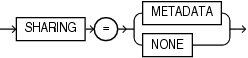14.63 SHARING Clause
The SHARING clause applies only when creating an object in an application root in the context of an application maintenance. This type of object is called an application common object and it can be shared with the application PDBs that belong to the application root.
SHARING clause can appear in the context of creating application common PL/SQL and SQL objects with these SQL statements.
Table 14-2 Summary of Possible Sharing Attributes by Application Common Object Type
| Application Common Object Statement | Possible SHARING Attributes | Syntax and Semantics |
|---|---|---|
| CREATE ANALYTIC VIEW | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE ATTRIBUTE DIMENSION | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE CLUSTER | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE CONTEXT | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE DIRECTORY | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE FUNCTION | METADATA, NONE | CREATE FUNCTION Statement |
| CREATE HIERARCHY | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE INDEXTYPE | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE JAVA | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE LIBRARY | METADATA, NONE | CREATE LIBRARY Statement |
| CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE OPERATOR | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE PROCEDURE | METADATA, NONE | CREATE PROCEDURE Statement |
| CREATE PACKAGE | METADATA, NONE | CREATE PACKAGE Statement |
| CREATE PACKAGE BODY | METADATA, NONE | CREATE PACKAGE BODY Statement |
| CREATE SEQUENCE | METADATA, DATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE SYNONYM | METADATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE TABLE | METADATA, DATA, EXTENDED DATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
| CREATE TRIGGER | METADATA, NONE | CREATE TRIGGER Statement |
| CREATE TYPE | METADATA, NONE | CREATE TYPE Statement |
| CREATE TYPE BODY | METADATA, NONE | CREATE TYPE BODY Statement |
| CREATE VIEW | METADATA, DATA, EXTENDED DATA, NONE | Oracle Database SQL Language Reference |
Topics
Syntax
sharing_clause ::=
Semantics
sharing_clause
Specifies how the object is shared using one of the following sharing attributes:
-
METADATA- A metadata link shares the metadata, but its data is unique to each container. This type of object is referred to as a metadata-linked application common object. -
NONE- The object is not shared and can only be accessed in the application root.
If you omit this clause during an application operation, then the database uses the value of the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter to determine the sharing attribute of the object. If the DEFAULT_SHARING initialization parameter does not have a value, then the default is METADATA.
Restrictions on SHARING clause
The sharing clause may only appear during an application installation, upgrade or patch in an application root. You must issue an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... BEGIN statement to start the operation and an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION ... END statement to end the operation. The sharing_clause is illegal outside this context and this implies the object is not shared.
You cannot change the sharing attribute of an object after it is created.
Generally, common objects cannot depend on local objects. The exceptions to this rule are :
- the common object being created is a synonym
- the common object being created depends on a local operator
If you try to create a common object that depends on local objects other than these two exceptions, it will result in the creation of a local object.
Related Topics
In other books:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for more information about application maintenance
-
Oracle Database Concepts for an example of patching an application using the automated technique
-
Oracle Database Reference for more information on the
DEFAULT_SHARINGinitialization parameter -
Oracle Database Reference for more information on the
ALL_OBJECTSview initializationSHARINGandAPPLICATIONcolumns -
Oracle Database Administrator’s Guide for complete information on creating application common objects