38 Planning for Read-Only Materialized Views
Before you begin to plan your read-only materialized view environment, it is important to understand the concepts and architecture related to materialized views. After you understand concepts and architecture of read-only materialized views, there are important considerations for planning a read-only materialized view environment.
- Considerations for Master Tables
For master tables, you must consider primary keys, foreign keys, and data types. - Planning for Master Databases and Materialized View Databases
Planning databases in a read-only materialized view environment includes preparing for materialized views and configuring materialized view logs.
Parent topic: Managing Read-Only Materialized Views
38.1 Considerations for Master Tables
For master tables, you must consider primary keys, foreign keys, and data types.
- Primary Keys and Master Tables
If possible, each master table should have a primary key. - Foreign Keys and Master Tables
When replicating tables with foreign key referential constraints, Oracle recommends that you always index foreign key columns and replicate these indexes, unless no updates and deletes are allowed in the parent table. Indexes are not replicated automatically. - Data Type Considerations for Master Tables
There are several considerations for data types and master tables. - Unsupported Table Types
Materialized views cannot be based on certain types of tables.
Parent topic: Planning for Read-Only Materialized Views
38.1.1 Primary Keys and Master Tables
If possible, each master table should have a primary key.
Where a primary key is not possible, each master table must have a set of columns that can be used as a unique identifier for each row of the table. If the tables that you plan to use in your replication environment do not have a primary key or a set of unique columns, then alter these tables accordingly. In addition, if you plan to create any primary key materialized views based on a master table, then that master must have a primary key.
Parent topic: Considerations for Master Tables
38.1.2 Foreign Keys and Master Tables
When replicating tables with foreign key referential constraints, Oracle recommends that you always index foreign key columns and replicate these indexes, unless no updates and deletes are allowed in the parent table. Indexes are not replicated automatically.
Parent topic: Considerations for Master Tables
38.1.3 Data Type Considerations for Master Tables
There are several considerations for data types and master tables.
You can create read-only materialized views based on master tables with columns that use the following data types:
-
VARCHAR2 -
NVARCHAR2 -
NUMBER -
DATE -
TIMESTAMP -
TIMESTAMPWITHTIMEZONE -
TIMESTAMPLOCALTIMEZONE -
INTERVALYEARTOMONTH -
INTERVALDAYTOSECOND -
RAW -
ROWID -
CHAR -
NCHAR -
CLOBwithBASICFILEstorage -
NCLOBwithBASICFILEstorage -
BLOBwithBASICFILEstorage -
XMLTypestored asCLOB -
User-defined types that do not use type inheritance or type evolution
-
Oracle-supplied types that do not use type inheritance or type evolution
Note:
XMLType stored as a CLOB is deprecated.
You cannot reference LOB columns in a WHERE clause of a materialized view's defining query.
You can create materialized views that use user-defined types, including column objects, object tables, REFs, varrays, and nested tables.
You cannot create materialized views based on master tables with columns that use the following data types:
-
FLOAT -
BINARY_FLOAT -
BINARY_DOUBLE -
LONG -
LONGRAW -
CLOBwithSECUREFILEstorage -
NCLOBwithSECUREFILEstorage -
BLOBwithSECUREFILEstorage -
BFILE -
XMLTypestored object relationally or as binary XML -
Expressiontype -
User-defined types that use type inheritance or type evolution
-
Oracle-supplied types that use type inheritance or type evolution
You should convert LONG data types to LOBs with BASICFILE storage.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about data types
Parent topic: Considerations for Master Tables
38.1.4 Unsupported Table Types
Materialized views cannot be based on certain types of tables.
You cannot create materialized views based on these types of tables:
-
Tables that have been compressed with the table compression feature
-
Tables with virtual columns
-
Temporary tables
-
Tables in a flashback data archive
Parent topic: Considerations for Master Tables
38.2 Planning for Master Databases and Materialized View Databases
Planning databases in a read-only materialized view environment includes preparing for materialized views and configuring materialized view logs.
- Characteristics of Master Databases and Materialized View Databases
When you are planning your replication environment, you must decide whether the databases participating in the replication environment will be master databases or materialized view databases. - Advantages of Master Databases
Master databases have several advantages. - Advantages of Materialized View Databases
Materialized view databases have certain advantages. - Preparing for Materialized Views
Most problems encountered with materialized view replication result from not preparing the environment properly. - Creating Materialized View Logs
Create a materialized view log on a master table so that materialized views based on the master table can be fast refreshed. - Logging Columns in a Materialized View Log
When you create a materialized view log, you can add columns to the log to enable fast refreshes of materialized views.
Parent topic: Planning for Read-Only Materialized Views
38.2.1 Characteristics of Master Databases and Materialized View Databases
When you are planning your replication environment, you must decide whether the databases participating in the replication environment will be master databases or materialized view databases.
Consider the characteristics and advantages of both types of databases when you are deciding whether a particular database in your environment should be a master database or a materialized view database. One replication environment can support both master databases and materialized view databases.
Table 38-1 Characteristics of Master Databases and Materialized View Databases
| Master Databases | Materialized View Databases |
|---|---|
|
Might communicate with a large number of materialized view databases |
Communicate with one master database |
|
Contain large amounts of data |
Contain small amounts of data that can be subsets of the master database's data |
38.2.2 Advantages of Master Databases
Master databases have several advantages.
Master databases have the following advantages:
-
Support for highly available data access by remote databases
-
Provide support data manipulation language (DML) changes
-
Can provide failover protection
38.2.3 Advantages of Materialized View Databases
Materialized view databases have certain advantages.
Materialized view databases have the following advantages:
-
Support disconnected computing
-
Can contain a subset of its master database's data
38.2.4 Preparing for Materialized Views
Most problems encountered with materialized view replication result from not preparing the environment properly.
Ensure that the following prerequisites are met before creating your materialized view environment:
-
Ensure that the required schemas exist.
-
Ensure that the required database links exist.
-
Ensure that the required privileges are granted.
-
Ensure that the sufficient job processes exit.
- Required Schemas at Materialized View Database
A schema containing a materialized view in a remote database must correspond to the schema that contains the master table in the master database. - Required Database Links for Materialized Views
The defining query of a materialized view can use one or more database links to reference remote table data. - Required Privileges
Both the creator and the owner of the materialized view must be able to issue the definingSELECTstatement of the materialized view. - Sufficient Job Processes
It is important that you have allocated sufficient job processes to handle the automation of your replication environment. The job processes automatically refresh materialized views.
38.2.4.1 Required Schemas at Materialized View Database
A schema containing a materialized view in a remote database must correspond to the schema that contains the master table in the master database.
Therefore, identify the schemas that contain the master tables that you want to replicate with materialized views. After you have identified the target schemas at the master database, create the corresponding accounts with the same names at the remote database. For example, if all master tables are in the sales schema of the ny.example.com database, then create a corresponding sales schema in the materialized view database sf.example.com.
Parent topic: Preparing for Materialized Views
38.2.4.2 Required Database Links for Materialized Views
The defining query of a materialized view can use one or more database links to reference remote table data.
Before creating materialized views, the database links you plan to use must be available. Furthermore, the account that a database link uses to access a remote database defines the security context under which Oracle Database creates and subsequently refreshes a materialized view.
To ensure proper behavior, a materialized view's defining query must use a database link that includes an embedded user name and password in its definition; you cannot use a public database link when creating a materialized view. A database link with an embedded name and password always establishes connections to the remote database using the specified account. Additionally, the remote account that the link uses must have the SELECT privileges necessary to access the data referenced in the materialized view's defining query.
Before creating your materialized views, you must create several administrative database links. Specifically, you should create a PUBLIC database link from the materialized view database to the master database. Doing so makes defining your private database links easier because you do not need to include the USING clause in each link.
For example, the following statement creates a public database link from a materialized view database to a master database:
CREATE PUBLIC DATABASE LINK orc1.example.com USING 'orc1.example.com';
After the administrative database links have been created, a private database link must be created connecting each replicated materialized view schema at the materialized view database to the corresponding schema at the master database. Be sure to embed the associated master database account information in each private database link at the materialized view database. For example, the hr schema at a materialized view database should have a private database link to the master database that connects using the hr user name and password.
For example, the following statement creates a private database link from a materialized view database to a master database:
CREATE DATABASE LINK orc1.example.com
CONNECT TO myuser IDENTIFIED BY password;
Figure 38-1 Recommended Schema and Database Link Configuration
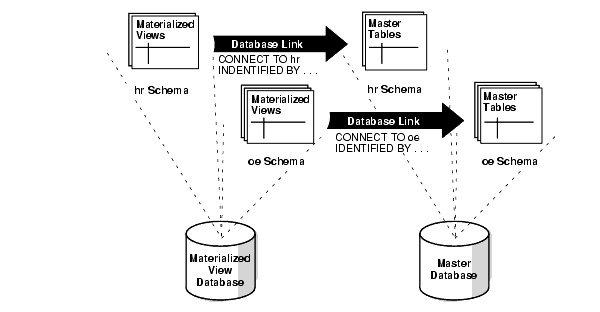
Description of "Figure 38-1 Recommended Schema and Database Link Configuration"
The defining query for the materialized view cannot be modified by Virtual Private Database (VPD). VPD must return a NULL policy for the schema that performs both the create and refresh of the materialized view. Creating a materialized view with a non-NULL VPD policy is allowed when the USING TRUSTED CONSTRAINTS clause is specified. In this case, ensure that the materialized view behaves correctly. Materialized view results are computed based on the rows and columns filtered by VPD policy. Therefore, you must coordinate the materialized view definition with the VPD policy to ensure the correct results.
See Also:
-
Distributed Database Concepts for more information about database links
-
Oracle Database Security Guide for more information about VPD
-
Oracle Label Security Administrator's Guide for information about Oracle Label Security
Parent topic: Preparing for Materialized Views
38.2.4.3 Required Privileges
Both the creator and the owner of the materialized view must be able to issue the defining SELECT statement of the materialized view.
The owner is the schema that contains the materialized view.
Parent topic: Preparing for Materialized Views
38.2.4.4 Sufficient Job Processes
It is important that you have allocated sufficient job processes to handle the automation of your replication environment. The job processes automatically refresh materialized views.
By the nature of materialized view replication, each materialized view database typically has one scheduled link to the master database and requires at least one job process. Materialized view databases typically require between one and three job processes, depending on user-defined jobs and the scheduled link. Also, you need at least one job process for each degree of parallelism.
Alternatively, if your users are responsible for manually refreshing the materialized view through an application interface, then you do not need to create a scheduled link and your materialized view database requires one less job process.
The job processes are defined using the JOB_QUEUE_PROCESSES initialization parameter. This initialization parameter is modifiable. Therefore, you can modify it while an instance is running. Oracle Database automatically determines the interval for job processes. That is, Oracle Database determines when the job processes should "wake up" to execute jobs.
See Also:
Parent topic: Preparing for Materialized Views
38.2.5 Creating Materialized View Logs
Create a materialized view log on a master table so that materialized views based on the master table can be fast refreshed.
Before creating materialized views for a remote materialized view database, ensure that you create the necessary materialized view logs at the master database. A materialized view log is necessary for every master table that supports at least one materialized view with fast refreshes.
To create a materialized view log, you need the following privileges:
-
CREATEANYTABLE -
CREATEANYTRIGGER -
SELECT(on the materialized view log's master table) -
COMMENTANYTABLE
To create a materialized view log:
Example 38-1 Creating a Materialized View Log
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON hr.employees;
Example 38-2 Creating a Materialized View Log on an Object Table
The following SQL statement creates the categories_typ user-defined type:
CREATE TYPE oe.category_typ AS OBJECT
(category_name VARCHAR2(50),
category_description VARCHAR2(1000),
category_id NUMBER(2));
/
When you create an object table based on this type, you can either specify that the object identifier should be system-generated or primary key-based:
CREATE TABLE oe.categories_tab_sys OF oe.category_typ
(category_id PRIMARY KEY)
OBJECT ID SYSTEM GENERATED;
CREATE TABLE oe.categories_tab_pkbased OF oe.category_typ
(category_id PRIMARY KEY)
OBJECT ID PRIMARY KEY;
For example, the following statement creates a materialized view log for the categories_tab_sys object table and specifies that the object identifier column be logged:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON oe.categories_tab_sys WITH OBJECT ID;
The following statement creates a materialized view log for the categories_tab_pkbased object table and specifies that the primary key column be logged along with the object identifier column:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON oe.categories_tab_pkbased WITH OBJECT ID, PRIMARY KEY;
38.2.6 Logging Columns in a Materialized View Log
When you create a materialized view log, you can add columns to the log to enable fast refreshes of materialized views.
Example 38-3 Logging Columns When Creating a Materialized View
To create the materialized view log on the oe.orders table with the orders.customer_id and orders.order_total columns added, issue the following statement:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON oe.orders WITH PRIMARY KEY (customer_id,order_total);
Example 38-4 Logging Columns of an Existing Materialized View
You can add the orders.customer_id and orders.order_total columns to the materialized view log on the oe.orders table by issuing the following statement:
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON oe.orders ADD (customer_id,order_total);
Example 38-5 Logging the Attributes of Column Objects
If you are using user-defined data types, then the attributes of column objects can be logged in the materialized view log. For example, the oe.customers table has the cust_address.postal_code attribute, which can be logged in the materialized view log by issuing the following statement:
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON oe.customers ADD (cust_address.postal_code);