23 Customizing the Use of Strong Authentication
You can configure multiple authentication methods under Oracle Database native network encryption and strong authentication.
- Connecting to a Database Using Strong Authentication
You can use password authentication to connect to a database that is configured to use strong authentication. - Disabling Strong Authentication and Native Network Encryption
You can use Oracle Net Manager to disable strong authentication and native network encryption. - Configuring Multiple Authentication Methods
Many networks use more than one authentication method on a single security server. - Configuring Oracle Database for External Authentication
You can use parameters to configure Oracle Database for network authentication.
Parent topic: Managing Strong Authentication
23.1 Connecting to a Database Using Strong Authentication
You can use password authentication to connect to a database that is configured to use strong authentication.
-
To connect to an Oracle database server using a user name and password when an Oracle network and strong authentication method has been configured, disable the external authentication.
You must first follow the instructions in Disabling Strong Authentication and Native Network Encryption to disable the external authentication before you can connect to an Oracle Database server using a user name and password when an Oracle network and strong authentication method has been configured.
-
With the external authentication disabled, connect to the database using the following format:
% sqlplus username@net_service_name Enter password: password
For example:
% sqlplus hr@emp Enter password: password
Note:
You can configure multiple authentication methods, including both externally authenticated users and password authenticated users, on a single database.
Parent topic: Customizing the Use of Strong Authentication
23.2 Disabling Strong Authentication and Native Network Encryption
You can use Oracle Net Manager to disable strong authentication and native network encryption.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Customizing the Use of Strong Authentication
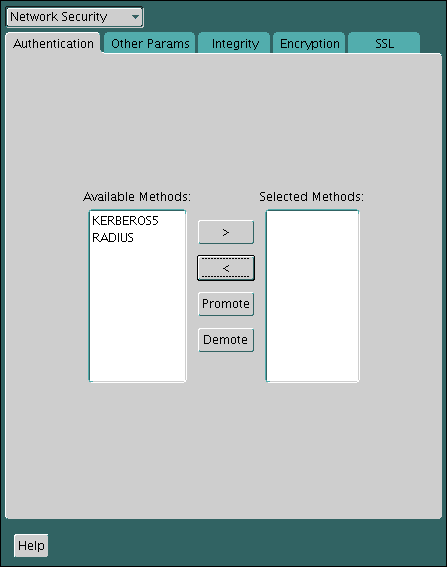
23.3 Configuring Multiple Authentication Methods
Many networks use more than one authentication method on a single security server.
Accordingly, Oracle Database lets you configure your network so that Oracle clients can use a specific authentication method, and Oracle database servers can accept any method specified.
You can set up multiple authentication methods on both client and server systems either by using Oracle Net Manager, or by using any text editor to modify the sqlnet.ora file. Use Oracle Net Manager to add authentication methods to both clients and servers.
Note:
SecurID functionality is available through RADIUS; RADIUS support is built into the RSA ACE/Server.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Customizing the Use of Strong Authentication
23.4 Configuring Oracle Database for External Authentication
You can use parameters to configure Oracle Database for network authentication.
- Setting the SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES Parameter in sqlnet.ora
TheSQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICESparameter defines the authentication method and version to be used. - Setting OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX to a Null Value
TheOS_AUTHENT_PREFIXparameter specifies a prefix that Oracle Database uses to authenticate users who attempt to connect to the server.
Parent topic: Customizing the Use of Strong Authentication
23.4.1 Setting the SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES Parameter in sqlnet.ora
The SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES parameter defines the authentication method and version to be used.
You must set the SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES parameter in the sqlnet.ora file for all clients and servers to enable each to use a supported authentication method.
-
Set the
SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICESparameter using the following syntax:SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES=(oracle_authentication_method)
For example, for all clients and servers using Kerberos authentication:
SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES=(KERBEROS5)
By default, the sqlnet.ora file is located in the ORACLE_HOME/network/admin directory or in the location set by the TNS_ADMIN environment variable. Ensure that you have properly set the TNS_ADMIN variable to point to the correct sqlnet.ora file.
See Also:
SQL*Plus User's Guide and Reference for more information and examples of setting theTNS_ADMIN variable
Parent topic: Configuring Oracle Database for External Authentication
23.4.2 Setting OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX to a Null Value
The OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX parameter specifies a prefix that Oracle Database uses to authenticate users who attempt to connect to the server.
Authentication service-based user names can be long, and Oracle user names are limited to 30 bytes. Oracle strongly recommends that you set the OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX parameter to a null value.
-
In the initialization file for the database instance, set
OS_AUTHENT_PREFIXas follows:OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX=""
Note:
-
The default value for
OS_AUTHENT_PREFIXisOPS$; however, you can set it to any string. -
If a database already has the
OS_AUTHENT_PREFIXset to a value other thanNULL(" "), then do not change it, because it can inhibit previously created, externally identified users from connecting to the Oracle server.
After you have set OS_AUTHENT_PREFIX to null, then you can create external users by using the following syntax:
CREATE USER os_authent_prefix_username IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY;
For example, to create the user king:
CREATE USER king IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY;
The advantage of creating a user in this way is that you no longer need to maintain different user names for externally identified users. This is true for all supported authentication methods.
Parent topic: Configuring Oracle Database for External Authentication