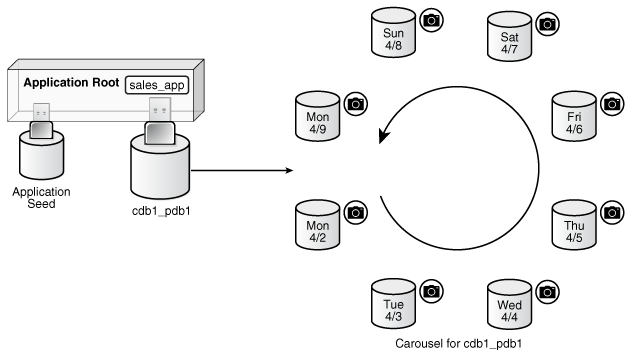
12 Administering a PDB Snapshot Carousel
You can configure a PDB snapshot carousel for a specified PDB, create snapshots manually or automatically, and set the maximum number of snapshots.
About PDB Snapshot Carousel
A PDB snapshot carousel is a library of PDB snapshots.
A PDB snapshot is a point-in-time copy of a PDB. The source PDB can be open read-only or read/write while the snapshot is created. You can create snapshots manually using the SNAPSHOT clause of CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE (or ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE), or automatically using the EVERY interval clause. If the storage system supports sparse clones, then the preceding command creates a sparse copy. Otherwise, the command creates a full copy.
See Also:
Oracle Database Licensing Information User Manual for details on which features are supported for different editions and services
Purpose of PDB Snapshot Carousel
A PDB snapshot carousel is useful for maintaining a library of recent PDB copies for point-in-time recovery and cloning.
Cloning PDBs for Development and Testing
In a typical development use case, you clone a production PDB for testing using a command of the form CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE newpdb FROM srcpdb. When the CDB is in ARCHIVELOG mode and local undo mode, the source production PDB can be opened in read/write mode and fully functional when you clone it, a technique known as hot cloning. The hot clone PDB is transactionally consistent with the source PDB as of the SCN at the completion of the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... OPEN statement.
The following steps illustrate a typical development scenario:
-
While the production PDB named
pdb1_prodis open and in use, create a refreshable clone PDB namedpdb1_test_master.A refreshable clone PDB can only be opened in read/only mode. To refresh the clone PDB from
pdb1_prod, you must close it. -
Run
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb1_test_master SNAPSHOT MODE EVERY 24 HOURS, which configures the PDB to generate automatic snapshots ofpdb1_test_masterevery day. -
When you need new PDBs for testing, create a full clone PDB by using the
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE … USING SNAPSHOTcommand. -
Create sparse snapshot copy PDBs of the full clone PDB using
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... SNAPSHOT COPY.
The following figure shows the creation of the clone pdb1_test_full1 from the PDB snapshot taken on April 5. The figure shows three snapshot copy PDBs created from pdb1_test_full1.
Figure 12-1 Automatic Snapshots of a Refreshable Clone PDB
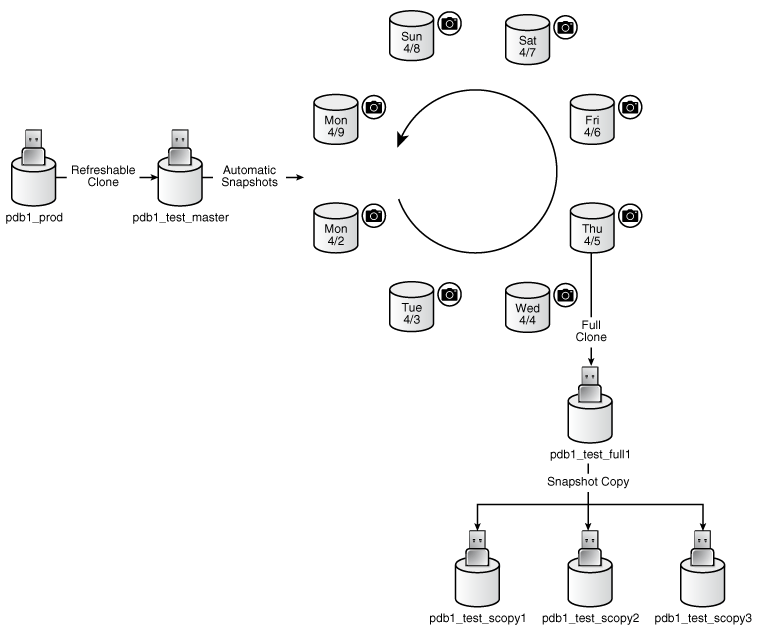
Description of "Figure 12-1 Automatic Snapshots of a Refreshable Clone PDB"
Point-in-Time Restore with PDB Snapshot Carousel
One strategy is to take a snapshot of a PDB every day at the same time. Another strategy is to take a PDB snapshot manually before data loads. In either case, a PDB snapshot carousel enables you to restore a PDB using any available PDB snapshot.
For example, a sales history PDB named pdb1_prod generates an automatic snapshot every day at 12:01 a.m. On the daily data load on the afternoon of Monday 4/9, you accidentally load the wrong data, corrupting the PDB. You can create a new production PDB based on the Monday 4/9 snapshot, drop the corrupted PDB, and then retry the data load.
Figure 12-2 Restore a Production PDB Using a Snapshot
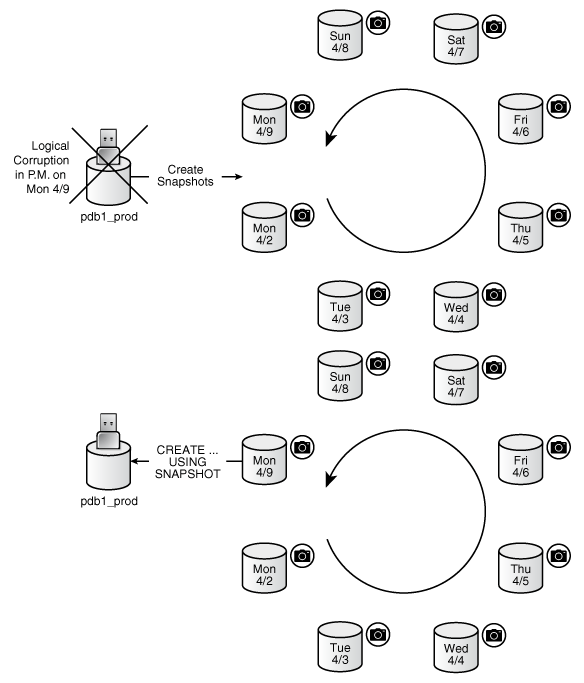
Description of "Figure 12-2 Restore a Production PDB Using a Snapshot"
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEsyntax and semantics -
Oracle Database Licensing Information User Manual for details on which features are supported for different editions and services
How PDB Snapshot Carousel Works
The carousel for a specific PDB is a circular library of copies for this PDB.
The database creates successive copies in the carousel either on demand or automatically. The database overwrites the oldest snapshot when the snapshot limit is reached.
Contents of a PDB Snapshot
The contents of a PDB snapshot depend on whether the underlying file system supports sparse files.
Snapshot Names
The name of a database-managed PDB snapshot is either user-specified or system-generated. For system-generated snapshot names, SNAP_ is prefixed to a unique identifier, which contains the snapshot SCN. For example, the following query shows three snapshots with system-generated names and the SCNs at which they were taken:
SET LINESIZE 200
SET PAGESIZE 50000
COL CON_ID FORMAT 999999
COL CON_NAME FORMAT a15
COL SNAPSHOT_NAME FORMAT a27
SELECT CON_ID, CON_NAME, SNAPSHOT_NAME, SNAPSHOT_SCN FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS;
CON_ID CON_NAME SNAPSHOT_NAME SNAPSHOT_SCN
------- --------------- --------------------------- ------------
5 HRPDB SNAP_1389467754_993556301 2925293
5 HRPDB SNAP_1389467754_993556306 2925679
5 HRPDB SNAP_1389467754_993556309 2925698Note:
See Oracle Database Licensing Information User Manual for details on which features are supported for different editions and services.
Full and Sparse Snapshots
The content of snapshots generated by ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... SNAPSHOT depends on the underlying file system. If the underlying file system supports sparse copies, then the PDB-level snapshots are sparse. Only the first PDB-managed PDB snapshot is full. Otherwise, the PDB snapshots contain full copies of the data files. The snapshot includes other files necessary to create a PDB from the snapshot.
Snapshot Directories
Every PDB has its own snapshot directory. Within this directory, each snapshot has its own subdirectory named after the SCN at which it was taken. The following query shows the sparse PDB snapshots for hrpdb, which has a DBID of 1389467754:
SET LINESIZE 200
SET PAGESIZE 50000
COL SNAPSHOT_NAME FORMAT a27
COL FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH FORMAT a65
SELECT SNAPSHOT_NAME, SNAPSHOT_SCN, FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS;
SNAPSHOT_NAME SNAPSHOT_SCN FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH
--------------------------- ------------ ---------------------------------------
SNAP_1389467754_993556301 2925293 /d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/
SNAP_1389467754_993556306 2925679 /d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/
SNAP_1389467754_993556309 2925698 /d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/Note:
If the snapshot were full instead of sparse, then the full snapshot path would specify an archive with the .pdb suffix.
The directory for /d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/ contains the following files:
archparlog_1_63_52d1986a_993552590.arc
o1_mf_salestbs_g03341t2_.dbf
o1_mf_sysext_g0333vqw_.dbf
o1_mf_undo_1_g033gd2j_.dbf
o1_mf_sysaux_g0333vqv_.dbf
o1_mf_system_g0333vqt_.dbf
HRPDB.xmlThe set includes the data files, archived redo log files, and an XML file that contains metadata about the PDB snapshot. The following du command shows that the size of the snapshot data files, which are sparse, is small relative to the size of the data files:
% du -h *dbf
16K o1_mf_salestbs_g03341t2_.dbf
16K o1_mf_sysaux_g0333vqv_.dbf
16K o1_mf_sysext_g0333vqw_.dbf
16K o1_mf_system_g0333vqt_.dbf
16K o1_mf_undo_1_g033gd2j_.dbf
The following data dictionary join shows the snapshot file names and types for snapshot 2925698:
SELECT f.SNAPSHOT_FILENAME, f.SNAPSHOT_FILETYPE
FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS s, DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE f
WHERE s.SNAPSHOT_SCN=f.SNAPSHOT_SCN
AND s.CON_ID=f.CON_ID
ORDER BY s.SNAPSHOT_SCN DESC;
SNAPSHOT_FILENAME SNAPSHOT
----------------------------------------------------------------- --------
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/o1_mf_sysaux_g0333vqv_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/o1_mf_system_g0333vqt_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/HRPDB.xml XML
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/o1_mf_sysext_g0333vqw_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/o1_mf_salestbs_g03341t2_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/o1_mf_undo_1_g033gd2j_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925698/archparlog_1_63_52d1986a_993552590.arc ARCH
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/o1_mf_sysext_g0333vqw_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/o1_mf_salestbs_g03341t2_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/o1_mf_undo_1_g033gd2j_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/o1_mf_sysaux_g0333vqv_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/archparlog_1_63_52d1986a_993552590.arc ARCH
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/HRPDB.xml XML
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925679/o1_mf_system_g0333vqt_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/HRPDB.xml XML
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/o1_mf_system_g0333vqt_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/o1_mf_sysaux_g0333vqv_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/o1_mf_undo_1_g033gd2j_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/o1_mf_salestbs_g03341t2_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/o1_mf_sysext_g0333vqw_.dbf DATA
/d1/snapshots/pdb_1389467754/2925293/archparlog_1_63_52d1986a_993552590.arc ARCHContents of a PDB Snapshot Carousel
The PDB snapshot carousel is the set of all existing snapshots for a PDB.
The MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS property specifies the maximum number of snapshots permitted in the carousel. The current setting is visible in the CDB_PROPERTIES view.
The following figure shows a carousel for cdb1_pdb1. In this example, the database takes a PDB snapshot automatically every day, maintaining a set of 8. After the first 8 snapshots have been created, every new snapshot replaces the oldest snapshot. For example, the Tuesday 4/10 snapshot replaces the Monday 4/2 snapshot; the Wednesday 4/11 snapshot replaces the Tuesday 4/3 snapshot; and so on.
If the file system supports sparse files, then all PDB snapshots in the carousel except the first one are sparse. The source PDB can remain in read/write mode. Sparse files significantly reduce the carousel storage space.
See Also:
Oracle Database Licensing Information User Manual for details on which features are supported for different editions and services
User Interface for PDB Snapshot Carousel
The SNAPSHOT MODE clause controls creation of snapshots, and determines whether creation is manual, automatic, or disabled.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE … SNAPSHOT Statement
To set the snapshot mode for a PDB, use one of the following values in the SNAPSHOT MODE clause of ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE or CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE:
-
MANUALThis clause, which is the default, enables the creation of manual snapshots of the PDB. To create a snapshot on demand, specify the
SNAPSHOT snapshot_nameclause in anALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEorCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement. -
EVERY snapshot_interval [MINUTES|HOURS]This clause enables the automatic creation of snapshots after an interval of time. The following restrictions apply to the interval specified:
-
The minutes value must be less than
3000. -
The hours value must be less than
2000.
The database assigns each automatic snapshot a system-generated name. Note that manual snapshots are also supported for the PDB when
EVERYis specified. -
-
NONEThis clause disables snapshot creation for the PDB.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for the syntax and semantics of the
SNAPSHOTclause
MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS Database Property
To set the maximum number of snapshots for a PDB, specify the MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS property in ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE or CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE. The default is for the property is 8, which is also the maximum value. When the maximum allowed number of snapshots has been created, the database purges the oldest snapshot. The CDB_PROPERTIES view shows the setting of MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for the syntax of the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement
Snapshot-Related Data Dictionary Views
The following data dictionary views provide snapshot information:
-
The
DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTSview records metadata about PDB snapshots, including snapshot name, creation SCN, creation time, and file name. -
The
DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILEview lists the names and types of the files in a PDB snapshot. This view is only populated when the snapshots are sparse. -
The
DBA_PDBSview has aSNAPSHOT_MODEandSNAPSHOT_INTERVALcolumn.
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference to learn about DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS, DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE, and DBA_PDBS
Setting the Maximum Number of Snapshots in a PDB Snapshot Carousel
You can set the maximum number of PDB snapshots for a PDB.
The MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS database property sets the maximum number of snapshots for every PDB in a PDB snapshot carousel. The default maximum is 8. You cannot set the property to a number greater than 8.
Prerequisites
The PDB must be open in read/write mode.
To set the maximum number of PDB snapshots for a PDB:
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the PDB for which you want to set the limit.
-
Optionally, query
CDB_PROPERTIESfor the current setting of theSET MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTSproperty. -
Run an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEorALTER DATABASEstatement with theSET MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTSclause.
Example 12-1 Setting the Maximum Number of PDB Snapshots for a PDB
The following query shows the maximum in the carousel for cdb1_pdb1 (sample output included):
SET LINESIZE 150
COL ID FORMAT 99
COL PROPERTY_NAME FORMAT a17
COL PDB_NAME FORMAT a9
COL VALUE FORMAT a3
COL DESCRIPTION FORMAT a43
SELECT r.CON_ID AS id, p.PDB_NAME, PROPERTY_NAME,
PROPERTY_VALUE AS value, DESCRIPTION
FROM CDB_PROPERTIES r, CDB_PDBS p
WHERE r.CON_ID = p.CON_ID
AND PROPERTY_NAME LIKE 'MAX_PDB%'
ORDER BY PROPERTY_NAME;
ID PDB_NAME PROPERTY_NAME VAL DESCRIPTION
-- --------- ----------------- --- ------------------------------------
3 CDB1_PDB1 MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS 8 maximum number of snapshots for a PDBThe following SQL statement sets the maximum number of PDB snapshots for the current PDB to 7:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SET MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS=7;Example 12-2 Dropping All Snapshots in a PDB Snapshot Carousel
To drop all snapshots in a PDB snapshot carousel, set the MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS database property to 0 (zero), as shown in the following statement:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SET MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS=0;This technique is faster than executing ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... DROP SNAPSHOT snapshot_name for every snapshot.
See Also:
Configuring Automatic PDB Snapshots
Configure a PDB for automatic snapshots by using the SNAPSHOT MODE EVERY clause when creating or altering a PDB.
Prerequisites
Note the following prerequisites for the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SNAPSHOT statement:
-
The CDB must be in local undo mode.
-
The administrator must have the privileges to create a PDB and drop a PDB.
To configure automatic snapshots when altering a PDB:
-
In SQL*Plus, log in as an administrator to the PDB whose snapshot mode you intend to configure.
-
Optionally, query
DBA_PDBSto determine the current snapshot mode. -
Run
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEwith theSNAPSHOT MODE EVERY intervalclause, specifying eitherMINUTESorHOURS.
To configure automatic snapshots when creating a PDB:
-
In SQL*Plus, log in as an administrator to the CDB root or application root.
-
Optionally, query
DBA_PDBSto determine the current snapshot mode. -
Run
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEwith theSNAPSHOT MODE EVERY intervalclause, specifying eitherMINUTESorHOURS.
Example 12-3 Configuring an Automatic Snapshot Every Day for an Existing PDB
This example assumes that you are logged in to the PDB whose snapshot mode you intend to change. Query the data dictionary to confirm that the PDB is currently in MANUAL mode (sample output included):
SELECT SNAPSHOT_MODE "S_MODE", SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL/60 "SNAP_INT_HRS"
FROM DBA_PDBS;
S_MODE SNAP_INT_HRS
------ ------------
MANUALChange the snapshot mode to every 24 hours:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SNAPSHOT MODE EVERY 24 HOURS;Confirm the change to automatic mode:
SELECT SNAPSHOT_MODE "S_MODE", SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL/60 "SNAP_INT_HRS"
FROM DBA_PDBS;
S_MODE SNAP_INT_HRS
------ ------------
AUTO 24Example 12-4 Creating a PDB That Takes Snapshots Every Two Hours
This example assumes that you are logged in to the CDB root. The following statement creates cdb1_pdb3 from an existing PDB named cdb1_pdb1, and configures it to take snapshots automatically every 2 hours:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE cdb1_pdb3 FROM cdb1_pdb1
FILE_NAME_CONVERT=('cdb1_pdb1','cdb1_pdb3')
SNAPSHOT MODE EVERY 120 MINUTES;Creating PDB Snapshots Manually
To create a PDB snapshot manually, specify the SNAPSHOT snapshot_name clause in ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE or CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE.
Prerequisites
Note the following prerequisites for the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SNAPSHOT statement:
-
The CDB must be in local undo mode. You can check the mode by using the following query, which returns
TRUEwhen local undo is enabled:SELECT * FROM DATABASE_PROPERTIES WHERE PROPERTY_NAME='LOCAL_UNDO_ENABLED'; -
The DBA must have the privileges to create and drop a PDB.
-
If you want the snapshots to be sparse, then the underlying storage system must support sparse files. In this case, only the first snapshot will be full.
To create a PDB snapshot:
-
In SQL*Plus, log in as an administrator to the PDB whose snapshot you intend to create.
-
Optionally, query
DBA_PDBS.SNAPSHOT_MODEto confirm that the snapshot mode is not set toNONE. -
Run an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement with theSNAPSHOTclause.
Example 12-5 Creating a PDB Snapshot with a User-Specified Name
The following SQL statements create two PDB snapshots of cdb1_pdb1, one before and one after a Wednesday data load:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SNAPSHOT cdb1_pdb1_b4WLOAD;
-- data load
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SNAPSHOT cdb1_pdb1_afWLOAD;The following query of DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS shows the locations of two snapshots of the PDB named cdb1_pdb1 (sample output included):
SET LINESIZE 150
COL CON_NAME FORMAT a9
COL ID FORMAT 99
COL SNAPSHOT_NAME FORMAT a17
COL SNAP_SCN FORMAT 9999999
COL FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH FORMAT a61
SELECT CON_ID AS ID, CON_NAME, SNAPSHOT_NAME,
SNAPSHOT_SCN AS snap_scn, FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH
FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS
ORDER BY SNAP_SCN;
ID SNAPSHOT_NAME SNAP_SCN FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH
--- ----------------- -------- -------------------------------------------------------------
4 CDB1_PDB1_B4WLOAD 5056465 /ade/b/813544604/oracle/dbs/snapshots/pdb_2935056285/5056465/
4 CDB1_PDB1_AFWLOAD 5056501 /ade/b/813544604/oracle/dbs/snapshots/pdb_2935056285/5056501/
If you do not specify a PDB snapshot name, then the database generates a unique name.
Example 12-6 Creating a PDB Snapshot with a System-Specified Name
The following SQL statement creates a snapshot, but does not specify a name:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE SNAPSHOT;The following sample query shows that the database assigned the snapshot a name prefixed with SNAP_:
SET LINESIZE 150
COL CON_NAME FORMAT a9
COL ID FORMAT 99
COL SNAPSHOT_NAME FORMAT a26
COL SNAP_SCN FORMAT 9999999
COL FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH FORMAT a61
SELECT CON_ID AS id, CON_NAME, SNAPSHOT_NAME,
SNAPSHOT_SCN AS snap_scn, FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH
FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS
ORDER BY SNAP_SCN;
ID SNAPSHOT_NAME SNAP_SCN FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH
--- -------------------------- -------- -------------------------------------------------------------
4 CDB1_PDB1_B4WLOAD 5056465 /ade/b/813544604/oracle/dbs/snapshots/pdb_2935056285/5056465/
4 CDB1_PDB1_AFWLOAD 5056501 /ade/b/813544604/oracle/dbs/snapshots/pdb_2935056285/5056501/
4 SNAP_2935056285_1031574118 5057389 /ade/b/813544604/oracle/dbs/snapshots/pdb_2935056285/5057389/Dropping a PDB Snapshot
You can drop a PDB snapshot by running an ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement with the DROP SNAPSHOT clause.
To drop all PDB snapshots based on a PDB, set the MAX_PDB_SNAPSHOTS property in the PDB to 0 (zero).
To drop a PDB snapshot:
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the PDB from which you created the PDB snapshot.
-
Run an
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement with theDROP SNAPSHOTclause.
Example 12-7 Dropping a PDB Snapshot
The following SQL statement drops a PDB snapshot named sales_snap:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE DROP SNAPSHOT sales_snap;See Also:
Viewing Metadata for PDB Snapshots
The data dictionary views DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS and DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE show the metadata for PDB snapshots.
DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS contains general information about the snapshot, including name, SCN, time, and path. DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE shows the path and file type of every file in a snapshot: data files, archived redo log files, and XML files.
Note:
DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE only shows sparse clone PDBs. To create sparse clones, the CLONEDB initialization parameter must be set to TRUE.
To view metadata for PDB snapshots:
-
In SQL*Plus, log in to the database as an administrative user.
-
Query
DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS.For example, run the following query (sample output included):
COL SNAPSHOT_NAME FORMAT a30 SELECT SNAPSHOT_NAME, SNAPSHOT_SCN, SNAPSHOT_TIME FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS; SNAPSHOT_NAME SNAPSHOT_SCN SNAPSHOT_TIME ------------------------------ ------------ ------------- HRPDB_SNAP_F 3678939 1536262569 HRPDB_SNAP_S 4954803 986473745 -
Query
DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE.For example, run the following join query (sample output included):
SET LINESIZE 120 COL SNAPSHOT_NAME FORMAT a12 COL SNAPSHOT_FILENAME FORMAT a54 SELECT SNAPSHOT_NAME, SNAPSHOT_FILENAME, SNAPSHOT_FILETYPE AS TYPE FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS s, DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE f WHERE s.SNAPSHOT_SCN=f.SNAPSHOT_SCN; SNAPSHOT_NAM SNAPSHOT_FILENAME TYPE ------------ ------------------------------------------------------ ---- HRPDB_SNAP_S /d1/snapshots/4954803/o1_mf_undo_1_fry1l5bq_.dbf DATA HRPDB_SNAP_S /d1/snapshots/4954803/o1_mf_salestbs_fry19m6h_.dbf DATA HRPDB_SNAP_S /d1/snapshots/4954803/o1_mf_sysext_fry19d1n_.dbf DATA HRPDB_SNAP_S /d1/snapshots/4954803/o1_mf_sysaux_fry19d1m_.dbf DATA HRPDB_SNAP_S /d1/snapshots/4954803/o1_mf_system_fry19d1k_.dbf DATA HRPDB_SNAP_S /d1/snapshots/4954803/HRPDB.xml XML HRPDB_SNAP_S /d1/snapshots/4954803/archparlog_1_274_b87ca51e_985963 814.arc ARCH
Example 12-8 Querying Metadata for Full PDB Snapshots
The following query shows two PDB snapshots. The snapshots are full, not sparse, as indicated by the .pdb extension.
SET LINESIZE 200
SET PAGESIZE 50000
COL ID FORMAT 99
COL CON_NAME FORMAT a7
COL SNAPSHOT_NAME FORMAT a25
COL SNAPSHOT_SCN FORMAT a7
COL FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH FORMAT a65
SELECT CON_ID AS ID, CON_NAME, SNAPSHOT_NAME,
SNAPSHOT_SCN, FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH
FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTS;
ID CON_NAM SNAPSHOT_NAME SNAPSHO FULL_SNAPSHOT_PATH
-- ------- ------------------------- ------- -------------------------------
5 HRPDB SNAP_3286480866_994766895 3160319 /d1/snap_3286480866_3160319.pdb
5 HRPDB SNAP_3286480866_994767095 3165758 /d1/snap_3286480866_3165758.pdbThe following query of DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE returns no rows because this view is only populated when PDB snapshots are sparse:
SQL> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM DBA_PDB_SNAPSHOTFILE;
COUNT(*)
----------
0