context process can be retrieved from a SELECT statement.
Consider the application server, AppSvr, which has assigned the client identifier 12345 to client SCOTT. The AppSvr application uses the SCOTT user to create a session. (In other words, it is not a connection pool.) The value assigned to the context attribute can come from anywhere, for example, from running a SELECT statement on a table that holds the responsibility codes for users. When the application context is populated, it is stored in memory. As a result, any action that needs the responsibility code can access it quickly with a SYS_CONTEXT call, without the overhead of accessing a table. The only advantage of a global context over a local context in this case is if SCOTT were changing applications frequently and used the same context in each application.
The following steps show how the global application context process sets the client identifier for SCOTT:
-
The administrator creates a global context namespace by using the following statement:
CREATE OR REPLACE CONTEXT hr_ctx USING hr.init ACCESSED GLOBALLY;
-
The administrator creates a PL/SQL package for the
hr_ctxapplication context to indicate that, for this client identifier, there is an application context calledresponsibilitywith a value of13in theHRnamespace.:CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE hr.init AS BEGIN DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT( namespace => 'hr_ctx', attribute => 'responsibility', value => '13', username => 'SCOTT', client_id => '12345' ); END; /This PL/SQL procedure is stored in the
HRdatabase schema, but typically it is stored in the schema of the security administrator. -
The AppSvr application issues the following command to indicate the connecting client identity each time
scottusesAppSvrto connect to the database:EXEC DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER('12345'); -
When there is a
SYS_CONTEXT('hr_ctx','responsibility')call within the database session, the database matches the client identifier,12345, to the global context, and then returns the value13. -
When exiting this database session,
AppSvrclears the client identifier by issuing the following procedure:EXEC DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIER( );
-
To release the memory used by the application context,
AppSvrissues the following procedure:DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_CONTEXT('hr_ctx', '12345');CLEAR_CONTEXTis needed when the user session is no longer active, either on an explicit logout, timeout, or other conditions determined by theAppSvrapplication.
Note:
After a client identifier in a session is cleared, it becomes a NULL value. This implies that subsequent SYS_CONTEXT calls only retrieve application contexts with NULL client identifiers, until the client identifier is set again using the SET_IDENTIFIER interface.
Parent topic: Global Application Context Processes
11.4.9.2 Global Application Context Process for Lightweight Users
You can set a global application contexts for lightweight users.
You can configure this access so that when other users log in, they cannot access the global application context.
The following steps show the global application context process for a lightweight user application. The lightweight user, robert, is not known to the database through the application.
-
The administrator creates the global context namespace by using the following statement:
CREATE CONTEXT hr_ctx USING hr.init ACCESSED GLOBALLY;
-
The
HRapplication server,AppSvr, starts and then establishes multiple connections to theHRdatabase as theappsmgruser. -
User
robertlogs in to theHRapplication server. -
AppSvrauthenticatesrobertto the application. -
AppSvrassigns a temporary session ID (or uses the application user ID),12345, for this connection. -
The session ID is returned to the Web browser used by
robertas part of a cookie or is maintained byAppSvr. -
AppSvrinitializes the application context for this client by calling thehr.initpackage, which issues the following statements:DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT( 'hr_ctx', 'id', 'robert', 'APPSMGR', 12345 ); DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT( 'hr_ctx', 'dept', 'sales', 'APPSMGR', 12345 );
-
AppSvrassigns a database connection to this session and initializes the session by issuing the following statement:DBMS_SESSION.SET_IDENTIFIER( 12345 );
-
All
SYS_CONTEXTcalls within this database session return application context values that belong only to the client session.For example,
SYS_CONTEXT('hr','id')returns the valuerobert. -
When finished with the session,
AppSvrissues the following statement to clean up the client identity:DBMS_SESSION.CLEAR_IDENTIFIER ( );
Even if another user logged in to the database, this user cannot access the global context set by AppSvr, because AppSvr specified that only the application with user APPSMGR logged in can see it. If AppSvr used the following, then any user session with client ID set to 12345 can see the global context:
DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT( 'hr_ctx', 'id', 'robert', NULL , 12345 ); DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT( 'hr_ctx', 'dept', 'sales', NULL , 12345 );
Setting USERNAME to NULL enables different users to share the same context.
Note:
Be aware of the security implication of different settings of the global context. NULL in the user name means that any user can access the global context. A NULL client ID in the global context means that a session with an uninitialized client ID can access the global context. To ensure that only the user who has logged on can access the session, specify USER instead of NULL.
You can query the client identifier set in the session as follows:
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CLIENT_IDENTIFIER') FROM DUAL;
The following output should appear:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CLIENT_IDENTIFIER')
-------------------------------------------------
12345A security administrator can see which sessions have the client identifier set by querying the V$SESSION view for the CLIENT_IDENTIFIER and USERNAME, for example:
COL client_identifier format a18 SELECT CLIENT_IDENTIFIER, USERNAME from V$SESSION;
The following output should appear:
CLIENT_IDENTIFIER USERNAME ------------------ -------- 12345 APPSMGR
To check the amount of global context area (in bytes) being used, use the following query:
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','GLOBAL_CONTEXT_MEMORY') FROM DUAL;The following output should appear:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','GLOBAL_CONTEXT_MEMORY')
----------------------------------------------
58411.5 Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
A client session-based application context is stored in the User Global Area (UGA).
- About Client Session-Based Application Contexts
Oracle Call Interface (OCI) functions can set and clear the User Global Area (UGA) user session information. - Setting a Value in the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
Oracle Call Interface (OCI) can set theCLIENTCONTEXTnamespace. - Retrieving the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
You can use Oracle Call Interface to retrieve theCLIEINTCONTEXTnamespace. - Example: Retrieving a Client Session ID Value for Client Session-Based Contexts
The OCIOCIStmtExecutecall can retrieve client session ID values for client session-based contexts. - Clearing a Setting in the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
You can use Oracle Call Interface to clear theCLIENTCONTEXTnamespace. - Clearing All Settings in the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
You can use Oracle Call Interface (OCI) to clear theCLIENTCONTEXTnamespace.
Parent topic: Using Application Contexts to Retrieve User Information
11.5.1 About Client Session-Based Application Contexts
Oracle Call Interface (OCI) functions can set and clear the User Global Area (UGA) user session information.
The advantage of this type of application context in a session-based application context is that an individual application can check for specific nondatabase user session data, rather than having the database perform this task. Another advantage is that the calls to set the application context value are included in the next call to the server, which improves performance.
However, be aware that application context security is compromised with a client session-based application context: any application user can set the client application context, and no check is performed in the database.
You configure the client session-based application context for the client application only. You do not configure any settings on the database server to which the client connects. Any application context settings in the database server do not affect the client session-based application context.
To configure a client session-based application context, use the OCIAppCtxSet OCI function. A client session-based application context uses the CLIENTCONTEXT namespace, updatable by any OCI client or by the existing DBMS_SESSION package for application context. Oracle Database performs no privilege or package security checks for this type.
The CLIENTCONTEXT namespace enables a single application transaction to both change the user context information and use the same user session handle to service the new user request. You can set or clear individual values for attributes in the CLIENTCONTEXT namespace, or clear all their values.
-
An OCI client uses the
OCIAppCtxfunction to set variable length data for the namespace, calledOCISessionHandle. The OCI network single, round-trip transport sends all the information to the server in one round-trip. On the server side, you can query the application context information by using theSYS_CONTEXTSQL function on the namespace. For example: -
A JDBC client uses the
oracle.jdbc.internal.OracleConnectionfunction to achieve the same purposes.
Any user can set, clear, or collect the information in the CLIENTCONTEXT namespace, because it is not protected by package-based security.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
11.5.2 Setting a Value in the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
Oracle Call Interface (OCI) can set the CLIENTCONTEXT namespace.
-
To set a value in the
CLIENTCONTEXTnamespace, use theOCIAppCTXSetcommand, in the following syntax:err = OCIAppCtxSet((void *) session_handle,(dvoid *)"CLIENTCONTEXT",(ub4) 13, (dvoid *)attribute_name, length_of_attribute_name (dvoid *)attribute_value, length_of_attribute_value, errhp, OCI_DEFAULT);
In this specification:
-
session_handlerepresents theOCISessionHandlenamespace. -
attribute_nameis the name of the attribute. For example,responsibility, with a length of14. -
attribute_valueis the value of the attribute. For example,manager, with a length of7.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
11.5.3 Retrieving the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
You can use Oracle Call Interface to retrieve the CLIEINTCONTEXT namespace.
-
To retrieve the
CLIENTCONTEXTnamespace, use theOCIStmtExecutecall with either of the following statements:-
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('CLIENTCONTEXT', 'attribute-1') FROM DUAL; -
SELECT VALUE FROM SESSION_CONTEXT WHERE NAMESPACE='CLIENTCONTEXT' AND ATTRIBUTE='attribute-1';
-
The attribute-1 value can be any attribute value that has already been set in the CLIENTCONTEXT namespace. Oracle Database only retrieves the set attribute; otherwise, it returns NULL. Typically, you set the attribute by using the OCIAppCtxSet call. In addition, you can embed a DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT call in the OCI code to set the attribute value.
Parent topic: Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
11.5.4 Example: Retrieving a Client Session ID Value for Client Session-Based Contexts
The OCI OCIStmtExecute call can retrieve client session ID values for client session-based contexts.
Example 11-10 shows how to use the OCIStmtExecute call to retrieve a client session ID value.
Example 11-10 Retrieving a Client Session ID Value for Client Session-Based Contexts
oratext clientid[31];
OCIDefine *defnp1 = (OCIDefine *) 0;
OCIStmt *statementhndle;
oratext *selcid = (oratext *)"SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('CLIENTCONTEXT',
attribute) FROM DUAL";
OCIStmtPrepare(statementhndle, errhp, selcid, (ub4) strlen((char *) selcid),
(ub4) OCI_NTV_SYNTAX, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT);
OCIDefineByPos(statementhndle, &defnp1, errhp, 1, (dvoid *)clientid, 31,
SQLT_STR, (dvoid *) 0, (ub2 *) 0, (ub2 *) 0, OCI_DEFAULT);
OCIStmtExecute(servhndle, statementhndle, errhp, (ub4) 1, (ub4) 0,
(CONST OCISnapshot *) NULL, (OCISnapshot *) NULL, OCI_DEFAULT);
printf("CLIENT_IDENTIFIER = %s \n", clientid);In this example:
-
oratext,OCIDefine,OCIStmt, andoratextcreate variables to store the client session ID, reference call forOCIDefine, the statement handle, and theSELECTstatement to use. -
OCIStmtPrepareprepares the statementselcidfor execution. -
OCIDefineByPosdefines the output variableclientidfor client session ID. -
OCIStmtExecuteexecutes the statement in theselcidvariable. -
printfprints the formatted output for the retrieved client session ID.
Parent topic: Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
11.5.5 Clearing a Setting in the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
You can use Oracle Call Interface to clear the CLIENTCONTEXT namespace.
-
To clear a setting in
CLIENTCONTEXT, set the value toNULLor to an empty string by using one of the following commands:-
The following command sets the empty string to zero:
(void) OCIAppCtxSet((void *) session_handle, (dvoid *)"CLIENTCONTEXT", 13, (dvoid *)attribute_name, length_of_attribute_name, (dvoid *)0, 0,errhp OCI_DEFAULT);
-
This following command sets the empty string to a blank value:
(void) OCIAppCtxSet((void *) session_handle, (dvoid *)"CLIENTCONTEXT", 13 (dvoid *)attribute_name, length_of_attribute_name, (dvoid *)"", 0,errhp, OCI_DEFAULT);
-
Parent topic: Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
11.5.6 Clearing All Settings in the CLIENTCONTEXT Namespace
You can use Oracle Call Interface (OCI) to clear the CLIENTCONTEXT namespace.
-
To clear the namespace, use the
OCIAppCtxClearAllcommand in the following form:err = OCIAppCtxClearAll((void *) session_handle, (dvoid *)"CLIENTCONTEXT", 13, errhp, OCI_DEFAULT);
Parent topic: Using Client Session-Based Application Contexts
11.6 Application Context Data Dictionary Views
Oracle Database provides data dictionary views that provide information about application contexts.
Table 11-3 lists these data dictionary views.
Table 11-3 Data Dictionary Views That Display Information about Application Contexts
| View | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Describes all context namespaces in the current session for which attributes and values were specified using the |
|
|
Describes the driving contexts defined for the synonyms, tables, and views accessible to the current user. (A driving context is a context used in a Virtual Private Database policy.) |
|
|
Provides all context namespace information in the database. Its columns are the same as those in the |
|
|
Provides the names of existing application contexts. Query the SELECT OBJECT_NAME FROM DBA_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE ='CONTEXT'; |
|
|
Describes all driving contexts in the database that were added by the |
|
|
Describes the context attributes and their values set for the current session. |
|
|
Describes the driving contexts defined for the synonyms, tables, and views owned by the current user. Its columns (except for |
|
|
Lists set attributes in the current PDB session. Users do not have access to this view unless you grant the user the |
|
|
Lists detailed information about each current PDB session. Users do not have access to this view unless you grant the user the |
Tip:
In addition to these views, check the database trace file if you find errors when running applications that use application contexts. The USER_DUMP_DEST initialization parameter sets the directory location of the trace files. You can find the value of this parameter by issuing SHOW PARAMETER USER_DUMP_DEST in SQL*Plus.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Using Application Contexts to Retrieve User Information