3 SQL Translation Framework Configuration
The SQL Translation Framework may be installed and configured using Oracle SQL Developer, or from the command line interface. In either case, the user must have the necessary permissions to install SQL Translator.
3.1 Installing and Configuring SQL Translation Framework with Oracle SQL Developer
You can use the DBA Navigator in Oracle SQL Developer 3.2 to install and manage the translator and translation profile.
3.1.1 Overview of Oracle SQL Developer Migration Support
The SQL Translation framework is installed as part of Oracle Database installation. However, it must be configured to recognize the non-Oracle SQL dialect of the application and you must install at least one translator to fully utilize the framework.
Before using the SQL Translation feature, you must migrate your data, schema, stored procedures, triggers, and views. Oracle implements database schema migration and data migration through Oracle SQL Developer functionality. Oracle SQL Developer simplifies the process of migrating a non-Oracle database to an Oracle Database through the use of Migration Wizard. The Migration wizard provides convenient and comprehensive guidance through the phases involved in migrating a database.
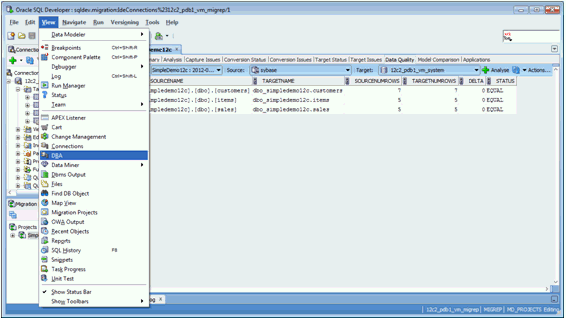
Oracle SQL Developer captures information from the source non-Oracle database and displays it in a captured model, which is a representation of the structure of the source database. This representation is stored in a migration repository, which is a collection of schema objects that Oracle SQL Developer uses to store migration information.
The information in the repository is used to generate the converted model, which is a representation of the structure of the destination database as it will be implemented in the Oracle database. You can then use the information in the captured model and the converted model to compare database objects, identify conflicts with Oracle reserved words, and manage the migration progress. When you are ready to migrate, generate the Oracle schema objects, and then migrate the data.
This section describes how to perform the subsequent tasks that enable automatic run-time migration. These examples use SQL Translator with a JDBC application that runs against a Sybase database; they can be easily adapted for other client/database configurations. Note that Oracle SQL Developer is shipped with an installed Sybase translator.
See Oracle SQL Developer User's Guide for more information.
3.1.2 Setting Up Oracle SQL Developer 3.2 for Windows
Oracle SQL Developer 3.2 is shipped with Oracle Database 11g JDBC drivers and there is no client for Windows in this release. If you are using a Windows system, then you must enable Oracle SQL Developer 3.2 to use Oracle Database 12c JDBC driver, so that all the features of the current release are enabled. Perform the following steps to achieve this:
-
Rename the
sqldeveloper\jdbc\libfolder tosqldeveloper\jdbc\lib_11g. -
Create a new empty folder as
sqldeveloper\jdbc\lib. -
Unzip Oracle Database 12c JDBC JAR files into the new
sqldeveloper\jdbc\libfolder.See Oracle Database JDBC Developer's Guide for more information about Oracle Database 12c JDBC files.
3.1.2.1 Setting Up Oracle SQL Developer 3.2 Startup
Oracle SQL Developer automatically uses JDBC drivers found in any ORACLE_HOME\client directory. To override this behavior and make Oracle SQL Developer use JDBC drivers in the sqldeveloper\jdbc\lib directory, create a new sqldeveloper.bat file in the sqldeveloper directory:
set ORACLE_HOME=%CD% start sqldeveloper.exe
3.1.3 Creating a Connection to Oracle Database
Create a connection to the Database with the credentials as shown in Figure 3-2:
Figure 3-2 Creating an Oracle Database Connection
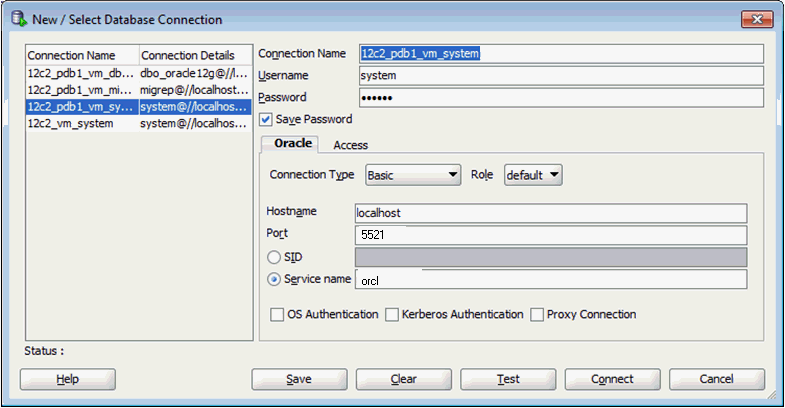
Description of "Figure 3-2 Creating an Oracle Database Connection"
You can use the following command to check the database you are connected to and the JDBC driver being used:
show jdbc
Setting Up Migration Preferences
You must set up the migration preferences in the following way:
- Select Preferences from the Tools menu.
- Select Generation Options from Migration option on the left panel, as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Setting Up Migration Preferences in Oracle SQL Developer
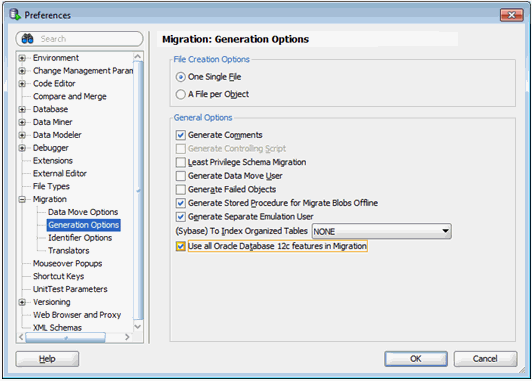
Description of "Figure 3-3 Setting Up Migration Preferences in Oracle SQL Developer"
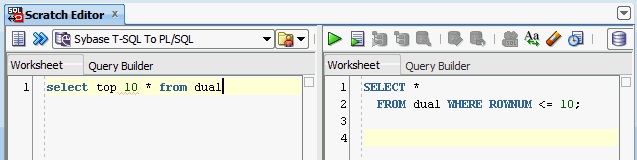
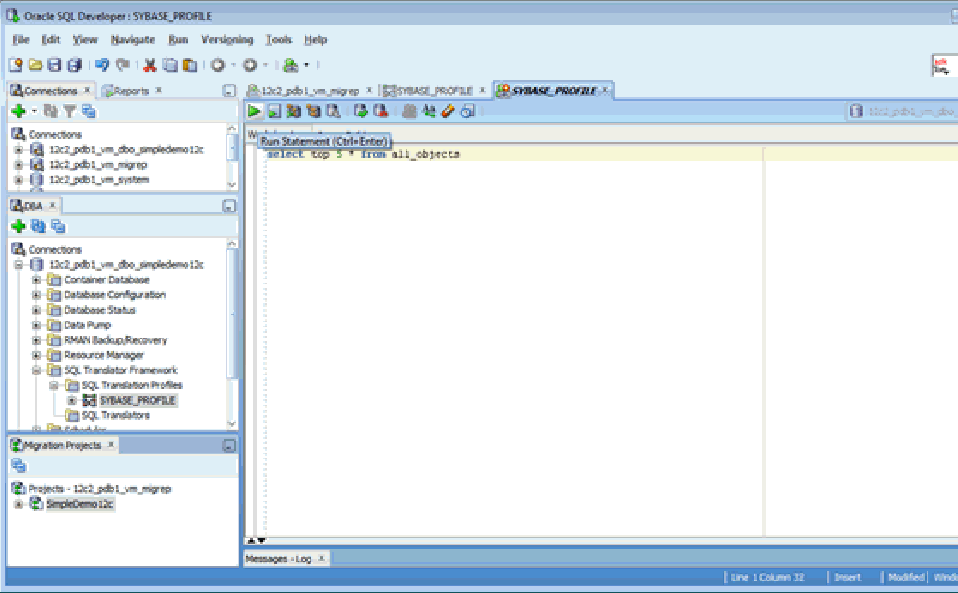
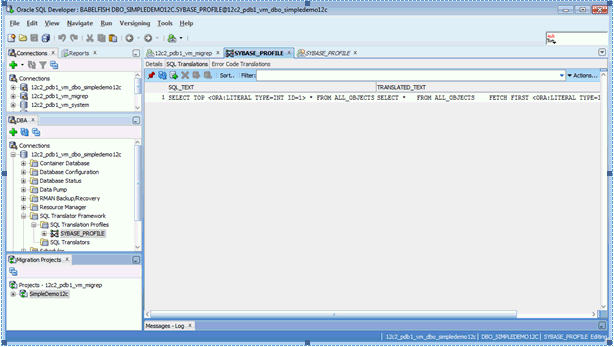
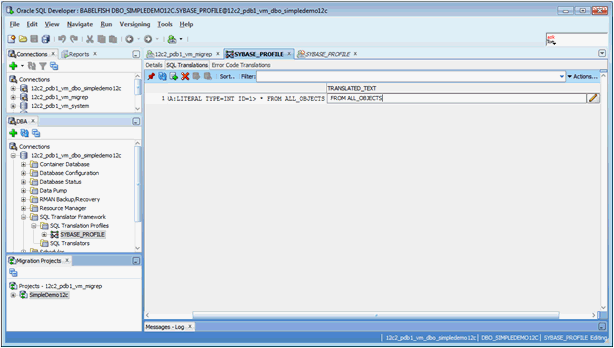
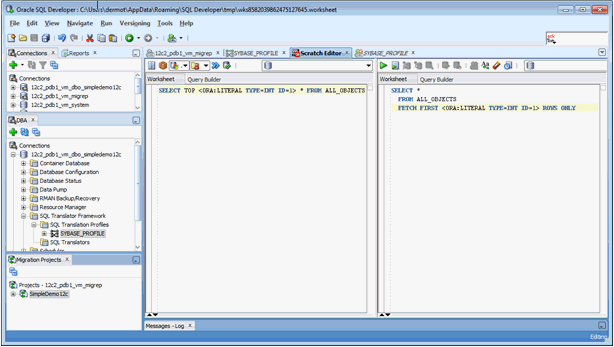
3.1.4 Testing SQL Translation
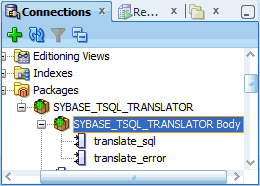
Perform the following steps to determine whether Sybase SQL Translator is properly installed or not:
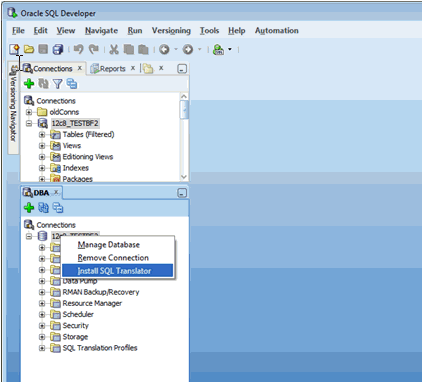
3.1.5 Creating a Translation Profile and Installing SQL Translator
Oracle SQL Developer is installed with Oracle Database 12c. It loads Java classes of the Sybase Translator, approximately 15 MB, into Oracle Database. Due to the size and the number of Java classes loaded, Oracle recommends you to install the translator locally, and not over a WAN.
If the translator is installed under a user profile that has a pre-existing migration repository, the translator picks up the context of the database, such as name changes. Therefore, you must create a new user with the following specifications:
-
CONNECT,RESOURCE, andCREATE VIEWprivileges -
Access to storage in the
SYSTEMand/orUSERtablespace
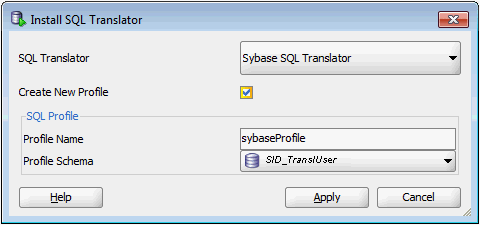
3.1.5.2 Creating a Translation Profile
To create a translation profile:
- From the SQL Translator drop-down box, select Sybase or SQL Translator.
- Check Create New Profile.
- Enter
SYBASE_PROFILEin Profile Name field. - In Profile Schema, select the name of the user created in section "Creating a Translation Profile and Installing SQL Translator".
- Click Apply.
3.2 Installing and Configuring SQL Translation Framework from Command Line
There are several processes that you must complete to successfully install and configure the SQL Translation Framework from command line interface.
3.2.1 Installing Oracle Sybase Translator
To install Oracle Sybase Translator, Use Oracle SQL Developer as described in "Installing and Configuring SQL Translation Framework with Oracle SQL Developer".
3.2.2 Setting up a SQL Translation Profile
Perform the following steps to set up a SQL Translation Profile through a command-line interface:
3.2.3 Setting Up a Database Service to Use the SQL Translation Profile
This section describes how to add a database service in a standard environment and in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment.
Setting Up a Database Service in a Standard Environment
To set up a database service in a standard environment:
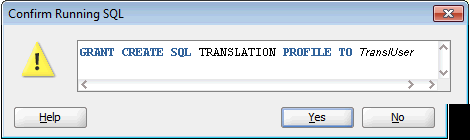
3.3 Granting Necessary Permissions for Installing the SQL Translator
This section discusses the privileges that you must have to install the SQL Translator. The SYBASE_PROFILE created here has the following two users:
-
MIGREP, where the translator is installed -
TARGET_USER, where the profile is installed
To grant privileges necessary for installing the SQL Translator: