3.21 SWITCH
Purpose
Use the SWITCH command to perform either of the following operations:
-
Update the file names for a database, tablespace, or data file to the latest image copies available for the specified files
-
Update the file names for data files and temp files for which you have issued a
SETNEWNAMEcommand
A SWITCH updates the names of the files in the RMAN repository, but
the database does not rename the files at the operating system level.
Prerequisites
RMAN must be connected to a target database. When switching tablespaces, data files, or temp files, the files must be offline. When switching the whole database, the database must not be open.
Usage Notes
The SWITCH command deletes the RMAN repository records for the data file copy from the recovery catalog and updates the control file records to status DELETED.
If RMAN is connected to a recovery catalog, and if the database is using a control file restored from backup, then SWITCH updates the control file with records of any data files known to the recovery catalog but missing from the control file.
Execute SWITCH ... TO COPY only at the RMAN prompt. Use SWITCH without TO COPY only within a RUN block.
Syntax
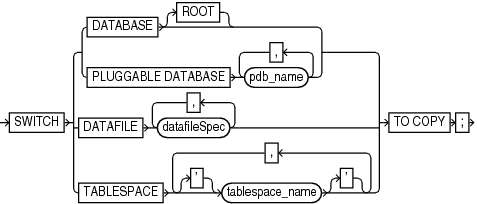
Semantics
switch
This subclause switches file names for a database, tablespace, or data file to the latest image copies available for the specified files. By executing this command, you avoid restoring data files from backups. Execute SWITCH ... TO COPY only at the RMAN prompt.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Renames the data files and control files to use the file names of image copies of these files. RMAN switches to the latest image copy of each database file. In a multitenant container database (CDB), switches file names for the root and all pluggable databases (PDBs) in the CDB. In a PDB, switches file names for the connected PDB. After a database switch, RMAN considers the previous database files as data file copies. |
|
|
Switches file names for the CDB root. Connect to the root as a common user with the
|
|
|
Renames the data files and control files in one or more PDBs to use the file names
of image copies of these files. Use a comma-delimited list to specify multiple
PDBs. Connect to the root as a common user or local user with the
|
|
|
Switches the specified data files to the latest image copies. After the switch, the control file no longer considers the specified data file as current. |
|
|
Switches all data files within the specified tablespace, as with To switch data files for a tablespace in a PDB, connect to the PDB. |
|
|
Switches the specified active database files to image copies. |
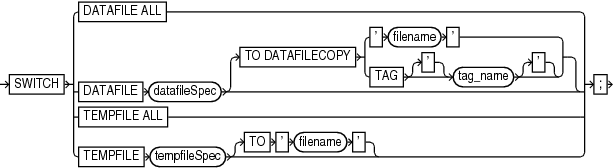
switchFile
This subclause updates the names for data files and temp files for which you have issued a SET NEWNAME command. Use this clause only within a RUN block.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Switches all data files for which a |
|
|
Specifies the data file for renaming. After the switch, the control file no longer considers the specified file as current. If you do not specify a |
TO DATAFILECOPY {'filename' |TAG tag_name} |
Specifies the input copy file for the switch, that is, the data file copy that you intend to rename (see Example 3-78). |
|
|
Switches all temp files for which a |
|
|
Specifies the temp file that you are renaming. If you do not specify a |
|
|
Renames the temp file to the specified name (see Example 3-77). The target database must be mounted but not open. |
Examples
Example 3-75 Switching to Image Copies to Avoid Restoring from Backup
Assume that a disk fails, rendering all data files in the users tablespace inaccessible. Image copies of all data files in this tablespace exist in the fast recovery area. After starting RMAN and connecting to the database as TARGET, you can run SWITCH to point the control file to the new data files and then run RECOVER as follows:
ALTER TABLESPACE users OFFLINE IMMEDIATE; SWITCH TABLESPACE users TO COPY; RECOVER TABLESPACE users; ALTER TABLESPACE users ONLINE;
Example 3-76 Switching Data File Names After a Restore to a New Location
Assume that a disk fails, forcing you to restore a data file to a new disk location. After starting RMAN and connecting to the database as TARGET, you can use the SET NEWNAME command to rename the data file, then RESTORE to restore the missing data file. You run SWITCH to point the control file to the new data file and then RECOVER. This example allocates both disk and tape channels.
RUN
{
ALLOCATE CHANNEL dev1 DEVICE TYPE DISK;
ALLOCATE CHANNEL dev2 DEVICE TYPE sbt;
ALTER TABLESPACE users OFFLINE IMMEDIATE;
SET NEWNAME FOR DATAFILE '/disk1/oradata/prod/users01.dbf'
TO '/disk2/users01.dbf';
RESTORE TABLESPACE users;
SWITCH DATAFILE ALL;
RECOVER TABLESPACE users;
ALTER TABLESPACE users ONLINE;
}Example 3-77 Renaming Tempfiles Using SET NEWNAME and SWITCH TEMPFILE ALL
This example demonstrates using SET NEWNAME to specify new names for several temp files, and SWITCH TEMPFILE ALL to rename the temp files to the specified names. The database must be closed at the beginning of this procedure. The temp files are re-created at the new locations when the database is opened.
CONNECT TARGET /
STARTUP FORCE MOUNT
RUN
{
SET NEWNAME FOR TEMPFILE 1 TO '/disk2/temp01.dbf';
SET NEWNAME FOR TEMPFILE 2 TO '/disk2/temp02.dbf';
SET NEWNAME FOR TEMPFILE 3 TO '/disk2/temp03.dbf';
SWITCH TEMPFILE ALL;
RESTORE DATABASE;
RECOVER DATABASE;
ALTER DATABASE OPEN;
}Example 3-78 Switching to a Data File Copy
The following command switches the data file in the TOOLS tablespace to the data file copy named /disk2/tools.copy:
RUN
{
ALTER TABLESPACE tools OFFLINE IMMEDIATE;
SWITCH DATAFILE '/disk1/oradata/prod/tools01.dbf'
TO DATAFILECOPY '/disk2/tools.copy';
RECOVER TABLESPACE tools;
ALTER TABLESPACE tools ONLINE;
}