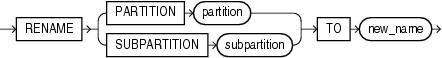ALTER INDEX
Purpose
Use the ALTER INDEX statement to change or rebuild an existing index.
See Also:
CREATE INDEX for information on creating an index
Prerequisites
The index must be in your own schema or you must have the ALTER ANY INDEX system privilege.
To execute the MONITORING USAGE clause, the index must be in your own schema.
To modify a domain index, you must have EXECUTE object privilege on the indextype of the index.
Object privileges are granted on the parent index, not on individual index partitions or subpartitions.
You must have tablespace quota to modify, rebuild, or split an index partition or to modify or rebuild an index subpartition.
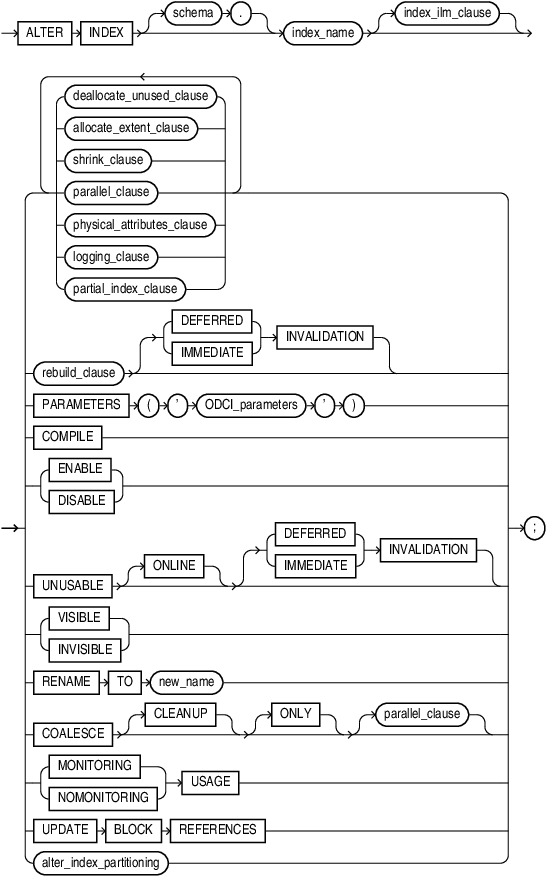
Syntax
alter_index::=
(deallocate_unused_clause::=, allocate_extent_clause::=, shrink_clause::=, parallel_clause::=, physical_attributes_clause::=, logging_clause::=, partial_index_clause::=, rebuild_clause::=, alter_index_partitioning::=)
(The ODCI_parameters are documented in Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide.)
allocate_extent_clause::=
shrink_clause::=
parallel_clause::=
physical_attributes_clause::=
logging_clause::=
partial_index_clause::=
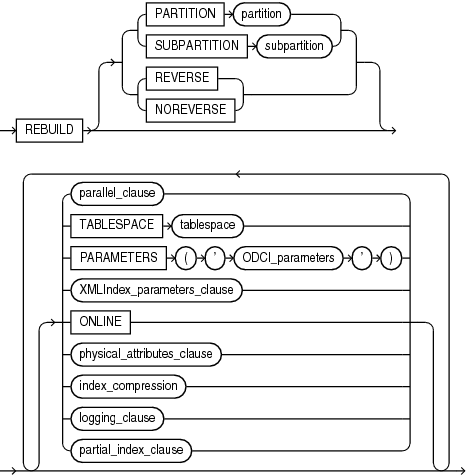
rebuild_clause::=
(parallel_clause::=, physical_attributes_clause::=, index_compression::=, logging_clause::=, partial_index_clause::=)
(The ODCI_parameters are documented in Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide. The XMLIndex_parameters_clause is documented in Oracle XML DB Developer's Guide.
prefix_compression::=
advanced_index_compression::=
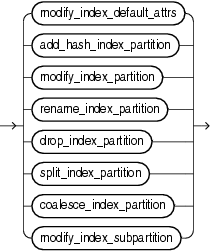
alter_index_partitioning::=
(modify_index_default_attrs::=, add_hash_index_partition::=, modify_index_partition::=, rename_index_partition::=, drop_index_partition::=, split_index_partition::=, coalesce_index_partition::=, modify_index_subpartition::=)
add_hash_index_partition::=
coalesce_index_partition::=
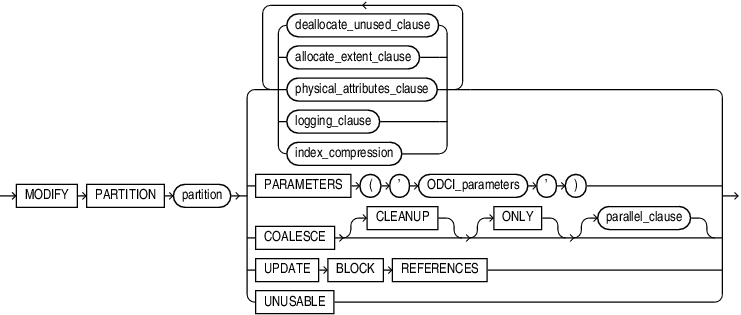
modify_index_partition::=
(deallocate_unused_clause::=, allocate_extent_clause::=, physical_attributes_clause::=, logging_clause::=, index_compression::=)
rename_index_partition::=
drop_index_partition::=
split_index_partition::=
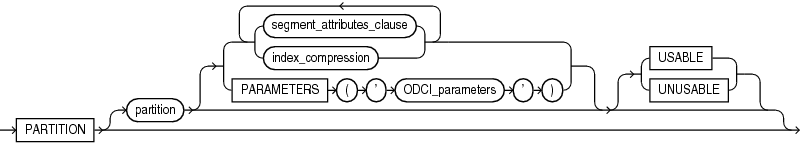
index_partition_description::=
(segment_attributes_clause::=, index_compression::=)
Note:
The USABLE and UNUSABLE keywords are not supported when index_partition_description is specified for the split_index_partition clause.
segment_attributes_clause::=
(physical_attributes_clause::=, TABLESPACE SET: not supported with ALTER INDEX, logging_clause::=)
modify_index_subpartition::=
Semantics
schema
Specify the schema containing the index. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the index is in your own schema.
index_name
Specify the name of the index to be altered.
Restrictions on Modifying Indexes
The modification of indexes is subject to the following restrictions:
-
If
indexis a domain index, then you can specify only thePARAMETERSclause, theRENAMEclause, therebuild_clause(with or without thePARAMETERSclause), theparallel_clause, or theUNUSABLEclause. No other clauses are valid. -
You cannot alter or rename a domain index that is marked
LOADINGorFAILED. If an index is markedFAILED, then the only clause you can specify isREBUILD.
See Also:
Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide for information on the LOADING and FAILED states of domain indexes
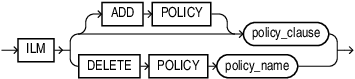
index_ilm_clause
Please refer to index_ilm_clause in CREATE INDEX for full semantics.
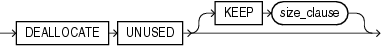
deallocate_unused_clause
Use the deallocate_unused_clause to explicitly deallocate unused space at the end of the index and make the freed space available for other segments in the tablespace.
If index is range-partitioned or hash-partitioned, then Oracle Database deallocates unused space from each index partition. If index is a local index on a composite-partitioned table, then Oracle Database deallocates unused space from each index subpartition.
Restrictions on Deallocating Space
Deallocation of space is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify this clause for an index on a temporary table.
-
You cannot specify this clause and also specify the
rebuild_clause.
Refer to deallocate_unused_clause for a full description of this clause.
KEEP integer
The KEEP clause lets you specify the number of bytes above the high water mark that the index will have after deallocation. If the number of remaining extents is less than MINEXTENTS, then MINEXTENTS is set to the current number of extents. If the initial extent becomes smaller than INITIAL, then INITIAL is set to the value of the current initial extent. If you omit KEEP, then all unused space is freed.
Refer to ALTER TABLE for a complete description of this clause.
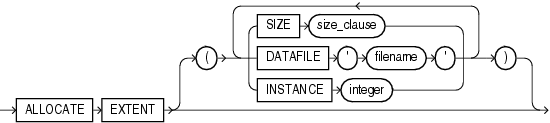
allocate_extent_clause
The allocate_extent_clause lets you explicitly allocate a new extent for the index. For a local index on a hash-partitioned table, Oracle Database allocates a new extent for each partition of the index.
Restriction on Allocating Extents
You cannot specify this clause for an index on a temporary table or for a range-partitioned or composite-partitioned index.
Refer to allocate_extent_clause for a full description of this clause.
shrink_clause
Use this clause to compact the index segments. Specifying ALTER INDEX ... SHRINK SPACE COMPACT is equivalent to specifying ALTER INDEX ... COALESCE.
For complete information on this clause, refer to shrink_clause in the documentation on CREATE TABLE.
Restriction on Shrinking Index Segments
You cannot specify this clause for a bitmap join index or for a function-based index.
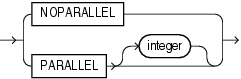
parallel_clause
Use the PARALLEL clause to change the default degree of parallelism for queries and DML on the index.
Restriction on Parallelizing Indexes
You cannot specify this clause for an index on a temporary table.
For complete information on this clause, refer to parallel_clause in the documentation on CREATE TABLE.
See Also:
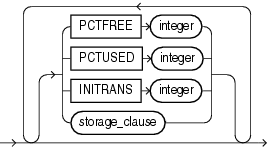
physical_attributes_clause
Use the physical_attributes_clause to change the values of parameters for a nonpartitioned index, all partitions and subpartitions of a partitioned index, a specified partition, or all subpartitions of a specified partition.
See Also:
-
the physical attributes parameters in CREATE TABLE
-
"Modifying Real Index Attributes: Example" and "Changing MAXEXTENTS: Example"
Restrictions on Index Physical Attributes
Index physical attributes are subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify this clause for an index on a temporary table.
-
You cannot specify the
PCTUSEDparameter at all when altering an index. -
You can specify the
PCTFREEparameter only as part of therebuild_clause, themodify_index_default_attrsclause, or thesplit_index_partitionclause.
storage_clause
Use the storage_clause to change the storage parameters for a nonpartitioned index, index partition, or all partitions of a partitioned index, or default values of these parameters for a partitioned index. Refer to storage_clause for complete information on this clause.
logging_clause
Use the logging_clause to change the logging attribute of the index. If you also specify the REBUILD clause, then this new setting affects the rebuild operation. If you specify a different value for logging in the REBUILD clause, then Oracle Database uses the last logging value specified as the logging attribute of the index and of the rebuild operation.
An index segment can have logging attributes different from those of the base table and different from those of other index segments for the same base table.
Restriction on Index Logging
You cannot specify this clause for an index on a temporary table.
See Also:
-
logging_clause for a full description of this clause
-
Oracle Database VLDB and Partitioning Guide for more information about parallel DML
partial_index_clause
Use the partial_index_clause to change the index to a full index or a partial index. Specify INDEXING FULL to change the index to a full index. Specify INDEXING PARTIAL to change the index to a partial index. This clause is valid only for indexes on partitioned tables. Refer to the partial_index_clause of CREATE INDEX for the full semantics of this clause.
RECOVERABLE | UNRECOVERABLE
These keywords are deprecated and have been replaced with LOGGING and NOLOGGING, respectively. Although RECOVERABLE and UNRECOVERABLE are supported for backward compatibility, Oracle strongly recommends that you use the LOGGING and NOLOGGING keywords.
RECOVERABLE is not a valid keyword for creating partitioned tables or LOB storage characteristics. UNRECOVERABLE is not a valid keyword for creating partitioned or index-organized tables. Also, it can be specified only with the AS subquery clause of CREATE INDEX.
rebuild_clause
Use the rebuild_clause to re-create an existing index or one of its partitions or subpartitions. If index is marked UNUSABLE, then a successful rebuild will mark it USABLE. For a function-based index, this clause also enables the index. If the function on which the index is based does not exist, then the rebuild statement will fail.
Note:
When you rebuild the secondary index of an index-organized table, Oracle Database preserves the primary key columns contained in the logical rowid when the index was created. Therefore, if the index was created with the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter set to less than 10.0.0, the rebuilt index will contain the index key and any of the primary key columns of the table that are not also in the index key. If the index was created with the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter set to 10.0.0 or greater, then the rebuilt index will contain the index key and all the primary key columns of the table, including those also in the index key.
Restrictions on Rebuilding Indexes
The rebuilding of indexes is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot rebuild an index on a temporary table.
-
You cannot rebuild a bitmap index that is marked
INVALID. Instead, you must drop and then re-create it. -
You cannot rebuild an entire partitioned index. You must rebuild each partition or subpartition, as described for the
PARTITIONclause. -
You cannot specify the
deallocate_unused_clausein the same statement as therebuild_clause. -
You cannot change the value of the
PCTFREEparameter for the index as a whole (ALTERINDEX) or for a partition (ALTERINDEX...MODIFYPARTITION). You can specifyPCTFREEin all other forms of theALTERINDEXstatement. -
For a domain index:
-
You can specify only the
PARAMETERSclause (either for the index or for a partition of the index) or theparallel_clause. No other rebuild clauses are valid. -
You can rebuild an index only if the index is not marked
IN_PROGRESS. -
You can rebuild an index partition only if the index is not marked
IN_PROGRESSorFAILEDand the partition is not markedIN_PROGRESS.
-
-
You cannot rebuild a local index, but you can rebuild a partition of a local index (
ALTERINDEX...REBUILDPARTITION). -
For a local index on a hash partition or subpartition, the only parameter you can specify is
TABLESPACE. -
You cannot rebuild an online index that is used to enforce a deferrable unique constraint.
PARTITION Clause
Use the PARTITION clause to rebuild one partition of an index. You can also use this clause to move an index partition to another tablespace or to change a create-time physical attribute.
The storage of partitioned database entities in tablespaces of different block sizes is subject to several restrictions. Refer to Oracle Database VLDB and Partitioning Guide for a discussion of these restrictions.
Restriction on Rebuilding Partitions
You cannot specify this clause for a local index on a composite-partitioned table. Instead, use the REBUILD SUBPARTITION clause.
See Also:
Oracle Database VLDB and Partitioning Guide for more information about partition maintenance operations and "Rebuilding Unusable Index Partitions: Example"
SUBPARTITION Clause
Use the SUBPARTITION clause to rebuild one subpartition of an index. You can also use this clause to move an index subpartition to another tablespace. If you do not specify TABLESPACE, then the subpartition is rebuilt in the same tablespace.
The storage of partitioned database entities in tablespaces of different block sizes is subject to several restrictions. Refer to Oracle Database VLDB and Partitioning Guide for a discussion of these restrictions.
Restriction on Modifying Index Subpartitions
The only parameters you can specify for a subpartition are TABLESPACE, ONLINE, and the parallel_clause.
REVERSE | NOREVERSE
Indicate whether the bytes of the index block are stored in reverse order:
-
REVERSEstores the bytes of the index block in reverse order and excludes the rowid when the index is rebuilt. -
NOREVERSEstores the bytes of the index block without reversing the order when the index is rebuilt. Rebuilding aREVERSEindex without theNOREVERSEkeyword produces a rebuilt, reverse-keyed index.
Restrictions on Reverse Indexes
Reverse indexes are subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot reverse a bitmap index or an index-organized table.
-
You cannot specify
REVERSEorNOREVERSEfor a partition or subpartition.
See Also:
parallel_clause
Use the parallel_clause to parallelize the rebuilding of the index and to change the degree of parallelism for the index itself. All subsequent operations on the index will be executed with the degree of parallelism specified by this clause, unless overridden by a subsequent data definition language (DDL) statement with the parallel_clause. The following exceptions apply:
-
If
ALTERSESSIONDISABLEPARALLELDDLwas specified before rebuilding the index, then the index will be rebuilt serially and the degree of parallelism for the index will be changed to 1. -
If
ALTERSESSIONFORCEPARALLELDDLwas specified before rebuilding the index, then the index will be rebuilt in parallel and the degree of parallelism for the index will be changed to the value that was specified in theALTERSESSIONstatement, orDEFAULTif no value was specified.
See Also:
TABLESPACE Clause
Specify the tablespace where the rebuilt index, index partition, or index subpartition will be stored. The default is the default tablespace where the index or partition resided before you rebuilt it.
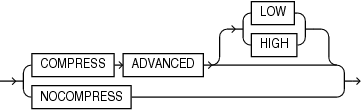
index_compression
Use the index_compression clauses to enable or disable index compression for the index. Specify the prefix_compression clause to enable or disable prefix compression for the index. Specify the advanced_index_compression clause to enable or disable advanced index compression for the index.
The index_compression clauses have the same semantics for CREATE INDEX and ALTER INDEX. For full information on these clauses, refer to index_compression in the documentation on CREATE INDEX.
ONLINE Clause
Specify ONLINE to allow DML operations on the table or partition during rebuilding of the index.
Restrictions on Online Indexes
Online indexes are subject to the following restrictions:
-
Parallel DML is not supported during online index building. If you specify
ONLINEand subsequently issue parallel DML statements, then Oracle Database returns an error. -
You cannot specify
ONLINEfor a bitmap join index or a cluster index. -
For a nonunique secondary index on an index-organized table, the number of index key columns plus the number of primary key columns that are included in the logical rowid in the index-organized table cannot exceed 32. The logical rowid excludes columns that are part of the index key.
logging_clause
Specify whether the ALTER INDEX ... REBUILD operation will be logged.
Refer to the logging_clause for a full description of this clause.
PARAMETERS Clause
This clause is valid only for domain indexes in a top-level ALTER INDEX statement and in the rebuild_clause. This clause specifies the parameter string that is passed uninterpreted to the appropriate ODCI indextype routine.
The maximum length of the parameter string is 1000 characters.
If you are altering or rebuilding an entire index, then the string must refer to index-level parameters. If you are rebuilding a partition of the index, then the string must refer to partition-level parameters.
If index is marked UNUSABLE, then modifying the parameters alone does not make it USABLE. You must also rebuild the UNUSABLE index to make it usable.
If you have installed Oracle Text, then you can rebuild your Oracle Text domain indexes using parameters specific to that product. For more information on those parameters, refer to Oracle Text Reference.
Restriction on the PARAMETERS Clause
You can modify index partitions only if index is not marked IN_PROGRESS or FAILED, no index partitions are marked IN_PROGRESS, and the partition being modified is not marked FAILED.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide for more information on indextype routines for domain indexes
-
CREATE INDEX for more information on domain indexes
XMLIndex_parameters_clause
This clause is valid only for XMLIndex indexes. This clause specifies the parameter string that defines the XMLIndex implementation.
The maximum length of the parameter string is 1000 characters.
If you are altering or rebuilding an entire index, then the string must refer to index-level parameters. If you are rebuilding a partition of the index, then the string must refer to partition-level parameters.
If index is marked UNUSABLE, then modifying the parameters alone does not make it USABLE. You must also rebuild the UNUSABLE index to make it usable.
See Also:
Oracle XML DB Developer's Guide for more information on XMLIndex, including the syntax and semantics of the XMLIndex_parameters_clause
Restriction on the XMLIndex_parameters_clause
You can modify index partitions only if index is not marked IN_PROGRESS or FAILED, no index partitions are marked IN_PROGRESS, and the partition being modified is not marked FAILED.
{ DEFERRED | IMMEDIATE } INVALIDATION
This clause lets you control when the database invalidates dependent cursors while rebuilding an index or while marking an index UNUSABLE.
-
If you specify
DEFERREDINVALIDATION, then the database avoids or defers invalidating dependent cursors, when possible. -
If you specify
IMMEDIATEINVALIDATION, then the database immediately invalidates dependent cursors, as it did in Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1) and prior releases. This is the default.
If you omit this clause, then the value of the CURSOR_INVALIDATION initialization parameter determines when cursors are invalidated.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide for more information on cursor invalidation
-
Oracle Database Reference for more information in the
CURSOR_INVALIDATIONinitialization parameter
COMPILE Clause
Use this clause to recompile an invalid index explicitly. For domain indexes, this clause is useful when the underlying indextype has been altered to support system-managed domain indexes, so that the existing domain index has been marked INVALID. In this situation, this ALTER INDEX statement migrates the domain index from a user-managed domain index to a system-managed domain index. For all types of indexes, this clause is useful when an index has been marked INVALID by an ALTER TABLE statement. In this situation, this ALTER INDEX statement revalidates the index without rebuilding it.
See Also:
The CREATE INDEXTYPE storage_table_clause and Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide for information on creating system-managed domain indexes
ENABLE Clause
ENABLE applies only to a function-based index that has been disabled, either by an ALTER INDEX ... DISABLE statement, or because a user-defined function used by the index was dropped or replaced. This clause enables such an index if these conditions are true:
-
The function is currently valid.
-
The signature of the current function matches the signature of the function when the index was created.
-
The function is currently marked as
DETERMINISTIC.
Restrictions on Enabling Function-based Indexes
The ENABLE clause is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify any other clauses of
ALTERINDEXin the same statement withENABLE. -
You cannot specify this clause for an index on a temporary table. Instead, you must drop and recreate the index. You can retrieve the creation DDL for the index using the
DBMS_METADATApackage.
DISABLE Clause
DISABLE applies only to a function-based index. This clause lets you disable the use of a function-based index. You might want to do so, for example, while working on the body of the function. Afterward you can either rebuild the index or specify another ALTER INDEX statement with the ENABLE keyword.
USABLE | UNUSABLE
Specify UNUSABLE to mark the index or index partition(s) or index subpartition(s) UNUSABLE. The space allocated for an index or index partition or subpartition is freed immediately when the object is marked UNUSABLE. An unusable index must be rebuilt, or dropped and re-created, before it can be used. While one partition is marked UNUSABLE, the other partitions of the index are still valid. You can execute statements that require the index if the statements do not access the unusable partition. You can also split or rename the unusable partition before rebuilding it. Refer to CREATE INDEX ... USABLE | UNUSABLE for more information.
ONLINE
Specify ONLINE to indicate that DML operations on the table or partition will be allowed while marking the index UNUSABLE. If you specify this clause, then the database will not drop the index segments.
Restrictions on Marking Indexes Unusable
The following restrictions apply to marking indexes unusable:
-
You cannot specify
UNUSABLEfor an index on a temporary table. -
When a global index is marked
UNUSABLEduring a partition maintenance operation, the database does not drop the unusable index segments.
VISIBLE | INVISIBLE
Use this clause to specify whether the index is visible or invisible to the optimizer. Refer to "VISIBLE | INVISIBLE" in CREATE INDEX for a full description of this clause.
RENAME Clause
Use this clause to rename an index. The new_index_name is a single identifier and does not include the schema name.
Restriction on Renaming Indexes
For a domain index, neither index nor any partitions of index can be marked IN_PROGRESS or FAILED.
See Also:
COALESCE Clause
Specify COALESCE to instruct Oracle Database to merge the contents of index blocks where possible to free blocks for reuse.
CLEANUP
Specify CLEANUP to remove orphaned index entries for records that were previously dropped or truncated by a table partition maintenance operation.
To determine whether an index contains orphaned index entries, you can query the ORPHANED_ENTRIES column of the USER_, DBA_, ALL_INDEXES data dictionary views. Refer to Oracle Database Reference for more information.
ONLY
Specify ONLY when you want to clean up the index without coalescing the index blocks.
parallel_clause
Use the parallel_clause to specify whether to parallelize the coalesce operation.
For complete information on this clause, refer to parallel_clause in the documentation on CREATE TABLE.
Restrictions on Coalescing Index Blocks
Coalescing of index blocks is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify this clause for an index on a temporary table.
-
Do not specify this clause for the primary key index of an index-organized table. Instead use the
COALESCEclause ofALTERTABLE.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information on space management and coalescing indexes
-
COALESCE Clause for information on coalescing the space of an index-organized table
-
shrink_clause for an alternative method of compacting index segments
MONITORING USAGE | NOMONITORING USAGE
Use this clause to determine whether Oracle Database should monitor index use.
-
Specify
MONITORINGUSAGEto begin monitoring the index. Oracle Database first clears existing information on index use, and then monitors the index for use until a subsequentALTERINDEX...NOMONITORINGUSAGEstatement is executed. -
To terminate monitoring of the index, specify
NOMONITORINGUSAGE.
To see whether the index has been used since this ALTER INDEX ... NOMONITORING USAGE statement was issued, query the USED column of the USER_OBJECT_USAGE data dictionary view.
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for information on the USER_OBJECT_USAGE data dictionary view
UPDATE BLOCK REFERENCES Clause
The UPDATE BLOCK REFERENCES clause is valid only for normal and domain indexes on index-organized tables. Specify this clause to update all the stale guess data block addresses stored as part of the index row with the correct database address for the corresponding block identified by the primary key.
For a domain index, Oracle Database executes the ODCIIndexAlter routine with the alter_option parameter set to AlterIndexUpdBlockRefs. This routine enables the cartridge code to update the stale guess data block addresses in the index.
Restriction on UPDATE BLOCK REFERENCES
You cannot combine this clause with any other clause of ALTER INDEX.
alter_index_partitioning
The partitioning clauses of the ALTER INDEX statement are valid only for partitioned indexes.
The storage of partitioned database entities in tablespaces of different block sizes is subject to several restrictions. Refer to Oracle Database VLDB and Partitioning Guide for a discussion of these restrictions.
Restrictions on Modifying Index Partitions
Modifying index partitions is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify any of these clauses for an index on a temporary table.
-
You can combine several operations on the base index into one
ALTERINDEXstatement (exceptRENAMEandREBUILD), but you cannot combine partition operations with other partition operations or with operations on the base index.
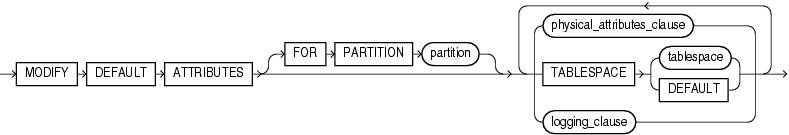
modify_index_default_attrs
Specify new values for the default attributes of a partitioned index.
Restriction on Modifying Partition Default Attributes
The only attribute you can specify for a hash-partitioned global index or for an index on a hash-partitioned table is TABLESPACE.
TABLESPACE
Specify the default tablespace for new partitions of an index or subpartitions of an index partition.
logging_clause
Specify the default logging attribute of a partitioned index or an index partition.
Refer to logging_clause for a full description of this clause.
FOR PARTITION
Use the FOR PARTITION clause to specify the default attributes for the subpartitions of a partition of a local index on a composite-partitioned table.
Restriction on FOR PARTITION
You cannot specify FOR PARTITION for a list partition.
See Also:
add_hash_index_partition
Use this clause to add a partition to a global hash-partitioned index. Oracle Database adds hash partitions and populates them with index entries rehashed from an existing hash partition of the index, as determined by the hash function. If you omit the partition name, then Oracle Database assigns a name of the form SYS_Pn. If you omit the TABLESPACE clause, then Oracle Database places the partition in the tablespace specified for the index. If no tablespace is specified for the index, then Oracle Database places the partition in the default tablespace of the user, if one has been specified, or in the system default tablespace.
modify_index_partition
Use the modify_index_partition clause to modify the real physical attributes, logging attribute, or storage characteristics of index partition partition or its subpartitions. For a hash-partitioned global index, the only subclause of this clause you can specify is UNUSABLE.
Specify this clause to merge the contents of index partition blocks where possible to free blocks for reuse.
CLEANUP
Specify CLEANUP to remove orphaned index entries for records that were previously dropped or truncated by a table partition maintenance operation.
To determine whether an index partition contains orphaned index entries, you can query the ORPHANED_ENTRIES column of the USER_, DBA_, ALL_PART_INDEXES data dictionary views. Refer to Oracle Database Reference for more information.
The UPDATE BLOCK REFERENCES clause is valid only for normal indexes on index-organized tables. Use this clause to update all stale guess data block addresses stored in the secondary index partition.
Restrictions on UPDATE BLOCK REFERENCES
This clause is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify the
physical_attributes_clausefor an index on a hash-partitioned table. -
You cannot specify
UPDATEBLOCKREFERENCESwith any other clause inALTERINDEX.
Note:
If the index is a local index on a composite-partitioned table, then the changes you specify here will override any attributes specified earlier for the subpartitions of index, as well as establish default values of attributes for future subpartitions of that partition. To change the default attributes of the partition without overriding the attributes of subpartitions, use ALTER TABLE ... MODIFY DEFAULT ATTRIBUTES FOR PARTITION.
See Also:
UNUSABLE Clause
This clause has the same function for index partitions that it has for the index as a whole. Refer to "USABLE | UNUSABLE".
index_compression
This clause is relevant for composite-partitioned indexes. Use this clause to change the compression attribute for the partition and every subpartition in that partition. Oracle Database marks each index subpartition in the partition UNUSABLE and you must then rebuild these subpartitions. Prefix compression must already have been specified for the index before you can specify the prefix_compression clause for a partition, or advanced index compression must have already been specified for the index before you can specify the advanced_index_compression clause for a partition. You can specify this clause only at the partition level. You cannot change the compression attribute for an individual subpartition.
You can use this clause for noncomposite index partitions. However, it is more efficient to use the rebuild_clause for noncomposite partitions, which lets you rebuild and set the compression attribute in one step.
rename_index_partition
Use the rename_index_partition clauses to rename index partition or subpartition to new_name.
Restrictions on Renaming Index Partitions
Renaming index partitions is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot rename the subpartition of a list partition.
-
For a partition of a domain index,
indexcannot be markedIN_PROGRESSorFAILED, none of the partitions can be markedIN_PROGRESS, and the partition you are renaming cannot be markedFAILED.
See Also:
drop_index_partition
Use the drop_index_partition clause to remove a partition and the data in it from a partitioned global index. When you drop a partition of a global index, Oracle Database marks the next index partition UNUSABLE. You cannot drop the highest partition of a global index.
See Also:
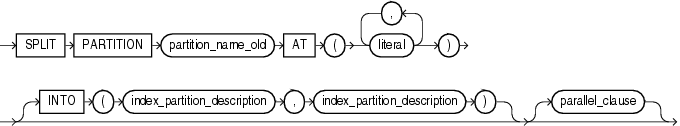
split_index_partition
Use the split_index_partition clause to split a partition of a global range-partitioned index into two partitions, adding a new partition to the index. This clause is not valid for hash-partitioned global indexes. Instead, use the add_hash_index_partition clause.
Splitting a partition marked UNUSABLE results in two partitions, both marked UNUSABLE. You must rebuild the partitions before you can use them.
Splitting a partition marked USABLE results in two partitions populated with index data. Both new partitions are marked USABLE.
AT Clause
Specify the new noninclusive upper bound for split_partition_1. The value_list must evaluate to less than the presplit partition bound for partition_name_old and greater than the partition bound for the next lowest partition (if there is one).
INTO Clause
Specify (optionally) the name and physical attributes of each of the two partitions resulting from the split.
See Also:
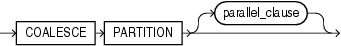
coalesce_index_partition
This clause is valid only for hash-partitioned global indexes. Oracle Database reduces by one the number of index partitions. Oracle Database selects the partition to coalesce based on the requirements of the hash function. Use this clause if you want to distribute index entries of a selected partition into one of the remaining partitions and then remove the selected partition.
modify_index_subpartition
Use the modify_index_subpartition clause to mark UNUSABLE or allocate or deallocate storage for a subpartition of a local index on a composite-partitioned table. All other attributes of such a subpartition are inherited from partition-level default attributes.
Examples
Storing Index Blocks in Reverse Order: Example
The following statement rebuilds index ord_customer_ix (created in "Creating an Index: Example") so that the bytes of the index block are stored in reverse order:
ALTER INDEX ord_customer_ix REBUILD REVERSE;
Rebuilding an Index in Parallel: Example
The following statement causes the index to be rebuilt from the existing index by using parallel execution processes to scan the old and to build the new index:
ALTER INDEX ord_customer_ix REBUILD PARALLEL;
Modifying Real Index Attributes: Example
The following statement alters the oe.cust_lname_ix index so that future data blocks within this index use 5 initial transaction entries:
ALTER INDEX oe.cust_lname_ix
INITRANS 5;
If the oe.cust_lname_ix index were partitioned, then this statement would also alter the default attributes of future partitions of the index. Partitions added in the future would then use 5 initial transaction entries and an incremental extent of 100K.
Enabling Parallel Queries: Example
The following statement sets the parallel attributes for index upper_ix (created in "Creating a Function-Based Index: Example") so that scans on the index will be parallelized:
ALTER INDEX upper_ix PARALLEL;
Renaming an Index: Example
The following statement renames an index:
ALTER INDEX upper_ix RENAME TO upper_name_ix;
Marking an Index Unusable: Examples
The following statements use the cost_ix index, which was created in "Creating a Range-Partitioned Global Index: Example". Partition p1 of that index was dropped in "Dropping an Index Partition: Example". The first statement marks index partition p2 as UNUSABLE:
ALTER INDEX cost_ix MODIFY PARTITION p2 UNUSABLE;
The next statement marks the entire index cost_ix as UNUSABLE:
ALTER INDEX cost_ix UNUSABLE;
Rebuilding Unusable Index Partitions: Example
The following statements rebuild partitions p2 and p3 of the cost_ix index, making the index once more usable: The rebuilding of partition p3 will not be logged:
ALTER INDEX cost_ix REBUILD PARTITION p2; ALTER INDEX cost_ix REBUILD PARTITION p3 NOLOGGING;
Changing MAXEXTENTS: Example
The following statement changes the maximum number of extents for partition p3 and changes the logging attribute:
/* This example will fail if the tablespace in which partition p3 resides is locally managed. */ ALTER INDEX cost_ix MODIFY PARTITION p3 STORAGE(MAXEXTENTS 30) LOGGING;
Renaming an Index Partition: Example
The following statement renames an index partition of the cost_ix index (created in "Creating a Range-Partitioned Global Index: Example"):
ALTER INDEX cost_ix RENAME PARTITION p3 TO p3_Q3;
Splitting a Partition: Example
The following statement splits partition p2 of index cost_ix (created in "Creating a Range-Partitioned Global Index: Example") into p2a and p2b:
ALTER INDEX cost_ix
SPLIT PARTITION p2 AT (1500)
INTO ( PARTITION p2a TABLESPACE tbs_01 LOGGING,
PARTITION p2b TABLESPACE tbs_02);Dropping an Index Partition: Example
The following statement drops index partition p1 from the cost_ix index:
ALTER INDEX cost_ix DROP PARTITION p1;
Modifying Default Attributes: Example
The following statement alters the default attributes of local partitioned index prod_idx, which was created in "Creating an Index on a Hash-Partitioned Table: Example". Partitions added in the future will use 5 initial transaction entries:
ALTER INDEX prod_idx
MODIFY DEFAULT ATTRIBUTES INITRANS 5;