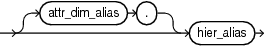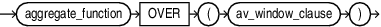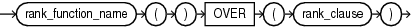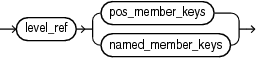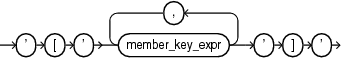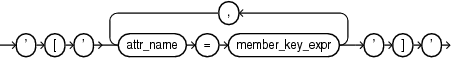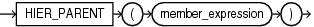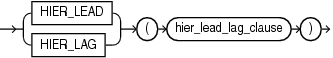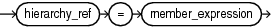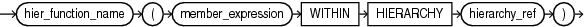Analytic View Expressions
You can use analytic view expressions to create calculated measures within the definition of an analytic view or in a query that selects from an analytic view.
Analytic view expressions differ from other types of expressions in that they reference elements of hierarchies and analytic views rather than tables and columns.
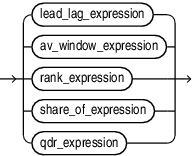
An analytic view expression is one of the following:
-
An
av_meas_expression, which is based on a measure in an analytic view -
An
av_hier_expression, which returns an attribute value of the related member
You use an analytic view expression as the calc_meas_expression parameter in a calc_measure_clause in a CREATE ANALYTIC VIEW statement and in the WITH or FROM clauses of a SELECT statement.
In defining a calculated measure, you may also use the following types of expression:
-
Simple
-
Case
-
Compound
-
Datetime
-
Interval
Tip:
You can view and run SQL scripts that create analytic views with calculated measures at the Oracle Live SQL website. The website has scripts and tutorials that demonstrate the creation and use of analytic views.Syntax
av_meas_expression::=
lead_lag_expression::=
lead_lag_function_name::=
lead_lag_clause::=
hierarchy_ref::=
av_window_expression::=
av_window_clause::=
preceding_boundary ::=
following_boundary::=
calc_meas_order_by_clause::=
share_of_expression::=
share_clause::=
member_expression::=
level_member_literal::=
pos_member_keys::=
named_member_keys::=
hier_navigation_expression::=
hier_ancestor_expression::=
hier_parent_expression::=
hier_lead_lag_expression::=
hier_lead_lag_clause::=
qdr_expression::=
qualifier::=
Semantics
av_meas_expression
An expression that performs hierarchical navigation to locate related measure values.
lead_lag_expression
An expression that specifies a lead or lag operation that locates a related measure value by navigating forward or backward by some number of members within a hierarchy.
The calc_meas_expression parameter is evaluated in the new context created by the lead_lag_expression. This context has the same members as the outer context, except that the member of the specified hierarchy is changed to the related member specified by the lead or lag operation. The lead or lag function is run over the hierarchy members specified by the lead_lag_clause parameter.
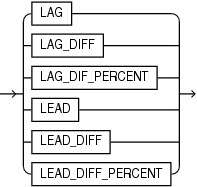
lead_lag_function_name
The lead or lag function may be one of the following:
-
LAGreturns the measure value of an earlier member. -
LAG_DIFFreturns the difference between the measure value of the current member and the measure value of an earlier member. -
LAG_DIFF_PERCENTreturns the percent difference between the measure value of the current member and the measure value of an earlier member. -
LEADreturns the measure value of a later member. -
LEAD_DIFFreturns the difference between the measure value of the current member and the measure value of a later member. -
LEAD_DIFF_PERCENTreturns the percent difference between the measure value of the current member and the measure value of a later member.
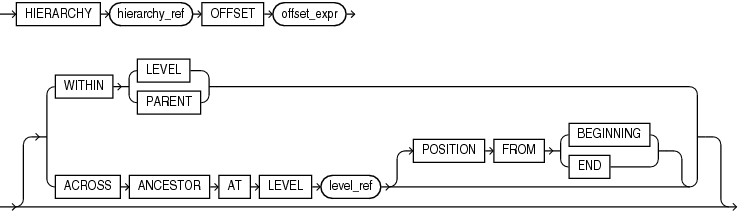
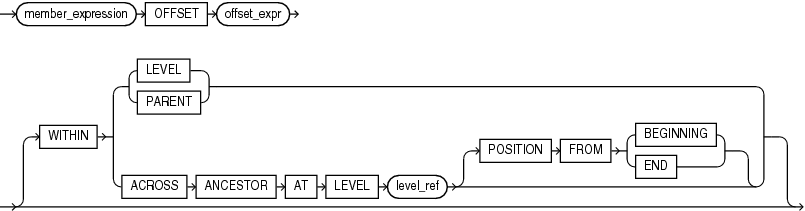
lead_lag_clause
Specifies the hierarchy to evaluate and an offset value. The parameters of the lead_lag_clause are the following:
-
HIERARCHYhierarchy_refspecifies the alias of a hierarchy as defined in the analytic view. -
OFFSEToffset_exprspecifies acalc_meas_expressionthat resolves to a number. The number specifies how many members to move either forward or backward from the current member. The ordering of members within a level is determined by the definition of the attribute dimension used by the hierarchy. -
WITHINLEVELspecifies locating the related member by moving forward or backward by the offset number of members within the members that have the same level depth as the current member. The ordering of members within the level is determined by the definition of the attribute dimension used by the hierarchy.The
WITHINLEVELoperation is the default if neither theWITHINLEVELnor theACROSSANCESTORATLEVELkeywords are specified. -
WITHINPARENTspecifies locating the related member by moving forward or backward by the offset number of members within the members that have the same parent as the current member. -
ACROSSANCESTORATLEVELlevel_refspecifies locating the related member by navigating up to the ancestor (or to the member itself if no ancestor exists) of the current member at the level specified bylevel_ref, and noting the position of each ancestor member (including the member itself) within its parent. Thelevel_refparameter is the name of a level in the specified hierarchy.Once the ancestor member is found, navigation moves either forward or backward the offset number of members within the members that have the same depth as the ancestor member. After locating the related ancestor, navigation proceeds back down the hierarchy from this member, matching the position within the parent as recorded on the way up (in reverse order). The position within the parent is either an offset from the first child or the last child depending on whether
POSITIONFROMBEGINNINGorPOSITIONFROMENDis specified. The default value isPOSITIONFROMBEGINNING. The ordering of members within the level is determined by the definition of the attribute dimension used by the hierarchy.
av_window_expression
An av_window_expression selects the set of members that are in the specified range starting from the current member and that are at the same depth as the current member. You can further restrict the selection of members by specifying a hierarchical relationship using a WITHIN phrase. Aggregation is then performed over the selected measure values to produce a single result for the expression.
The parameters for an av_window_expression are the following:
-
aggregate_functionis any existing SQL aggregate function exceptCOLLECT,GROUP_ID,GROUPING,GROUPING_ID,SYS_XMLAGG,XMLAGG, and any multi-argument function. A user defined aggregate function is also allowed. The arguments to the aggregate function arecalc_meas_expressionexpressions. These expressions are evaluated using the outer context, with the member of the specified hierarchy changed to each member in the related range. Therefore, each expression argument is evaluated once per related member. The results are then aggregated using theaggregate_function. -
OVER(av_window_clause)specifies the hierarchy to use and the boundaries of the window to consider.
See Also:
av_window_clause
The av_window_clause parameter selects a range of members related to the current member. The range is between the members specified by the preceding_boundary or following_boundary parameters. The range is always computed over members at the same level as the current member.
The parameters for a av_window_clause are the following:
-
HIERARCHYhierarchy_refspecifies the alias of the hierarchy as defined in the analytic view. -
BETWEENpreceding_boundaryorfollowing_boundarydefines the set of members to relate to the current member. -
WITHINLEVELselects the related members by applying the boundary clause to all members of the current level. This is the default when theWITHINkeyword is not specified. -
WITHINPARENTselects the related members by applying the boundary clause to all members that share a parent with the current member. -
WITHINANCESTORATLEVELselects the related members by applying the boundary clause to all members at the current depth that share an ancestor (or is the member itself) at the specified level with the current member. The value of the window expression isNULLif the current member is above the specified level. If the level is not in the specified hierarchy, then an error occurs.
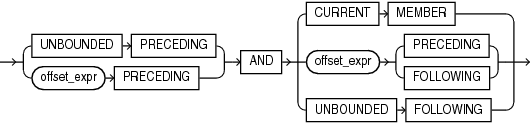
preceding_boundary
The preceding_boundary parameter defines a range of members from the specified number of members backward in the level from the current member and forward to the specified end of the boundary. The following parameters specify the range:
-
UNBOUNDEDPRECEDINGbegins the range at the first member in the level. -
offset_exprPRECEDINGbegins the range at theoffset_exprnumber of members backward from the current member. Theoffset_exprexpression is acalc_meas_expressionthat resolves to a number. If the offset number is greater than the number of members from the current member to the first member in the level, than the first member is used as the start of the range. -
CURRENTMEMBERends the range at the current member. -
offset_exprPRECEDINGends the range at the member that isoffset_exprbackward from the current member. -
offset_exprFOLLOWINGends the range at the member that isoffset_exprforward from the current member. -
UNBOUNDEDFOLLOWINGends the range at the last member in the level.
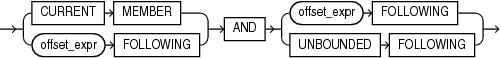
following_boundary
The following_boundary parameter defines a range of members from the specified number of members from the current member forward to the specified end of the range. The following parameters specify the range:
-
CURRENTMEMBERbegins the range at the current member. -
offset_exprFOLLOWINGbegins the range at the member that isoffset_exprforward from the current member. -
offset_exprFOLLOWINGends the range at the member that isoffset_exprforward from the current member. -
UNBOUNDEDFOLLOWINGends the range at the last member in the level.
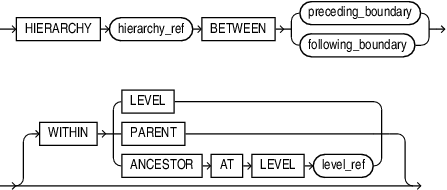
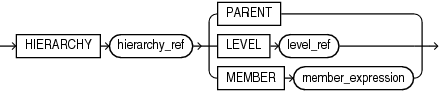
hierarchy_ref
A reference to a hierarchy of an analytic view. The hier_alias parameter specifies the alias of a hierarchy in the definition of the analytic view. You may use double quotes to escape special characters or preserve case, or both.
The optional attr_dim_alias parameter specifies the alias of an attribute dimension in the definition of the analytic view. You may use the attr_dim_alias parameter to resolve the ambiguity if the specified hierarchy alias conflicts with another hierarchy alias in the analytic view or if an attribute dimension is used more than once in the analytic view definition. You may use the attr_dim_alias parameter even when a name conflict does not exist.
rank_expression
Hierarchical rank calculations rank the related members of the specified hierarchy based on the order of the specified measure values and return the rank of the current member within those results.
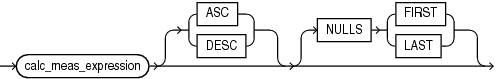
Hierarchical rank calculations locate a set of related members in the specified hierarchy, rank all the related members based on the order of the specified measure values, and then return the rank of the current member within those results. The related members are a set of members at the same level as the current member. You may optionally restrict the set by some hierarchical relationship, but the set always includes the current member. The ordering of the measure values is determined by the calc_meas_order_by_clause of the rank_clause.
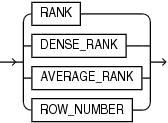
rank_function_name
Each hierarchical ranking function assigns an order number to each related member based on the calc_meas_order_by_clause, starting at 1. The functions differ in the way they treat measure values that are the same.
The functions and the differences between them are the following:
-
RANK, which assigns the same rank to identical measure values. The rank after a set of tied values is the number of tied values plus the tied order value; therefore, the ordering may not be consecutive numbers. -
DENSE_RANK, which assigns the same minimum rank to identical measure values. The rank after a set of tied values is always one more than the tied value; therefore, the ordering always has consecutive numbers. -
AVERAGE_RANK, assigns the same average rank to identical values. The next value after the average rank value is the number of identical values plus 1, that sum divided by 2, plus the average rank value. For example, for the series of five values 4, 5, 10, 5, 7,AVERAGE_RANKreturns 1, 1.5, 1.5, 3, 4. For the series 2, 12, 10, 12, 17, 12, the returned ranks are 1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 5. -
ROW_NUMBER, which assigns values that are unique and consecutive across the hierarchy members. If thecalc_meas_order_by_clauseresults in equal values then the results are non-deterministic.
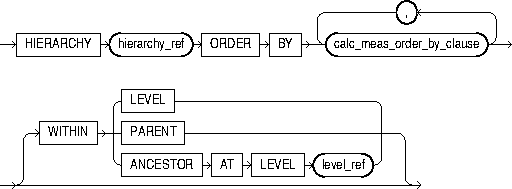
rank_clause
The rank_clause locates a range of hierarchy members related to the current member. The range is some subset of the members in the same level as the current member. The subset is determined from the WITHIN clause.
Valid values for the WITHIN clause are:
-
WITHIN LEVEL, which specifies that the related members are all the members of the current level. This is the default subset if theWITHINkeyword is not specified. -
WITHIN PARENT, which specifies that the related members all share a parent with the current member -
WITHIN ANCESTOR AT LEVEL, which specifies that the related members are all of the members of the current level that share an ancestor (or self) at the specified level with the current member.
share_of_expression
A share_of_expression expression calculates the ratio of an expression's value for the current context over the expression's value at a related context. The expression is a calc_meas_expression that is evaluated at the current context and the related context. The share_clause specification determines the related context to use.
share_clause
A share_clause modifies the outer context by setting the member for the specified hierarchy to a related member.
The parameters of the share clause are the following:
-
HIERARCHYhierarchy_refspecifies the name of the hierarchy that is the outer context for theshare_of_expressioncalculations. -
PARENTspecifies that the related member is the parent of the current member. -
LEVELlevel_refspecifies that the related member is the ancestor (or is the member itself) of the current member at the specified level in the hierarchy. If the current member is above the specified level, thenNULLis returned for the share expression. If the level is not in the hierarchy, then an error occurs. -
MEMBERmember_expressionspecifies that the related member is the member returned after evaluating themember_expressionin the current context. If the value of the specified member isNULL, thenNULLis returned for the share expression.
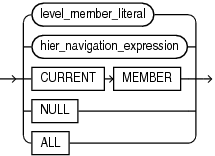
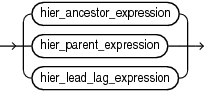
member_expression
A member_expression evaluates to a member of the specified hierarchy. The hierarchy can always be determined from the outer expression (enforced by the syntax). A member_expression can be one of the following:
-
level_member_literalis an expression that evaluates to a hierarchy member. -
hier_navigation_expris an expression that relates one member of the hierarchy to another member. -
CURRENTMEMBERspecifies the member of the hierarchy as determined by the outer context. -
NULLis a way to specify a non-existent member. -
ALLspecifies the single topmost member of every hierarchy.
level_member_literal
A level_member_literal is an expression that resolves to a single member of the hierarchy. The expression contains the name of the level and one or more member keys. The member key or keys may be identified by position or by name. If the specified level is not in the context hierarchy, then an error occurs.
pos_member_keys
The member_key_expr expression resolves to the key value for the member. When specified by position, all components of the key must be given in the order found in the ALL_HIER_LEVEL_ID_ATTRS dictionary view. For a hierarchy in which the specified level is not determined by the child level, then all member key values of all such child levels must be provided preceding the current level's member key or keys. Duplicate key components are only specified the first time they appear.
The primary key is used when level_member_literal is specified using the pos_member_keys phrase. You can reference an alternate key by using the named_member_keys phrase.
named_member_keys
The member_key_expr expression resolves to the key value for the member. The attr_name parameter is an identifier for the name of the attribute. If all of the attribute names do not make up a key or alternate key of the specified level, then an error occurs.
When specified by name, all components of the key must be given and all must use the attribute name = value form, in any order. For a hierarchy in which the specified level is not determined by the child level, then all member key values of all such child levels must be provided, also using the named form. Duplicate key components are only specified once.
hier_navigation_expression
A hier_navigation_expression expression navigates from the specified member to a different member in the hierarchy.
hier_ancestor_expression
Navigates from the specified member to the ancestor member (or to the member itself) at the specified level or depth. The depth is specified as an expression that must resolve to a number. If the member is at a level or depth above the specified member or the member is NULL, then NULL is returned for the expression value. If the specified level is not in the context hierarchy, then an error occurs.
hier_parent_expression
Navigates from the specified member to the parent member.
hier_lead_lag_expression
Navigates from the specified member to a related member by moving forward or backward some number of members within the context hierarchy. The HIER_LEAD keyword returns a later member. The HIER_LAG keyword returns an earlier member.
hier_lead_lag_clause
Navigates the offset_expr number of members forward or backward from the specified member. The ordering of members within a level is specified in the definition of the attribute dimension.
The optional parameters of hier_lead_lag_clause are the following:
-
WITHINLEVELlocates the related member by moving forward or backwardoffset_exprmembers within the members that have the same depth as the current member. The ordering of members within the level is determined by the definition of the attribute dimension. TheWITHINLEVELoperation is the default if neither theWITHINnor theACROSSkeywords are used. -
WITHINPARENTlocates the related member by moving forward or backwardoffset_exprmembers within the members that have the same depth as the current member, but only considers members that share a parent with the current member. The ordering of members within the level is determined by the definition of the attribute dimension. -
WITHINACROSSANCESTORATLEVELlocates the related member by navigating up to the ancestor of the current member (or to the member itself) at the specified level, noting the position of each ancestor member (including the member itself) within its parent. Once the ancestor member is found, navigation moves forward or backwardoffset_exprmembers within the members that have the same depth as the ancestor member.After locating the related ancestor, navigation moves back down the hierarchy from that member, matching the position within the parent as recorded on the way up (in reverse order). The position within the parent is either an offset from the first child or the last child depending on whether
POSITIONFROMBEGINNINGorPOSITIONFROMENDis specified, defaulting toPOSITIONFROMBEGINNING. The ordering of members within the level is determined by the definition of the attribute dimension.
qdr_expression
A qdr_expression is a qualified data reference that evaluates the specified calc_meas_expression in a new context and sets the hierarchy member to the new value.
qualifier
A qualifier modifies the outer context by setting the member for the specified hierarchy to the member resulting from evaluating member_expression. If member_expression is NULL, then the result of the qdr_expression selection is NULL.
av_hier_expression
An av_hier_expression performs hierarchy navigation to locate an attribute value of the related member. An av_hier_expression may be a top-level expression, whereas a hier_navigation_expression may only be used as a member_expression argument.
For example, in the following query HIER_MEMBER__NAME is an av_hier_expression and HIER_PARENT is a hier_navigation_expression.
HIER_MEMBER_NAME(HIER_PARENT(CURRENT MEMBER) WITHIN HIERARCHY product_hier))
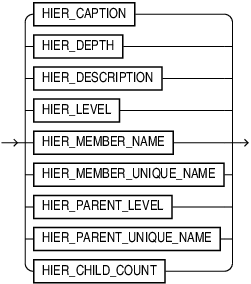
hier_function_name
The hier_function_name values are the following:
-
HIER_CAPTION, which returns the caption of the related member in the hierarchy. -
HIER_DEPTH, which returns one less than the number of ancestors between the related member and the ALL member in the hierarchy. The depth of the ALL member is 0. -
HIER_DESCRIPTION, which returns the description of the related member in the hierarchy. -
HIER_LEVEL, which returns as a string value the name of the level to which the related member belongs in the hierarchy. -
HIER_MEMBER_NAME, which returns the member name of the related member in the hierarchy. -
HIER_MEMBER_UNIQUE_NAME, which returns the member unique name of the related member in the hierarchy.
Examples of Analytic View Expressions
This topic contains examples that show calculated measures defined in the MEASURES clause of an analytic view and in the ADD MEASURES clause of a SELECT statement.
The examples are the following:
For more examples, see the tutorials on analytic views at the SQL Live website at https://livesql.oracle.com/apex/livesql/file/index.html.
Examples of LAG Expressions
These calculated measures different LAG operations.
-- These calculated measures are from the measures_clause of the
-- sales_av analytic view.
MEASURES
(sales FACT sales, -- A base measure
units FACT units, -- A base measure
sales_prior_period AS -- Calculated measures
(LAG(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier OFFSET 1)),
sales_year_ago AS
(LAG(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier OFFSET 1
ACROSS ANCESTOR AT LEVEL year)),
chg_sales_year_ago AS
(LAG_DIFF(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier OFFSET 1
ACROSS ANCESTOR AT LEVEL year)),
pct_chg_sales_year_ago AS
(LAG_DIFF_PERCENT(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier OFFSET 1
ACROSS ANCESTOR AT LEVEL year)),
sales_qtr_ago AS
(LAG(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier OFFSET 1
ACROSS ANCESTOR AT LEVEL quarter)),
chg_sales_qtr_ago AS
(LAG_DIFF(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier OFFSET 1
ACROSS ANCESTOR AT LEVEL quarter)),
pct_chg_sales_qtr_ago AS
(LAG_DIFF_PERCENT(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier OFFSET 1
ACROSS ANCESTOR AT LEVEL quarter))
)Example of a Window Expression
This calculated measure uses a window operation.
MEASURES
(sales FACT sales,
units FACT units,
sales_qtd AS
(SUM(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier
BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT MEMBER
WITHIN ANCESTOR AT LEVEL QUARTER)),
sales_ytd AS
(SUM(sales) OVER (HIERARCHY time_hier
BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT MEMBER
WITHIN ANCESTOR AT LEVEL YEAR))
)Examples of SHARE OF Expressions
These calculated measures use SHARE OF expressions.
MEASURES
(sales FACT sales,
units FACT units,
sales_shr_parent_prod AS
(SHARE_OF(sales HIERARCHY product_hier PARENT)),
sales_shr_parent_geog AS
(SHARE_OF(sales HIERARCHY geography_hier PARENT)),
sales_shr_region AS
(SHARE_OF(sales HIERARCHY geography_hier LEVEL REGION))
)Examples of QDR Expressions
These calculated measures use the QUALIFY keyword to specify qualified data reference expressions.
MEASURES
(sales FACT sales,
units FACT units,
sales_2011 AS
(QUALIFY (sales, time_hier = year['11'])),
sales_pct_chg_2011 AS
((sales - (QUALIFY (sales, time_hier = year['11']))) /
(QUALIFY (sales, time_hier = year['11'])))
)Example of an Added Measure Using the RANK Function
In this example, the units_geog_rank_level measure uses the RANK function to rank geography hierarchy members within a level based on units.
SELECT geography_hier.member_name AS "Region",
units AS "Units",
units_geog_rank_level AS "Rank"
FROM ANALYTIC VIEW (
USING sales_av HIERARCHIES (geography_hier)
ADD MEASURES (
units_geog_rank_level AS (
RANK() OVER (
HIERARCHY geography_hier
ORDER BY units desc nulls last
WITHIN LEVEL))
)
)
WHERE geography_hier.level_name IN ('REGION')
ORDER BY units_geog_rank_level;The following is the result of the query.
Regions Units Rank
------------- --------- ----
Asia 56017849 1
South America 23904155 2
North America 20523698 3
Africa 12608308 4
Europe 8666520 5
Oceania 427664 6